Unveiling the Human Experience: Empathy Mapping in Design Thinking
Related Articles: Unveiling the Human Experience: Empathy Mapping in Design Thinking
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Human Experience: Empathy Mapping in Design Thinking. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Human Experience: Empathy Mapping in Design Thinking

In the realm of design thinking, where innovation thrives on understanding human needs, empathy mapping emerges as a powerful tool for delving into the minds and hearts of users. This technique, a cornerstone of human-centered design, provides a structured framework for visualizing the emotional landscape of a user, their thoughts, actions, and motivations. It serves as a bridge between the designer’s perspective and the user’s experience, fostering deeper insights and leading to more effective solutions.
The Essence of Empathy Mapping
Empathy mapping is essentially a visual representation of a user’s experience, capturing their thoughts, feelings, needs, and pain points. It is a collaborative exercise, often conducted in teams, where participants gather and analyze qualitative data about the user, creating a comprehensive picture of their emotional journey.
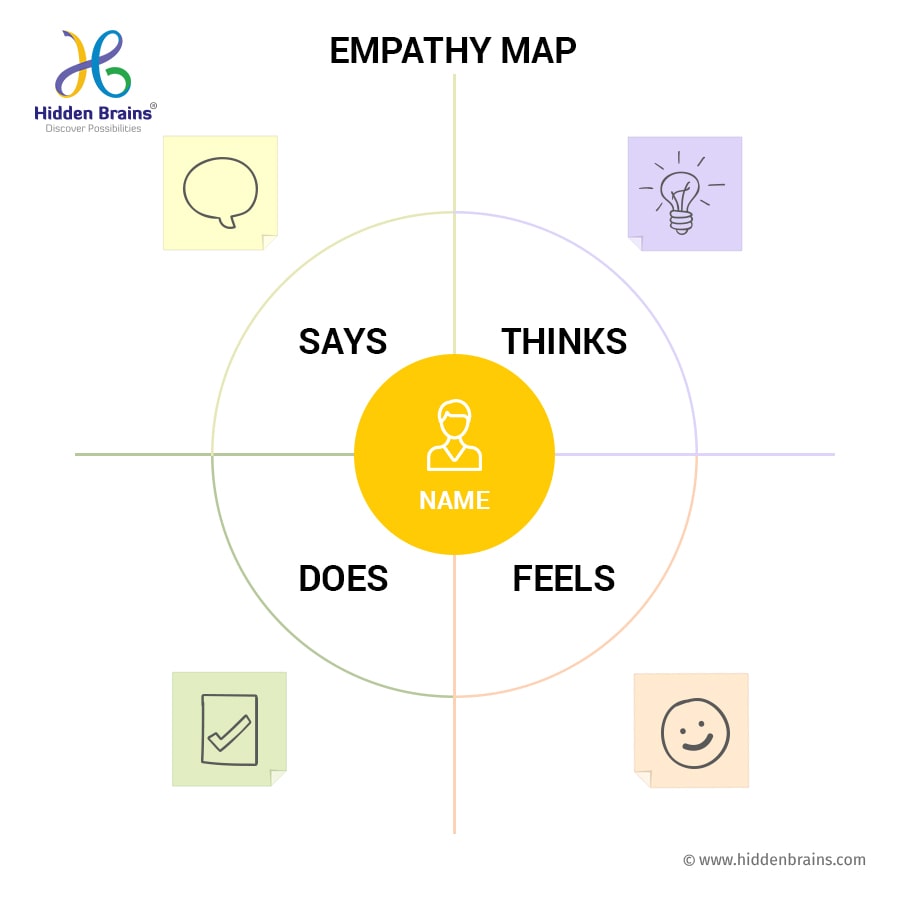
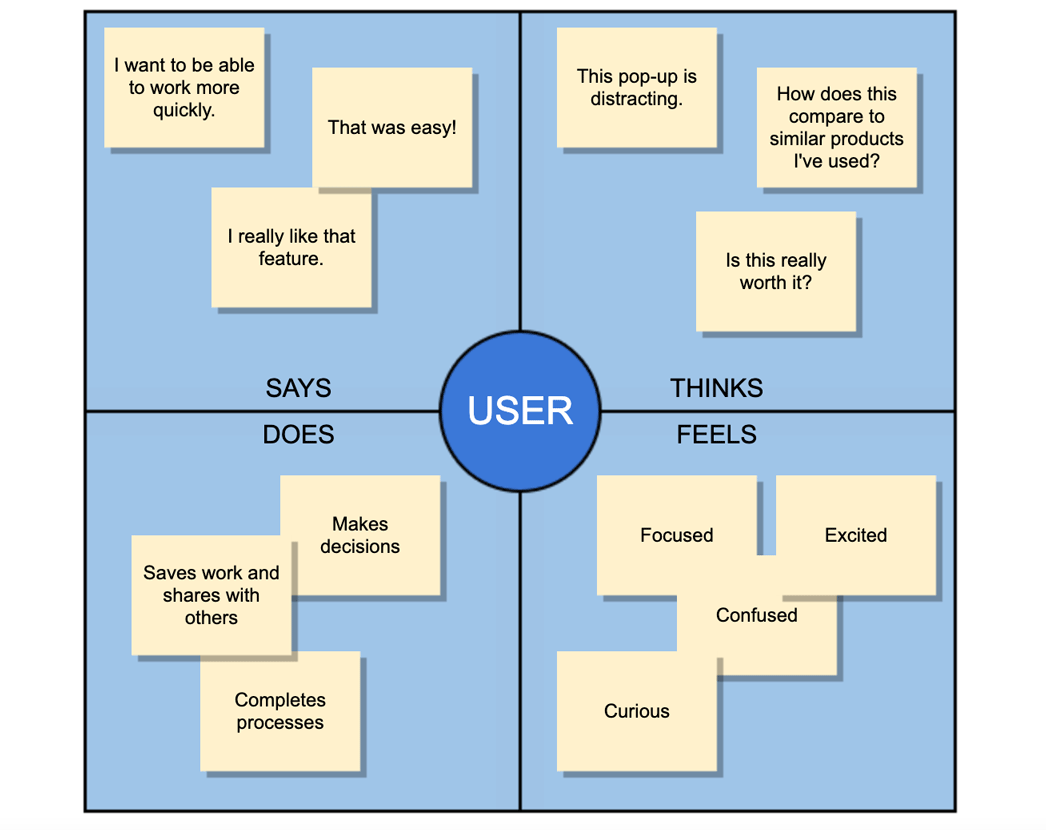
Structure and Components of an Empathy Map
An empathy map typically comprises four quadrants, each representing a different aspect of the user’s experience:
- Says: This quadrant captures the user’s explicit statements, their verbal expressions of thoughts, opinions, and needs. It reveals what they say about their experiences, both positive and negative.
- Thinks: This quadrant delves into the user’s internal thoughts, their beliefs, assumptions, and knowledge related to the product or service. It explores their cognitive understanding and perceptions.
- Feels: This quadrant focuses on the user’s emotions, capturing their feelings, anxieties, frustrations, and aspirations. It reveals the emotional landscape surrounding their interaction with the product or service.
- Does: This quadrant describes the user’s actions, behaviors, and routines related to the product or service. It provides insights into how they engage with it in their daily lives.
The Power of Empathy Mapping in Design Thinking
Empathy mapping plays a crucial role in design thinking by:
- Fostering User-Centered Design: By understanding the user’s perspective, empathy mapping ensures that design solutions are centered around their needs, aspirations, and pain points.
- Identifying Unmet Needs: Through the process of mapping out user emotions, thoughts, and actions, designers can uncover hidden needs and opportunities for innovation that might otherwise go unnoticed.
- Generating Innovative Solutions: By gaining a deep understanding of the user’s experience, designers can develop solutions that are not only functional but also emotionally resonant and meaningful.
- Enhancing Collaboration: Empathy mapping promotes collaboration within design teams, fostering shared understanding and alignment around user needs.
- Facilitating Communication: By providing a visual representation of the user’s experience, empathy mapping facilitates clear and effective communication between designers, stakeholders, and users.
