Unveiling the Power of Position Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Mapping
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Position Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Mapping
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Position Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Position Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Position Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Mapping
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Position Maps
- 3.2 The Benefits of Utilizing Position Maps
- 3.3 Creating a Position Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.4 Types of Position Maps: Exploring Different Approaches
- 3.5 Position Map Template: A Practical Framework for Mapping
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions about Position Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Creating Effective Position Maps
- 3.8 Conclusion: Position Maps – A Strategic Compass for Business Success
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Position Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Mapping

In the dynamic world of business, success hinges on a clear understanding of where your company stands within its competitive landscape. A position map, also known as a perceptual map or competitive mapping tool, provides a visual representation of this landscape, offering a strategic advantage by illuminating key areas of focus and potential for growth.
This article delves into the intricacies of position map templates, outlining their purpose, benefits, and practical applications. We will explore how these powerful tools can empower businesses to make informed decisions, refine their marketing strategies, and ultimately, achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
Understanding the Essence of Position Maps
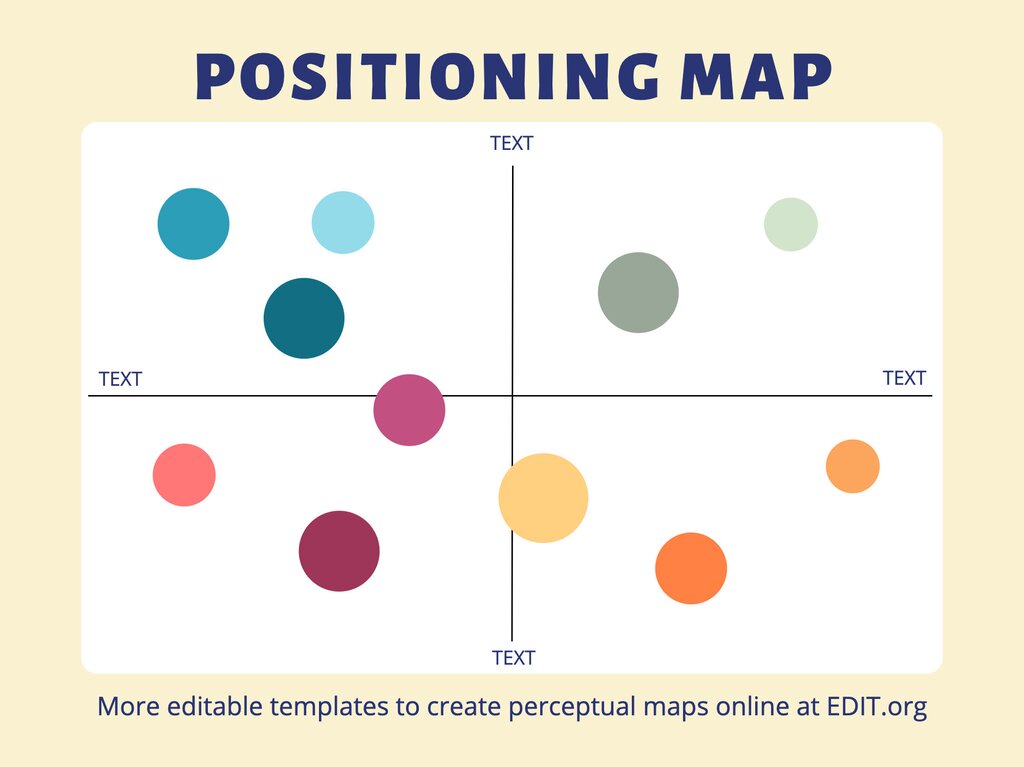
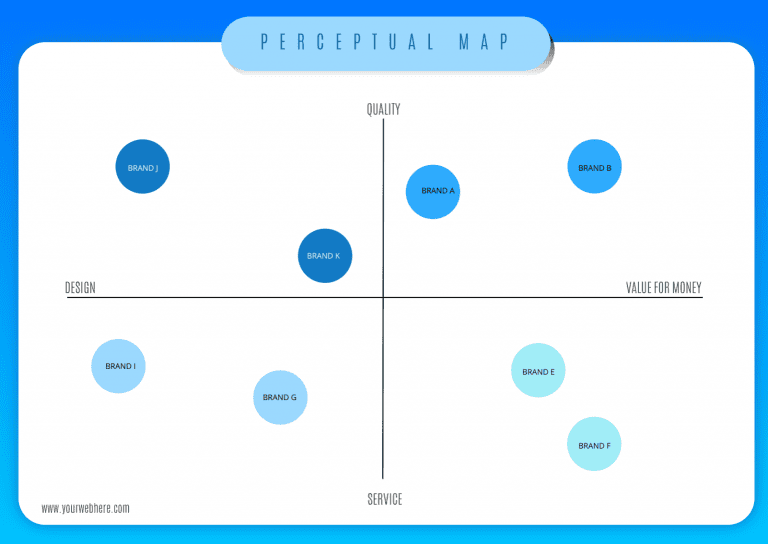
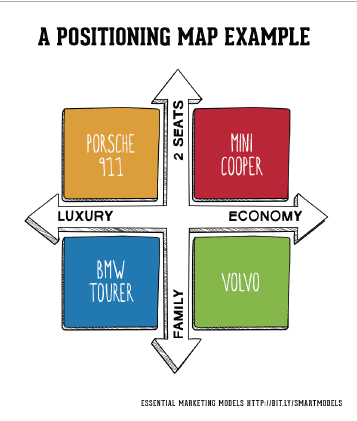
A position map is a visual representation that plots competing products or services based on their perceived attributes or features. These attributes can be diverse, ranging from price and quality to customer service and brand image. The resulting map provides a clear picture of where a company stands in relation to its competitors, revealing potential opportunities and areas for improvement.
