us border wall map
Related Articles: us border wall map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to us border wall map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the U.S.-Mexico Border: A Comprehensive Look at the Physical Barrier

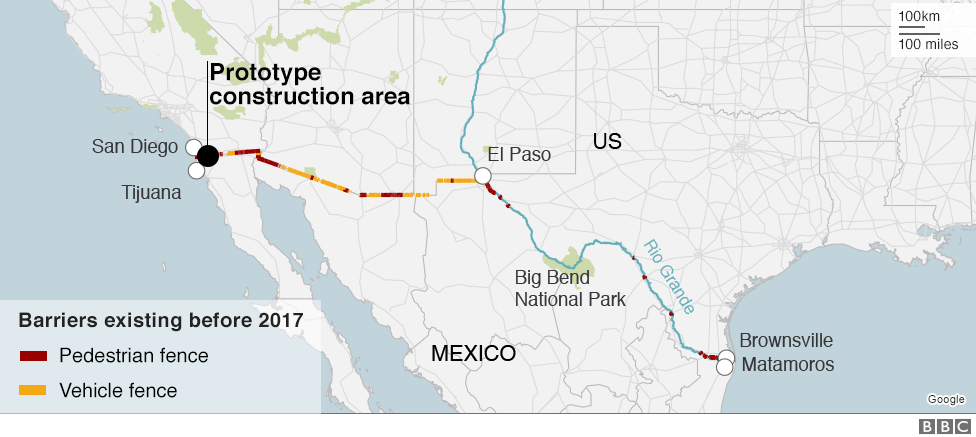
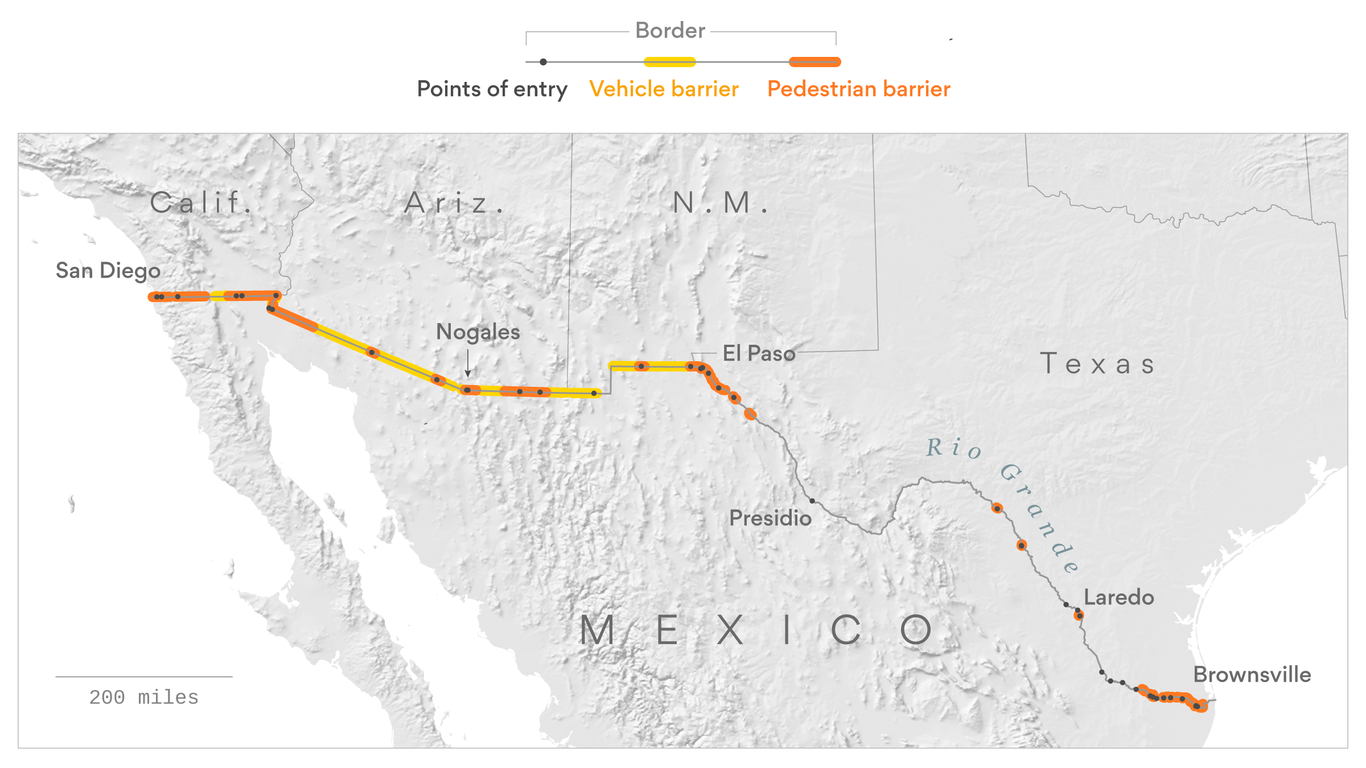
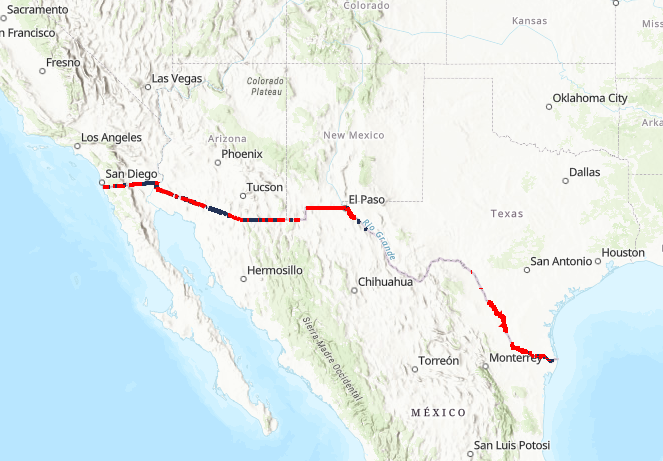
The U.S.-Mexico border, stretching over 1,954 miles from the Pacific Ocean to the Gulf of Mexico, is a complex and dynamic landscape. It is also the site of significant political and social discourse, particularly concerning the physical barrier that separates the two nations. Understanding the physical characteristics of this border, including the existing barriers, is crucial for comprehending the ongoing debate and its potential implications.
The Evolution of Border Barriers:
The history of border barriers along the U.S.-Mexico border is long and multifaceted. While the concept of a physical barrier dates back to the early 20th century, the current iteration of the border wall is largely a product of the 21st century.
- Early Barriers: The first significant barrier was constructed in the early 1900s, primarily focused on preventing the movement of cattle and other livestock. These early barriers were rudimentary, often consisting of simple fences and barbed wire.
- The "Border Fence" Era: In the 1990s, the "Border Fence" initiative emerged, aiming to deter illegal immigration and drug trafficking. This initiative led to the construction of several miles of pedestrian fencing, primarily in urban areas, and vehicle barriers in remote areas.
- The 21st Century Surge: The 21st century witnessed a significant escalation in border security measures. The "Secure Fence Act of 2006" authorized the construction of over 700 miles of fencing along the border. This initiative, combined with subsequent expansions, led to the construction of a vast network of barriers, encompassing various types of fencing, walls, and other physical obstacles.
The Current State of the Border Wall:
Today, the U.S.-Mexico border features a diverse array of barriers, each with distinct characteristics and strategic placement.
- Vehicle Barriers: These are typically tall steel structures designed to prevent the passage of vehicles. They are often deployed in remote areas where vehicle crossings pose a significant security threat.
- Pedestrian Fencing: This type of barrier is primarily found in urban areas and is designed to deter pedestrian crossings. The height and design of pedestrian fencing vary, with some sections featuring concertina wire or other deterrents.
- Walls: The most recent additions to the border barrier system are concrete walls, primarily constructed in the southwestern portion of the border. These walls are typically taller and more robust than traditional fencing, intended to deter more determined crossings.