Beyond the Basics: Deepening the Empathy Mapping Process
While the standard four-quadrant structure provides a solid foundation, empathy mapping can be further enriched through various techniques:
- User Personas: Creating detailed user personas, based on empathy mapping insights, helps to personalize the user experience and ensure design solutions are tailored to specific user groups.
- Journey Mapping: Combining empathy mapping with journey mapping allows for a deeper understanding of the user’s experience across multiple touchpoints, from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement.
- User Research Techniques: Integrating empathy mapping with qualitative research methods, such as interviews, focus groups, and observations, provides rich data to inform the mapping process.
FAQs about Empathy Mapping
Q: What are some common challenges faced when conducting empathy mapping?
A: Common challenges include:
- Data Collection: Gathering sufficient and accurate qualitative data about users can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Bias: Designers’ own biases and assumptions can influence the interpretation of user data, leading to inaccurate empathy mapping.
- Collaboration: Achieving consensus within a team regarding user insights and interpretations can be challenging.
Q: How can empathy mapping be used in different industries?
A: Empathy mapping is applicable across various industries, including:
- Product Design: Understanding user needs for designing intuitive and user-friendly products.
- Service Design: Optimizing service experiences to meet customer expectations and enhance satisfaction.
- Marketing: Developing targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with customer emotions and motivations.
- Healthcare: Designing patient-centered care solutions that address emotional and physical needs.
Q: What are some tips for effective empathy mapping?
A:
- Define the Scope: Clearly define the target user group and the specific product or service being explored.
- Gather Diverse Data: Utilize a variety of qualitative research methods to gather rich and varied data about user experiences.
- Collaborate and Iterate: Involve multiple stakeholders in the mapping process and continuously refine the map based on new insights.
- Visualize and Communicate: Create clear and engaging visuals to communicate empathy mapping findings to stakeholders and users.
Conclusion: The Power of Understanding
Empathy mapping stands as a powerful tool in the design thinking toolkit, enabling designers to understand the human experience and create solutions that resonate with users on a deeper level. By fostering empathy, designers can craft products and services that meet not just functional needs but also emotional aspirations, leading to greater user satisfaction and enduring impact. As we continue to navigate an increasingly complex world, empathy mapping serves as a vital reminder that understanding the human experience is the foundation of truly impactful design.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Human Experience: Empathy Mapping in Design Thinking. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!