The core elements of a position map include:
- Axes: These represent the key attributes or dimensions used to differentiate products or services within the market. For instance, a map for smartphones might use price and functionality as its axes.
- Competitors: Each competitor is plotted on the map based on their perceived position along the chosen axes. This positioning is often based on market research, customer perceptions, and industry analysis.
- Target Audience: The map can also incorporate information about the target audience’s preferences and perceptions, providing insights into how different segments value the attributes represented on the axes.
The Benefits of Utilizing Position Maps
Position maps offer a wealth of benefits for businesses seeking to gain a competitive edge. These advantages include:
1. Enhanced Market Understanding: By visually representing the competitive landscape, position maps provide a clear understanding of the market dynamics. This knowledge empowers businesses to identify potential gaps in the market, areas of differentiation, and opportunities for innovation.
2. Strategic Product Positioning: Position maps help businesses understand how their products or services are perceived by the target audience. This allows for strategic positioning based on customer preferences and competitive pressures. By identifying gaps in the market, businesses can strategically position their offerings to attract specific customer segments.
3. Effective Marketing Strategy Development: Position maps provide a solid foundation for developing targeted marketing campaigns. By understanding the attributes that drive customer preference and competitor positioning, businesses can tailor their messaging and communication strategies to resonate with their target audience.
4. Improved Decision Making: Position maps offer a valuable tool for making informed decisions regarding product development, pricing, marketing, and competitive strategies. By providing a clear visual representation of the market landscape, these maps facilitate strategic discussions and informed decision-making processes.
5. Competitive Advantage Identification: Through the analysis of competitor positioning, businesses can identify areas where they possess a competitive advantage. This knowledge enables the development of strategies that leverage these strengths, maximizing their impact on the market.
Creating a Position Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Crafting a comprehensive and insightful position map requires a structured approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating a position map that effectively captures the competitive landscape:
1. Define the Target Market: The first step involves clearly defining the target market for the product or service being analyzed. This includes identifying the specific customer segments, their needs, and their purchasing behaviors.
2. Identify Key Attributes: Determine the key attributes or dimensions that differentiate products or services within the target market. These attributes should be relevant to customer preferences and align with the competitive landscape.
3. Select Competitors: Identify the key competitors within the chosen market. This list should include both direct and indirect competitors, encompassing all players that influence the target market.
4. Gather Data: Collect data on the perceived positions of each competitor along the chosen attributes. This data can be gathered through market research, customer surveys, industry analysis, and expert opinions.
5. Plot Competitors: Using the gathered data, plot each competitor on the map based on their perceived positions along the selected attributes. This step involves assigning numerical values to each competitor’s position on the chosen axes.
6. Analyze the Map: Once the competitors are plotted, analyze the resulting map to identify key insights. This includes identifying clusters of competitors, gaps in the market, and potential areas for differentiation.
7. Refine and Iterate: The position map is a dynamic tool that should be regularly reviewed and updated. As the market evolves, competitors shift their positions, and customer preferences change, the map should be refined to reflect these changes.
Types of Position Maps: Exploring Different Approaches
While the fundamental principles remain consistent, position maps can be tailored to specific needs and objectives. Here are some common types of position maps:
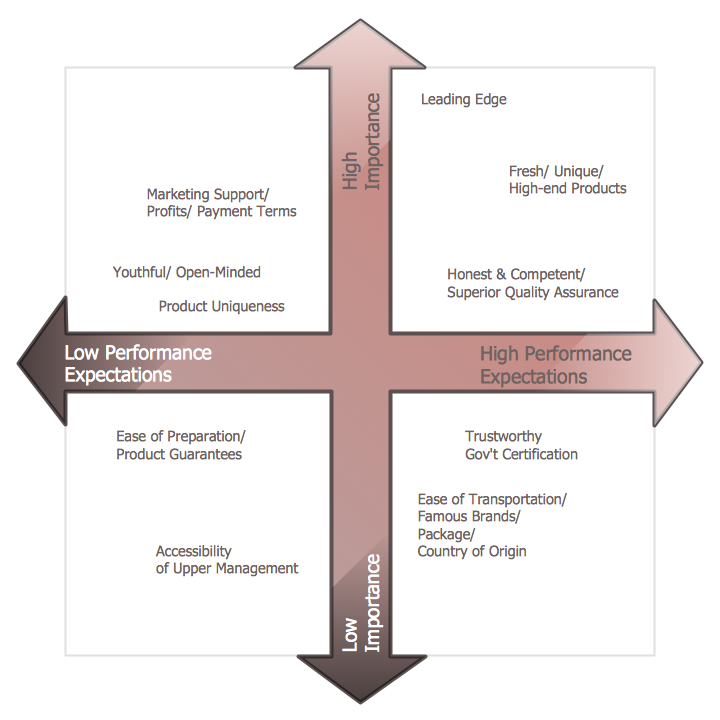
1. Perceptual Maps: These maps focus on customer perceptions of products or services based on specific attributes. They are commonly used to understand how different brands are perceived by the target audience and identify opportunities for differentiation.
