Unveiling the Secrets of the MAP Sensor: How It Regulates Your Engine’s Performance
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the MAP Sensor: How It Regulates Your Engine’s Performance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the MAP Sensor: How It Regulates Your Engine’s Performance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the MAP Sensor: How It Regulates Your Engine’s Performance

The modern internal combustion engine is a marvel of engineering, a complex system of interconnected parts working in harmony to convert fuel into motion. One crucial component within this intricate system is the Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor. This unassuming device plays a pivotal role in determining the engine’s fuel-air mixture, directly impacting its power, efficiency, and emissions. Understanding how the MAP sensor works is essential for comprehending the intricate dance between fuel and air that powers your vehicle.
The MAP Sensor: A Pressure Gauge for Engine Efficiency
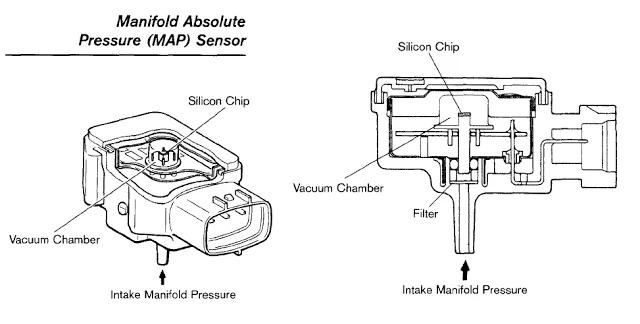
The MAP sensor, often referred to as a manifold pressure sensor, acts as a pressure gauge for the engine’s intake manifold. This manifold is a crucial element in the engine’s breathing process, collecting air from the intake system and distributing it to the cylinders. The pressure within the manifold fluctuates based on the engine’s speed, load, and throttle position.
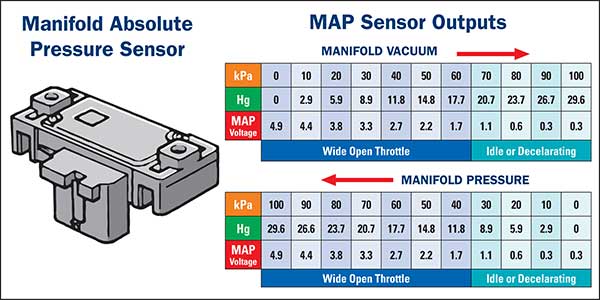
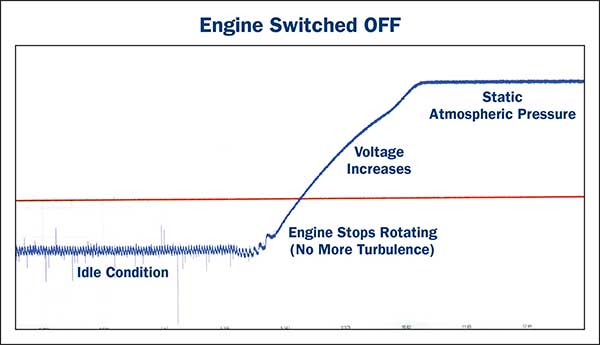
The MAP sensor’s primary function is to measure this fluctuating pressure and convert it into a voltage signal that the engine control unit (ECU) can interpret. This voltage signal serves as a vital piece of information for the ECU, allowing it to precisely regulate the fuel injection system and optimize the air-fuel mixture.
Delving Deeper: How the MAP Sensor Measures Pressure
The MAP sensor itself is typically a small, cylindrical device with a diaphragm inside. This diaphragm is sensitive to changes in pressure within the intake manifold. As the pressure fluctuates, the diaphragm flexes, altering the resistance within a built-in electrical circuit. This change in resistance is then converted into a voltage signal, which is transmitted to the ECU.
The ECU: Interpreting the MAP Sensor’s Message
The ECU, the engine’s central control unit, receives the voltage signal from the MAP sensor and interprets it to understand the pressure within the intake manifold. This information is crucial for the ECU to determine the engine’s load and the appropriate amount of fuel needed for optimal combustion.
Optimizing the Air-Fuel Mixture: The MAP Sensor’s Role
The ECU uses the MAP sensor’s data, along with other inputs like throttle position, engine speed, and oxygen sensor readings, to calculate the ideal air-fuel ratio for the current operating conditions. A precise air-fuel mixture is essential for optimal engine performance:
- Rich Mixture: An excess of fuel can lead to incomplete combustion, resulting in reduced fuel efficiency and increased emissions.
- Lean Mixture: A lack of fuel can cause engine knocking or misfires, potentially damaging engine components.
The MAP sensor’s role in ensuring the correct air-fuel mixture is paramount for:
- Engine Power: A well-balanced mixture ensures efficient combustion, maximizing power output.
- Fuel Efficiency: A leaner mixture, when appropriate, optimizes fuel consumption.
- Emissions Control: Maintaining the correct air-fuel ratio minimizes harmful emissions.
Beyond the Basics: The MAP Sensor in Action
The MAP sensor’s influence extends beyond simply determining the air-fuel ratio. Its data is used by the ECU for a variety of functions, including:
- Throttle Control: The ECU uses MAP sensor data to control the throttle position, ensuring smooth acceleration and efficient engine operation.
- Ignition Timing: The MAP sensor helps the ECU adjust ignition timing based on engine load and speed, optimizing combustion and reducing emissions.
- Emissions Control System: The MAP sensor plays a crucial role in the operation of the emissions control system, ensuring proper functioning of components like the catalytic converter.
Understanding the Importance of the MAP Sensor
A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to a cascade of problems, impacting engine performance, fuel economy, and emissions. Common symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor include:
- Rough Idle: The engine may idle unevenly or stall due to an incorrect air-fuel mixture.
- Reduced Power: The engine may struggle to accelerate or experience a loss of power.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: An incorrect air-fuel mixture can lead to higher fuel consumption.
- Emissions Issues: A faulty MAP sensor can result in higher emissions, potentially leading to failed emissions tests.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the MAP Sensor
Q: How often should a MAP sensor be replaced?
A: MAP sensors are generally quite durable and can last for several years or even the lifetime of the vehicle. However, like any sensor, they can eventually fail due to wear and tear, exposure to extreme temperatures, or contamination. Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify potential issues early on.
Q: Can I test a MAP sensor myself?
A: While testing a MAP sensor yourself is possible, it requires specialized tools and knowledge. It’s generally recommended to consult a professional mechanic for accurate diagnosis and repair.
Q: Can a faulty MAP sensor cause engine damage?
A: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to incorrect air-fuel mixtures, potentially causing engine damage if left unaddressed. For example, a consistently lean mixture can cause engine knocking or misfires, leading to premature wear and tear on engine components.
Tips: Maintaining Your MAP Sensor
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect the MAP sensor for signs of damage, dirt, or debris. Ensure the sensor is securely connected and free from any obstructions.
- Clean Air Filter: A dirty air filter can restrict airflow and affect the MAP sensor’s readings. Change the air filter regularly according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Professional Inspection: If you suspect a MAP sensor issue, have it inspected by a qualified mechanic. They can use diagnostic tools to test the sensor’s functionality and determine if it needs replacement.
Conclusion: The MAP Sensor’s Enduring Significance
The MAP sensor, though often overlooked, is an integral part of the engine’s intricate system. Its role in regulating the air-fuel mixture is critical for optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Understanding how the MAP sensor works is crucial for ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. By prioritizing regular maintenance and addressing any potential issues promptly, you can keep your MAP sensor functioning properly and enjoy the benefits of a healthy and responsive engine.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the MAP Sensor: How It Regulates Your Engine’s Performance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!