Unveiling Afghanistan’s Rugged Terrain: A Comprehensive Look at the Topographic Map
Related Articles: Unveiling Afghanistan’s Rugged Terrain: A Comprehensive Look at the Topographic Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Afghanistan’s Rugged Terrain: A Comprehensive Look at the Topographic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Afghanistan’s Rugged Terrain: A Comprehensive Look at the Topographic Map
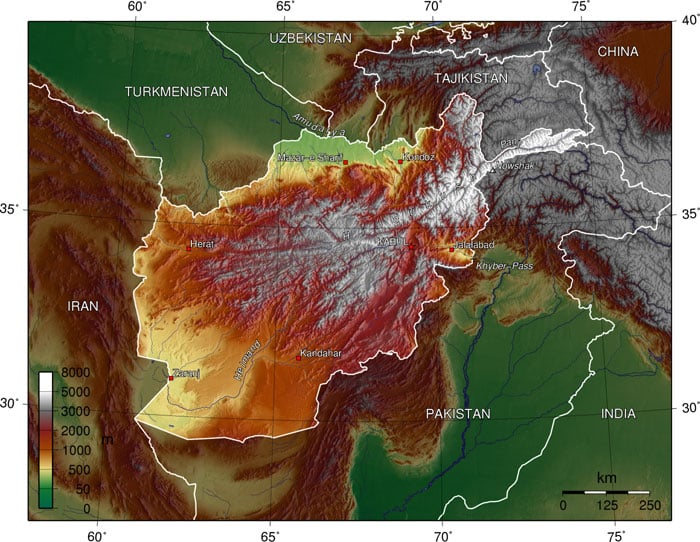
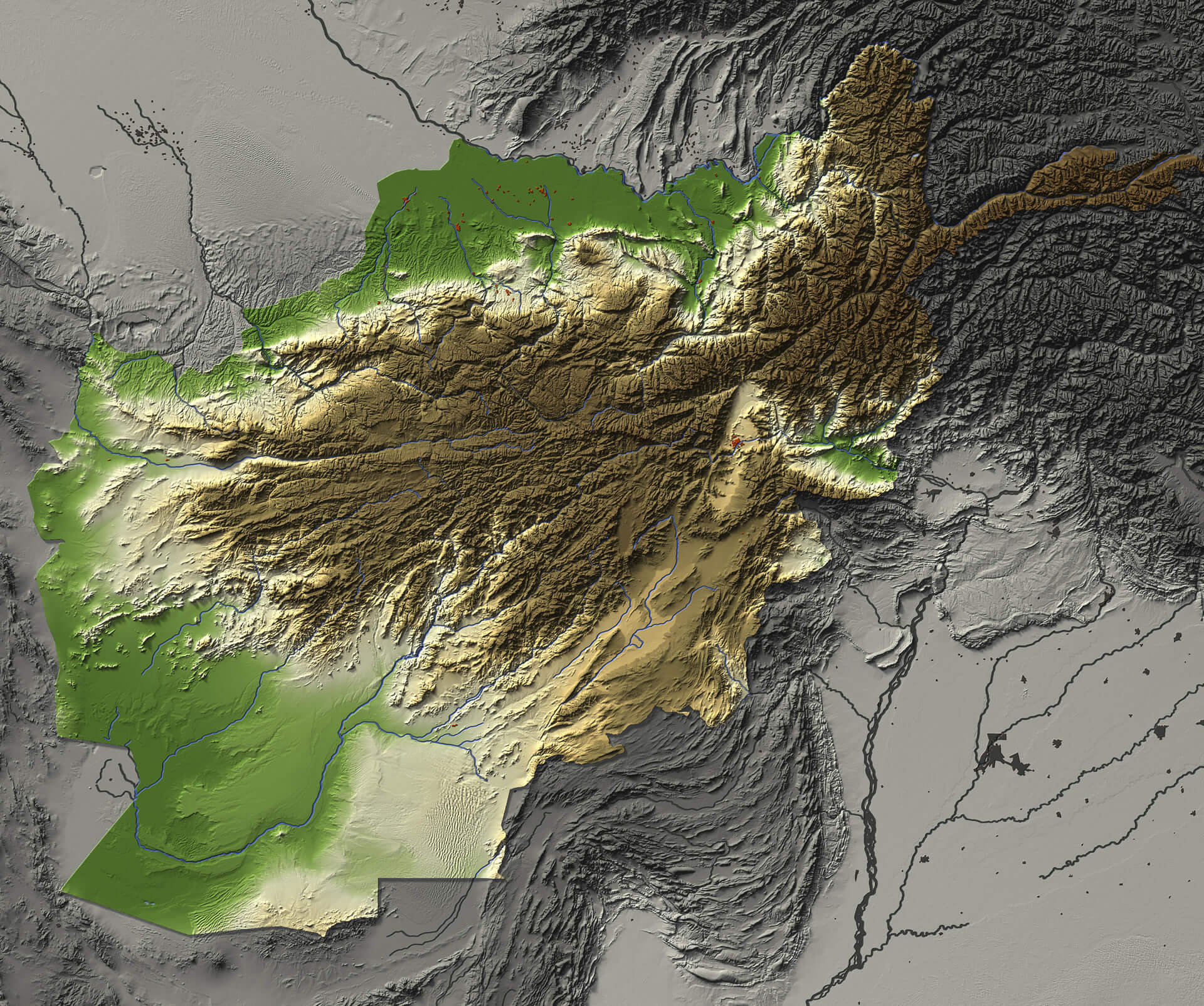
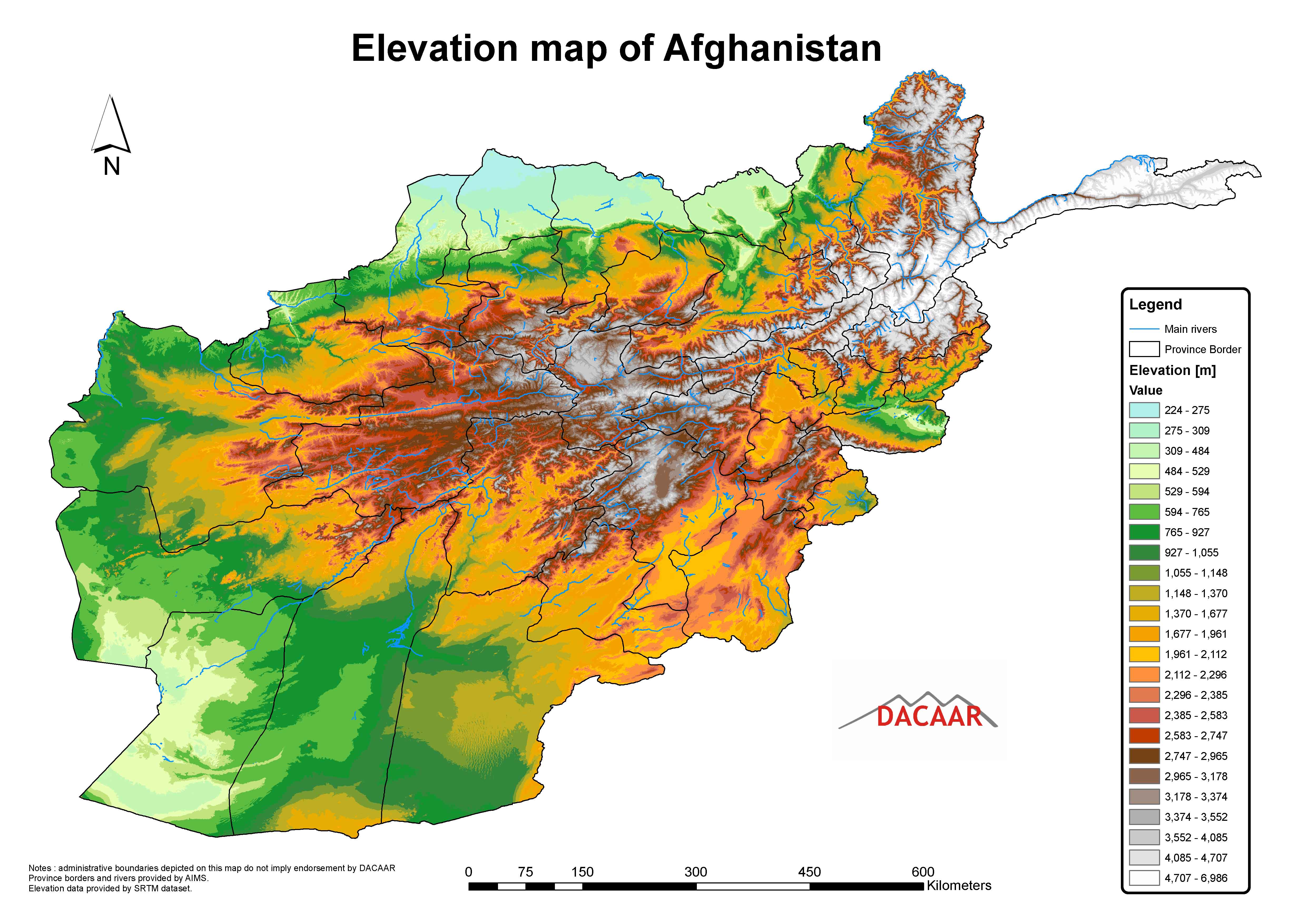
Afghanistan, a landlocked nation nestled in Central Asia, is renowned for its rugged and diverse topography. Understanding the intricate interplay of mountains, deserts, plains, and river valleys is crucial for comprehending the country’s history, culture, and development. A topographic map serves as an invaluable tool, providing a detailed visual representation of Afghanistan’s complex terrain, its impact on human activity, and its strategic significance.
A Tapestry of Diverse Terrain:
The Afghan topographic map reveals a landscape sculpted by tectonic forces and centuries of erosion. The towering Hindu Kush mountain range, a formidable barrier spanning the country’s north-central region, dominates the landscape. This majestic range, with peaks exceeding 7,000 meters, serves as a natural divide, influencing weather patterns and shaping the lives of those residing in its shadow.
