Unveiling the Global Landscape of Hunger: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World Hunger Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Landscape of Hunger: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World Hunger Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Global Landscape of Hunger: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World Hunger Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Landscape of Hunger: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World Hunger Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Global Landscape of Hunger: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World Hunger Map
- 3.1 The Anatomy of a Hunger World Map
- 3.2 The Importance of the Hunger World Map
- 3.3 Understanding the Factors Contributing to Hunger
- 3.4 FAQs About the Hunger World Map
- 3.5 Tips for Interpreting the Hunger World Map
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Global Landscape of Hunger: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World Hunger Map

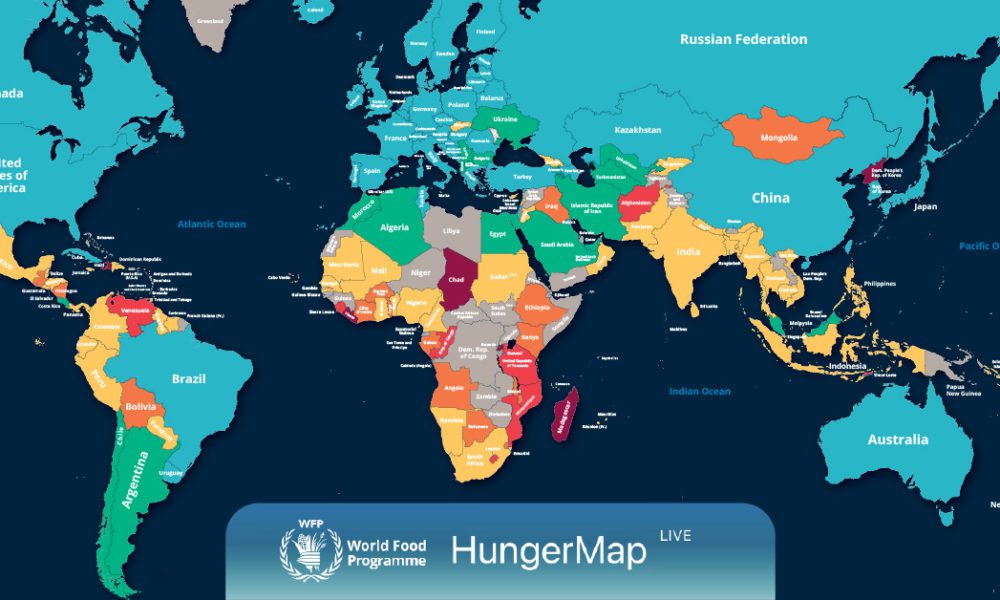
The world hunger map is a powerful visual representation of a complex global issue: food insecurity. It paints a stark picture of the regions and populations most vulnerable to hunger, malnutrition, and its devastating consequences. Understanding this map is crucial for informing policy decisions, guiding humanitarian efforts, and ultimately, working towards a world free from hunger.
The Anatomy of a Hunger World Map
A typical hunger world map uses color gradients or other visual cues to depict the severity of food insecurity across different countries and regions. The data used to create these maps is sourced from various organizations, including the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the World Food Programme (WFP), and the World Health Organization (WHO).
These maps typically incorporate various indicators to paint a comprehensive picture of hunger, including:
- Prevalence of Undernourishment: This indicator reflects the proportion of the population that does not consume enough food to meet their dietary energy requirements.
- Prevalence of Stunting: This indicator measures the percentage of children under five years old whose height is significantly lower than expected for their age, indicating chronic malnutrition.
- Prevalence of Wasting: This indicator measures the percentage of children under five years old whose weight is significantly lower than expected for their height, indicating acute malnutrition.
- Food Insecurity: This indicator measures the percentage of the population that lacks regular access to adequate food.
The Importance of the Hunger World Map
The hunger world map serves several vital purposes:
- Raising Awareness: It visually highlights the geographic disparities in food security, drawing attention to areas where hunger is most prevalent. This awareness can mobilize public opinion and pressure governments to address the issue.
- Informing Policy: The map provides crucial data for policymakers to understand the scale and distribution of hunger, enabling them to tailor policies and allocate resources effectively.
- Guiding Humanitarian Aid: By identifying regions with the highest prevalence of hunger, the map helps humanitarian organizations prioritize their efforts and target assistance where it is most needed.
- Monitoring Progress: The map allows for tracking changes in hunger levels over time, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness of interventions and the progress made towards achieving food security goals.
Understanding the Factors Contributing to Hunger
While the hunger world map provides a visual snapshot of the problem, it is essential to understand the complex factors that contribute to food insecurity. These include:
- Poverty: Poverty is a major driver of hunger, as it limits access to nutritious food and healthcare.
- Conflict and Instability: War and conflict disrupt food production, distribution, and access, leading to widespread food insecurity.
- Climate Change: Extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, can decimate crops and livestock, leading to food shortages and price increases.
- Inequality: Unequal distribution of resources and income exacerbate food insecurity, leaving marginalized communities vulnerable to hunger.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Limited access to transportation, storage facilities, and markets can hinder food production and distribution, contributing to food insecurity.
FAQs About the Hunger World Map
1. What is the difference between hunger and malnutrition?
Hunger refers to the physical sensation of needing food, while malnutrition encompasses a broader range of nutritional deficiencies, including undernourishment, stunting, and wasting.
2. How often is the hunger world map updated?
The data used to create the hunger world map is updated regularly, usually on an annual or biennial basis, depending on the source.
3. Can the hunger world map be used to predict future trends in food insecurity?
While the map provides a snapshot of current food insecurity, it can be used to identify trends and predict future scenarios based on factors like population growth, climate change, and economic development.
4. What can individuals do to help address hunger?
Individuals can contribute to fighting hunger by supporting organizations working to address food insecurity, advocating for policies that promote food security, and making conscious choices about their food consumption.
5. Is the hunger world map a perfect representation of food insecurity?
While the map provides valuable information, it is important to acknowledge that it is a simplified representation of a complex issue. It does not capture the nuances of food insecurity at the local level and should be used in conjunction with other data sources.
Tips for Interpreting the Hunger World Map
- Consider the context: Understand the factors contributing to hunger in different regions and the specific challenges faced by vulnerable populations.
- Look beyond the numbers: While quantitative data is important, consider the human stories behind the statistics and the impact of hunger on individuals and communities.
- Engage with the data: Use the map to explore specific regions, identify trends, and understand the underlying causes of food insecurity.
- Take action: Use the information gained from the map to advocate for change, support organizations working to combat hunger, and make informed decisions about your own food choices.
Conclusion
The hunger world map serves as a critical tool for understanding the global landscape of food insecurity. It highlights the disparities in access to food, informs policy decisions, guides humanitarian efforts, and motivates action to address this critical issue. By utilizing the map’s insights and working together, we can strive to create a world where everyone has access to enough nutritious food to live a healthy and fulfilling life.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Global Landscape of Hunger: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World Hunger Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!