Unveiling the Dynamics of Snow Cover Across the United States: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Dynamics of Snow Cover Across the United States: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Dynamics of Snow Cover Across the United States: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Dynamics of Snow Cover Across the United States: A Comprehensive Guide
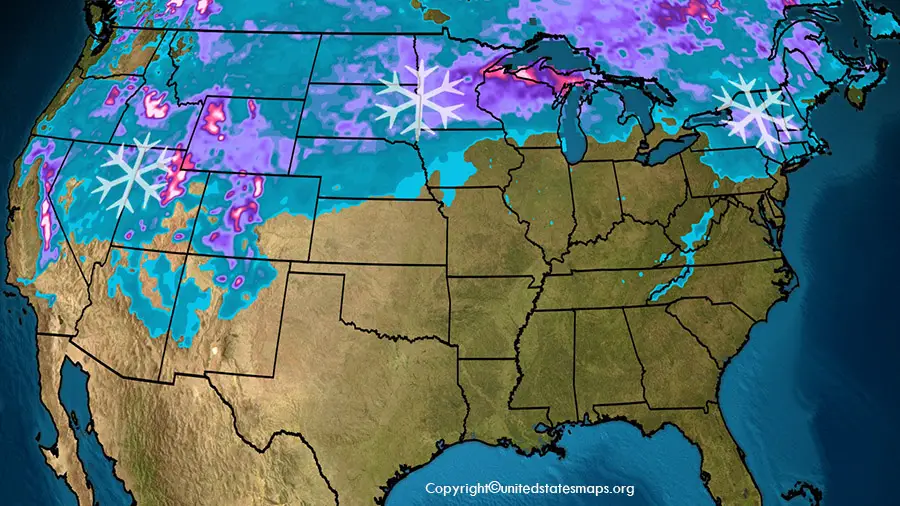
The United States, a vast and geographically diverse nation, experiences a wide range of weather conditions, with snow cover playing a significant role in shaping its ecosystems, economies, and daily lives. Understanding the distribution, extent, and variability of snow cover across the country is crucial for various sectors, from agriculture and transportation to water resources management and climate monitoring. This article delves into the intricacies of snow cover in the United States, exploring its significance, the tools used to monitor it, and the factors influencing its patterns.
The Importance of Snow Cover: A Multifaceted Role
Snow cover is not merely a picturesque winter scene; it plays a vital role in the intricate balance of the natural world. Its significance extends across various domains:
- Water Resources: Snow acts as a natural reservoir, storing vast amounts of water in its frozen form. As temperatures rise, snow melts, replenishing rivers, lakes, and groundwater, providing essential water resources for agriculture, industry, and human consumption.
- Hydrological Cycle: Snow cover plays a crucial role in regulating the hydrological cycle. Its presence influences the timing and magnitude of streamflow, impacting water availability throughout the year.
- Agriculture: Snow cover acts as an insulator, protecting crops and soil from extreme cold and frost damage. It also provides moisture for spring growth, contributing to agricultural productivity.
- Ecosystems: Snow cover influences the habitat of numerous species, providing insulation for wildlife, regulating plant growth, and influencing the distribution of various flora and fauna.
- Transportation: Snow cover significantly impacts transportation infrastructure, particularly in mountainous regions and during winter months. Its presence can disrupt road networks, air travel, and other modes of transport.
- Climate Regulation: Snow cover plays a significant role in regulating Earth’s climate by reflecting solar radiation back into space, contributing to a cooling effect. Changes in snow cover can have cascading effects on regional and global climates.
Monitoring Snow Cover: Tools and Techniques
Monitoring snow cover is essential for understanding its dynamics, predicting potential impacts, and informing decision-making. Various tools and techniques are employed for this purpose:
- Satellite Imagery: Satellite-based remote sensing provides a comprehensive and continuous view of snow cover across vast areas. Sensors on satellites capture images in different wavelengths, allowing scientists to distinguish snow from other surfaces.
- Ground-based Observations: Ground-based observations, such as snow depth measurements, snow water equivalent (SWE) measurements, and snow density measurements, provide detailed information about snow conditions at specific locations.