To the west, the Pamir Mountains, known for their stark beauty and challenging terrain, extend into Afghanistan, contributing to the country’s overall rugged character. The eastern region is characterized by the Kunar and Nuristan mountain ranges, which, while less imposing than the Hindu Kush, are equally significant in defining local environments.
Beyond the Mountains: Plains, Deserts, and Valleys:
The Afghan landscape is not solely defined by its mountains. The country also encompasses vast plains, such as the Kandahar Plain in the south, and the Helmand Valley, famed for its fertile land and agricultural potential. These plains, though contrasting with the mountainous regions, are equally vital to the country’s economy and livelihood.
The vast, arid expanse of the Dasht-e Margo, or "Desert of Death," located in the southwest, underscores the aridity that characterizes much of Afghanistan. This harsh environment poses significant challenges to human settlement and resource management, highlighting the need for careful planning and sustainable practices.
The Life-Giving Rivers:
Afghanistan’s rivers, while often flowing through challenging terrain, play a critical role in sustaining life and supporting human activity. The Amu Darya, the country’s most significant river, flows along the northern border, serving as a vital source of water for irrigation and transportation. Other major rivers, such as the Helmand, the Kabul, and the Harirud, wind their way through the country, providing essential water resources for agriculture, drinking, and industry.
Strategic Significance and Geopolitical Implications:
Afghanistan’s topographic map is not merely a visual representation of its physical landscape; it also offers insights into the country’s strategic importance and geopolitical complexities. The towering mountains, while posing challenges to transportation and communication, also serve as natural barriers, making Afghanistan a difficult country to conquer.
The strategic location of Afghanistan, nestled between Central Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East, has made it a crossroads of civilizations and a focal point for geopolitical interests throughout history. The country’s diverse terrain, its strategic location, and its rich resources have contributed to its complex history and its ongoing challenges.