Mapping the Border Wall:
Various online resources provide detailed maps of the U.S.-Mexico border wall, offering valuable insights into its location, extent, and types of barriers. These maps are essential tools for understanding the physical reality of the border and its implications.
- Government Agencies: The U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) website provides comprehensive information about the border wall, including maps, statistics, and construction updates.
- Independent Organizations: Non-profit organizations and research institutions often publish maps and reports on the border wall, providing alternative perspectives and analysis.
- Interactive Maps: Numerous websites offer interactive maps, allowing users to explore the border wall in detail, zoom in on specific areas, and access additional information.
Beyond the Physical Barrier:
While the physical barrier is a prominent aspect of the U.S.-Mexico border, it is essential to recognize that it is just one component of a complex border security apparatus. Other critical elements include:
- Technology: Advanced surveillance systems, sensors, and drones are deployed to monitor the border, detect illegal crossings, and support law enforcement operations.
- Personnel: A vast network of Border Patrol agents, customs officers, and other law enforcement personnel work tirelessly to secure the border and enforce immigration laws.
- International Cooperation: Cooperation between the U.S. and Mexico is crucial for addressing transnational crime, managing migration flows, and promoting economic development along the border.
The Impact of the Border Wall:
The ongoing construction and expansion of the border wall have sparked intense debate and controversy. Proponents argue that it is essential for deterring illegal immigration, controlling drug trafficking, and enhancing national security. Opponents contend that the wall is ineffective, costly, environmentally damaging, and perpetuates harmful stereotypes and xenophobia.
- Environmental Impacts: The construction of the wall has raised concerns about its impact on wildlife habitats, water resources, and cultural sites.
- Economic Impacts: The wall’s construction has created jobs in certain sectors, but its economic impact on border communities remains a subject of debate.
- Social Impacts: The wall’s presence has been seen as a symbol of division and separation, impacting communities on both sides of the border.
The Future of the Border Wall:
The future of the border wall remains uncertain. The political landscape surrounding border security continues to evolve, and the debate over the wall’s effectiveness, costs, and impacts is likely to continue.
FAQs:
- What is the purpose of the U.S.-Mexico border wall? The primary purpose of the border wall is to deter illegal immigration and drug trafficking.
- How long is the U.S.-Mexico border wall? The total length of the wall is subject to debate and varies depending on how "wall" is defined. The current length of physical barriers, including fencing and walls, is estimated to be around 450 miles.
- Is the border wall effective in deterring illegal immigration? The effectiveness of the wall in deterring illegal immigration is a highly contested issue. Some studies suggest that the wall has had a minimal impact on overall immigration levels, while others argue that it has contributed to a shift in crossing patterns.
- What are the environmental impacts of the border wall? The construction of the wall has raised concerns about its impact on wildlife habitats, water resources, and cultural sites.
- What is the cost of the U.S.-Mexico border wall? The total cost of the wall is estimated to be billions of dollars, with the exact figure subject to debate and varying depending on the scope of the project.
Tips:
- Consult Multiple Sources: When researching the U.S.-Mexico border wall, consult a variety of sources, including government websites, academic journals, news articles, and non-profit organizations.
- Consider Different Perspectives: Be aware of the diverse perspectives on the border wall, including those of proponents, opponents, and neutral observers.
- Examine the Evidence: Evaluate the evidence presented in support of different arguments, considering the methodology, data sources, and potential biases.
- Engage in Critical Thinking: Approach the topic of the border wall with a critical mindset, questioning assumptions, identifying potential biases, and considering alternative explanations.
Conclusion:
The U.S.-Mexico border wall is a complex and multifaceted issue with far-reaching implications. Understanding the physical characteristics of the wall, its history, and its impact on the environment, economy, and social fabric is crucial for informed debate and decision-making. The ongoing debate over the wall underscores the need for comprehensive analysis, critical thinking, and a commitment to seeking solutions that address the challenges and opportunities presented by the U.S.-Mexico border.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into us border wall map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