- Weather Stations: Weather stations equipped with snow depth sensors and other instruments collect data on snow accumulation, melt rates, and other relevant parameters.
- Numerical Models: Computer models, incorporating data from various sources, can simulate snow cover dynamics, predict future snow conditions, and assess the potential impacts of climate change.
Factors Influencing Snow Cover Patterns
Snow cover patterns across the United States are influenced by a complex interplay of factors:
- Latitude: The amount of snow cover generally decreases as latitude decreases. Regions further north experience longer winters and more snowfall, while southern regions receive less snow.
- Elevation: Higher elevations typically receive more snow due to colder temperatures and increased precipitation. Mountainous areas often have significant snow cover, even in regions with mild winters.
- Topography: The shape of the land can influence snow distribution, with windward slopes receiving more snow than leeward slopes.
- Climate: Climate patterns, including temperature, precipitation, and wind, significantly influence snow accumulation, melt rates, and overall snow cover patterns.
- Human Activities: Land-use changes, such as deforestation and urbanization, can impact snow cover by altering local microclimates and influencing snowmelt rates.
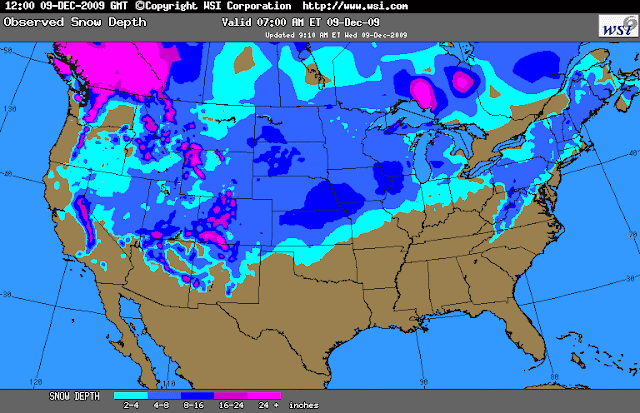
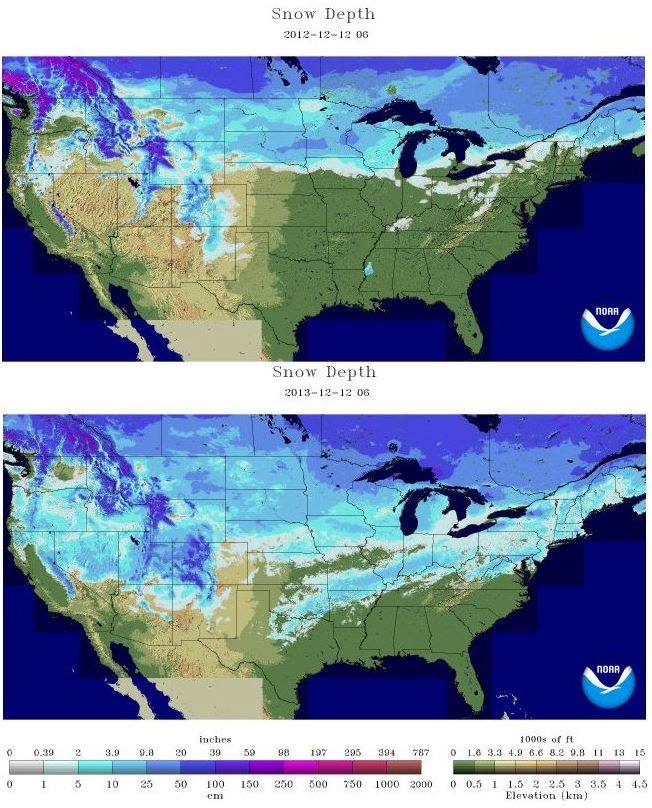
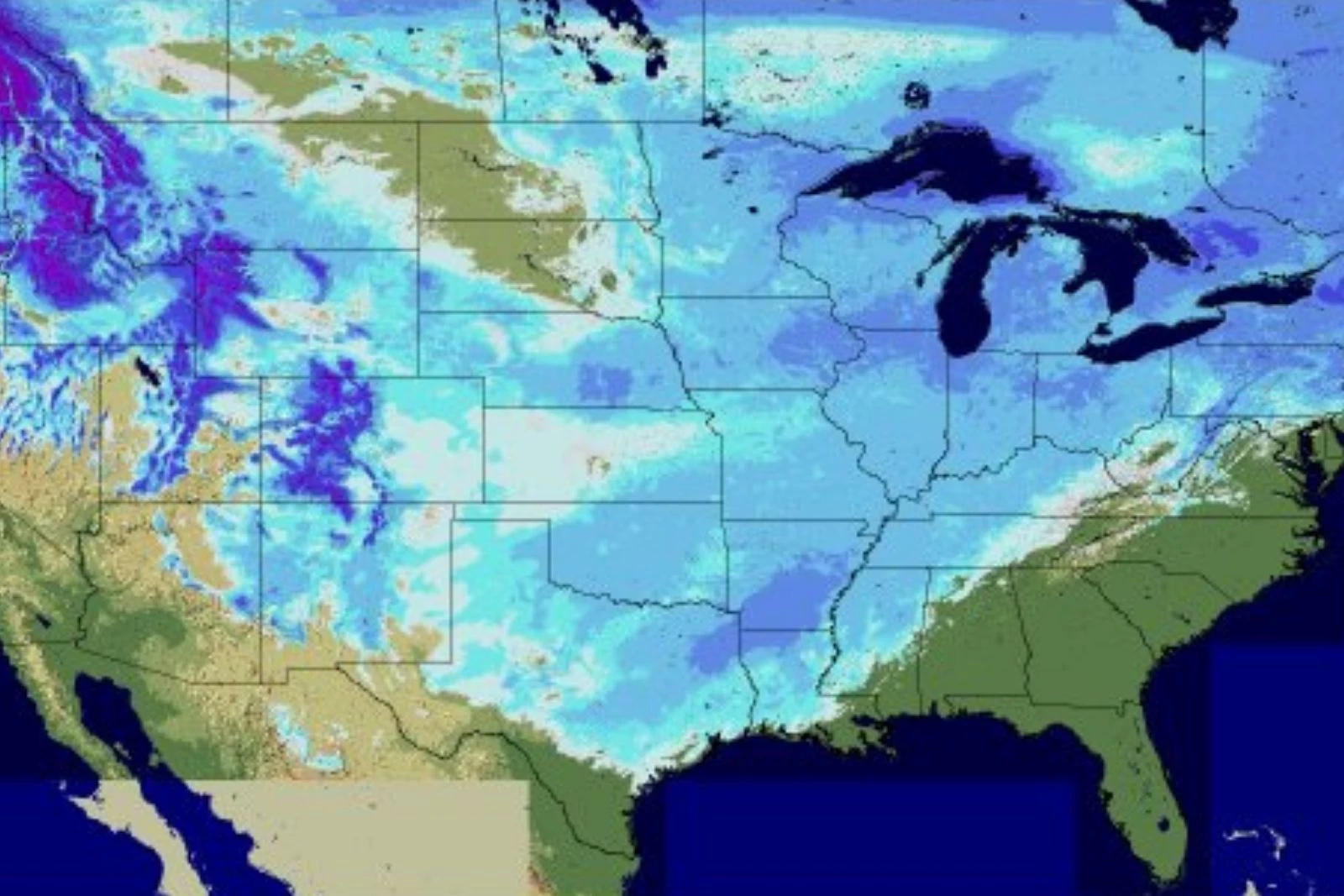
United States Snow Cover Map: A Visual Representation