2. Competitive Maps: These maps focus on the competitive landscape, plotting competitors based on their market share, pricing, product features, and other relevant factors. They are useful for understanding the competitive dynamics and identifying potential threats and opportunities.
3. Value Maps: These maps focus on the value proposition offered by different products or services. They plot competitors based on their value proposition, customer benefits, and perceived price-to-value ratio. Value maps are particularly useful for understanding how different products or services cater to specific customer needs and preferences.
4. Brand Positioning Maps: These maps focus on the positioning of brands within the market. They plot brands based on their perceived attributes, such as image, quality, and brand personality. Brand positioning maps are helpful for understanding how brands are perceived by the target audience and identifying opportunities for brand differentiation.
Position Map Template: A Practical Framework for Mapping
To facilitate the creation of position maps, various templates are available. These templates provide a structured framework, simplifying the process of gathering data, plotting competitors, and analyzing the resulting map.
A typical position map template includes:
- Axes: The template provides space for defining the two primary axes that represent the key attributes or dimensions used to differentiate products or services within the market.
- Competitors: The template includes a list of competitors, allowing for the systematic plotting of each competitor’s perceived position along the chosen axes.
- Data Collection: The template often incorporates space for recording data on each competitor’s position along the axes, based on market research, customer surveys, or other relevant sources.
- Analysis: The template may include space for analyzing the resulting map, identifying key insights, and drawing strategic conclusions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Position Maps
1. What are the limitations of position maps?
While position maps offer valuable insights, they are not without limitations. The accuracy of the map depends on the quality of data collected and the assumptions made about customer perceptions. Additionally, position maps are a snapshot in time and may not reflect dynamic market shifts or evolving customer preferences.
2. How often should position maps be updated?
Position maps should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the market, competitor positioning, and customer preferences. Ideally, maps should be updated at least annually, or more frequently if significant market shifts occur.
3. What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating position maps?
Common mistakes include:
- Choosing irrelevant attributes: The chosen attributes should be relevant to customer preferences and the competitive landscape.
- Using too many attributes: Including too many attributes can make the map cluttered and difficult to interpret.
- Ignoring qualitative data: Qualitative data, such as customer feedback and industry expert opinions, can provide valuable insights that complement quantitative data.
- Overlooking dynamic changes: Position maps are a snapshot in time and should be updated regularly to reflect evolving market dynamics.
4. How can I use a position map to develop a competitive advantage?
By analyzing the position map, businesses can identify areas where they possess a competitive advantage or where they can differentiate themselves from competitors. This knowledge can be leveraged to develop strategies that exploit these advantages and strengthen their market position.
5. What are some examples of successful position map applications?
Position maps have been successfully used by various companies across different industries. For instance, Apple used position maps to understand the competitive landscape for smartphones and strategically position the iPhone as a premium device with a focus on design and user experience. Similarly, Southwest Airlines used position maps to identify a niche in the airline industry, focusing on low-cost, point-to-point flights.
Tips for Creating Effective Position Maps
1. Focus on Relevant Attributes: Choose attributes that are directly relevant to customer preferences and differentiate products or services within the market.
2. Use Clear and Concise Language: Ensure that the axes and labels are clear and concise, avoiding technical jargon or ambiguous language.
3. Incorporate Data from Multiple Sources: Gather data from various sources, including market research, customer surveys, industry analysis, and expert opinions.
4. Regularly Review and Update: Position maps are dynamic tools that should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the market and customer preferences.
5. Use the Map to Inform Decision Making: Leverage the insights gained from the position map to inform strategic decisions related to product development, pricing, marketing, and competitive strategies.
Conclusion: Position Maps – A Strategic Compass for Business Success
Position maps provide a powerful tool for businesses seeking to navigate the complexities of the competitive landscape. By visually representing the market dynamics, these maps offer a clear understanding of competitor positioning, customer preferences, and potential opportunities for differentiation.
Through the careful selection of attributes, data collection, and analysis, businesses can leverage position maps to develop effective marketing strategies, refine product offerings, and ultimately, achieve sustainable competitive advantage. By embracing the insights gleaned from these strategic tools, businesses can chart a course towards success in a dynamic and ever-evolving market.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Position Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!