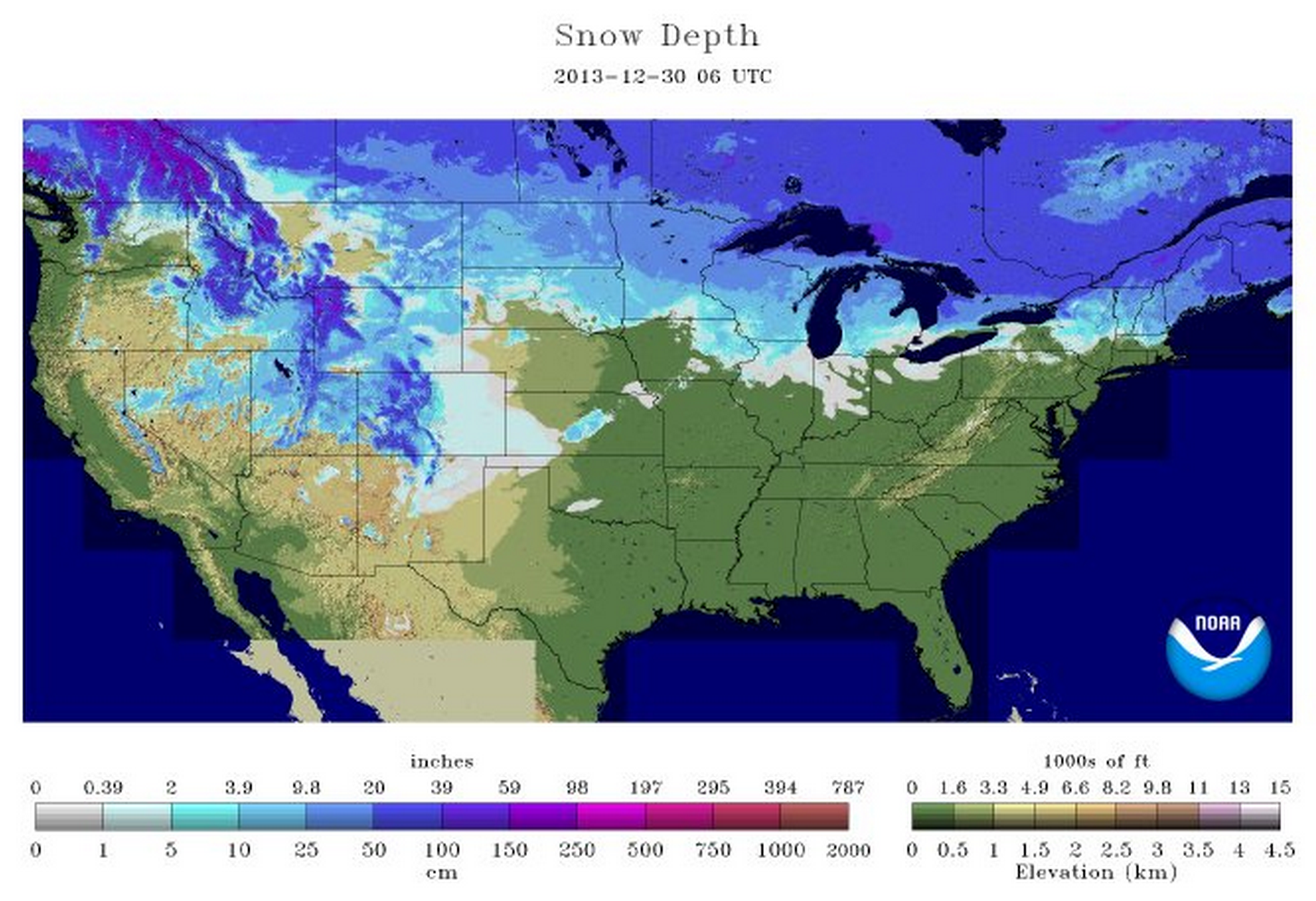
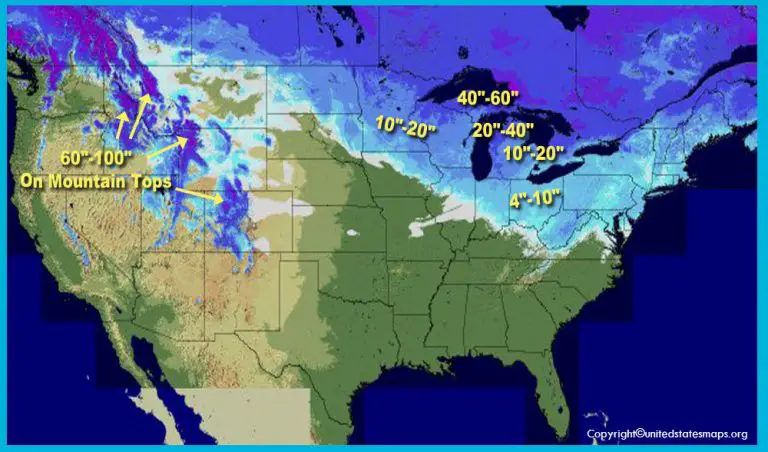
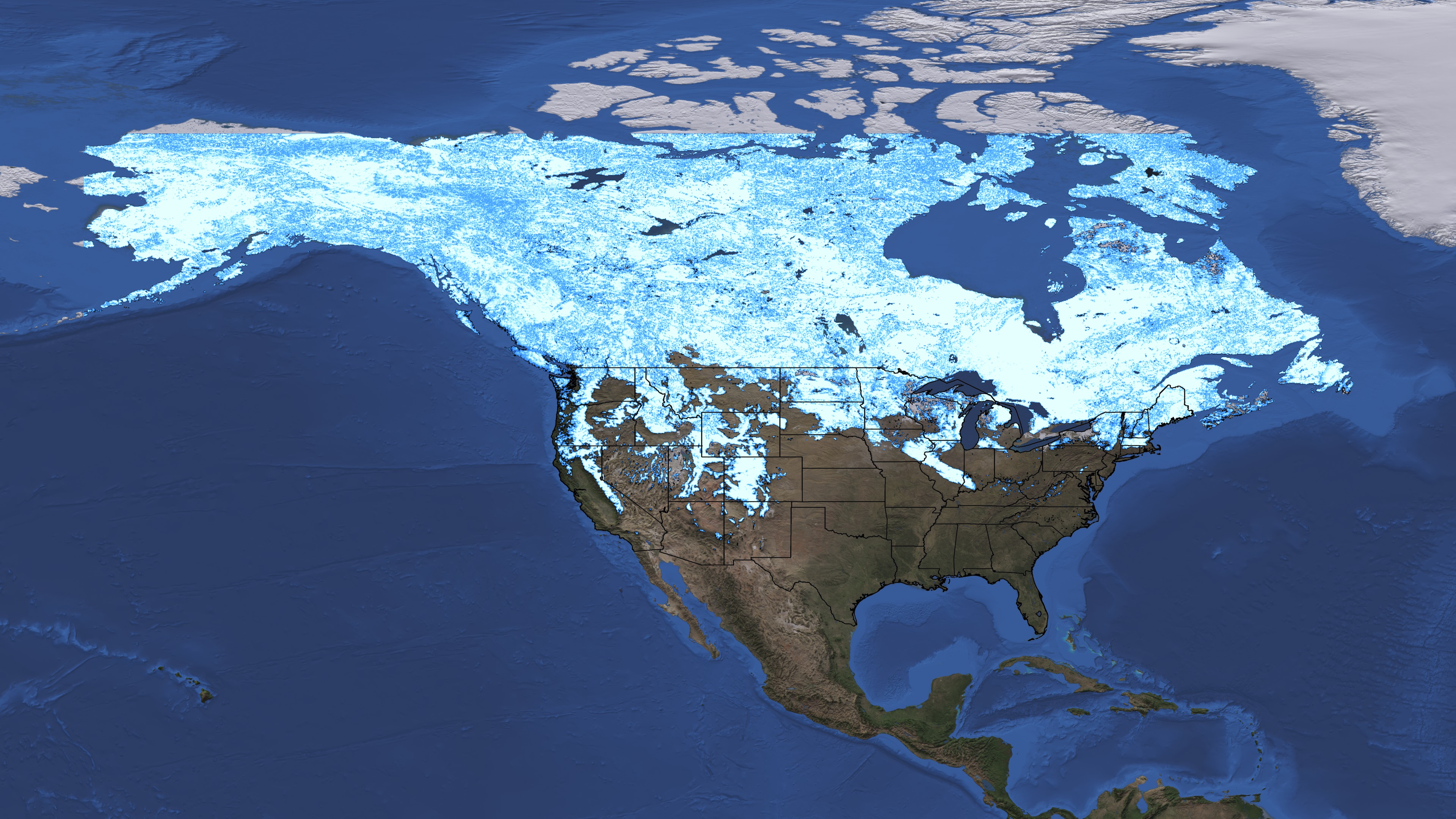
The United States Snow Cover Map provides a visual representation of the extent and distribution of snow cover across the country. This map is generated using data from various sources, including satellite imagery, ground-based observations, and weather stations. It typically depicts snow cover as a shaded area, with different colors representing varying snow depths or snow water equivalents.
Benefits of the United States Snow Cover Map
The United States Snow Cover Map offers numerous benefits for various sectors:
- Water Resource Management: The map helps water resource managers understand the availability of water resources, predict potential water shortages, and optimize water allocation.
- Agriculture: Farmers can use the map to assess the potential impact of snow cover on their crops, plan irrigation strategies, and make informed decisions about planting and harvesting schedules.
- Transportation: Transportation authorities can use the map to monitor snow conditions, plan snow removal operations, and ensure safe and efficient transportation networks.
- Climate Monitoring: The map provides valuable data for monitoring changes in snow cover over time, assessing the impacts of climate change, and developing adaptation strategies.
- Ecosystem Management: The map helps ecologists understand the distribution and abundance of species influenced by snow cover, identify potential threats to biodiversity, and implement effective conservation measures.
FAQs about United States Snow Cover Map
Q: What is the best website to find the United States Snow Cover Map?
A: Several websites provide access to United States Snow Cover Maps, including:
- National Operational Hydrologic Remote Sensing Center (NOHRSC): This website offers a variety of snow cover maps, including daily and seasonal maps.
- National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC): The NSIDC provides a wide range of snow cover data, including maps, time series, and research tools.
- National Weather Service (NWS): The NWS website offers snow cover maps for specific regions of the United States.
Q: How often is the United States Snow Cover Map updated?
A: The frequency of updates varies depending on the data source and the specific map. Some maps are updated daily, while others are updated weekly or monthly.
Q: What information is included on the United States Snow Cover Map?
A: The United States Snow Cover Map typically displays the extent and distribution of snow cover, with different colors representing varying snow depths or snow water equivalents. Some maps may also include information on snow accumulation, snowmelt rates, and other relevant parameters.
Q: How accurate is the United States Snow Cover Map?
A: The accuracy of the United States Snow Cover Map depends on the data source, the resolution of the imagery, and the specific mapping techniques employed. However, modern satellite imagery and advanced mapping algorithms provide relatively accurate representations of snow cover.
Q: How can I use the United States Snow Cover Map?
A: The United States Snow Cover Map can be used for various purposes, including:
- Research: Scientists can use the map to study snow cover dynamics, assess the impacts of climate change, and develop models to predict future snow conditions.
- Management: Water resource managers, agricultural officials, transportation authorities, and other stakeholders can use the map to make informed decisions based on current snow cover conditions.
- Education: The map can be used to educate the public about the importance of snow cover, its role in the environment, and the potential impacts of climate change.
Tips for Using the United States Snow Cover Map
- Understand the Data Source: Be aware of the data source used to create the map, as this can influence the accuracy and limitations of the information.
- Consider the Time Scale: The map represents snow cover conditions at a specific point in time, so it is essential to consider the time scale of the data.
- Use Other Data Sources: Combine the information from the snow cover map with other data sources, such as weather reports, ground-based observations, and climate models, to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of snow conditions.
- Interpret the Data Carefully: Snow cover patterns can be complex, so it is crucial to interpret the data carefully and consider the various factors that can influence snow distribution.
Conclusion
The United States Snow Cover Map provides a valuable tool for understanding the dynamics of snow cover across the country. It offers a visual representation of snow distribution, highlighting its significance for water resources, agriculture, transportation, climate, and ecosystems. By monitoring snow cover, we can gain insights into its role in the environment, anticipate potential impacts, and make informed decisions to manage resources and adapt to climate change. Understanding the intricacies of snow cover and utilizing the information provided by maps and other monitoring tools is crucial for ensuring the sustainability of our natural resources and the well-being of our society.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Dynamics of Snow Cover Across the United States: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!