The Impact on Human Life:
The rugged terrain of Afghanistan has profoundly shaped the lives of its inhabitants. The mountainous regions have historically fostered strong tribal identities and unique cultural traditions. The harsh environment has also led to a reliance on traditional farming methods and pastoralism, shaping the country’s economy and social structure.
The challenging terrain has also impacted infrastructure development, transportation, and communication. The construction of roads and other infrastructure projects in mountainous regions poses significant engineering challenges, making it difficult to connect remote communities and facilitate economic development.
Understanding Afghanistan’s Topography: A Vital Tool for Development:
The Afghan topographic map serves as a vital tool for understanding the country’s diverse landscape and its impact on human life. By providing a detailed visual representation of the terrain, the map facilitates:
- Effective Resource Management: Identifying water resources, fertile land, and mineral deposits is crucial for sustainable development.
- Infrastructure Planning: Understanding the topography allows for the optimal placement of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Disaster Response: The map helps identify areas vulnerable to natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, and landslides, enabling effective disaster preparedness and response.
- Conflict Resolution: The topography plays a significant role in conflict dynamics. Understanding the terrain can aid in peacekeeping efforts and conflict resolution.
- Environmental Conservation: The map helps identify areas of ecological significance and supports efforts to protect biodiversity and preserve natural resources.
FAQs about Afghanistan’s Topographic Map:
1. What is the highest point in Afghanistan?
The highest point in Afghanistan is Noshaq, which rises to 7,492 meters (24,580 feet) above sea level.
2. What are the major mountain ranges in Afghanistan?
The major mountain ranges in Afghanistan include the Hindu Kush, the Pamir Mountains, the Kunar Mountains, and the Nuristan Mountains.
3. What are the main rivers in Afghanistan?
The main rivers in Afghanistan are the Amu Darya, the Helmand, the Kabul, and the Harirud.
4. What are the major plains in Afghanistan?
The major plains in Afghanistan include the Kandahar Plain and the Helmand Valley.
5. How does the topography of Afghanistan impact its climate?
The towering mountains create a rain shadow effect, leading to arid conditions in the lowlands and wetter conditions in the mountainous regions.
6. How has the topography of Afghanistan shaped its culture?
The rugged terrain has fostered strong tribal identities and unique cultural traditions in the mountainous regions.
7. How does the topography of Afghanistan affect its economy?
The challenging terrain has impacted infrastructure development, transportation, and communication, posing challenges to economic development.
8. What are the challenges of accessing remote areas in Afghanistan due to its topography?
The mountainous terrain makes it difficult to construct roads and other infrastructure projects, limiting access to remote communities.
9. How can the topographic map of Afghanistan be used for environmental conservation?
The map helps identify areas of ecological significance and supports efforts to protect biodiversity and preserve natural resources.
10. What are the implications of Afghanistan’s topography for conflict resolution?
The topography plays a significant role in conflict dynamics, and understanding the terrain can aid in peacekeeping efforts and conflict resolution.
Tips for Using Afghanistan’s Topographic Map:
- Consult a variety of sources: Utilize different maps and data sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the terrain.
- Pay attention to elevation contours: The contours indicate the shape and elevation of the land, providing insights into the terrain’s steepness and accessibility.
- Consider the scale of the map: Choose a map with an appropriate scale for the specific area you are studying.
- Use online mapping tools: Interactive online maps provide additional features such as satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and 3D views.
- Combine the topographic map with other data sources: Integrate the map with data on climate, vegetation, population density, and infrastructure to gain a more complete picture.
Conclusion:
Afghanistan’s topographic map is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s diverse and challenging landscape. From its towering mountains to its vast plains, from its life-giving rivers to its arid deserts, the map reveals a complex and intricate terrain that has profoundly shaped the country’s history, culture, and development.
By understanding the intricacies of Afghanistan’s topography, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the country’s unique challenges and opportunities. The map serves as a valuable resource for policymakers, researchers, humanitarian workers, and anyone seeking to understand this fascinating and complex nation.

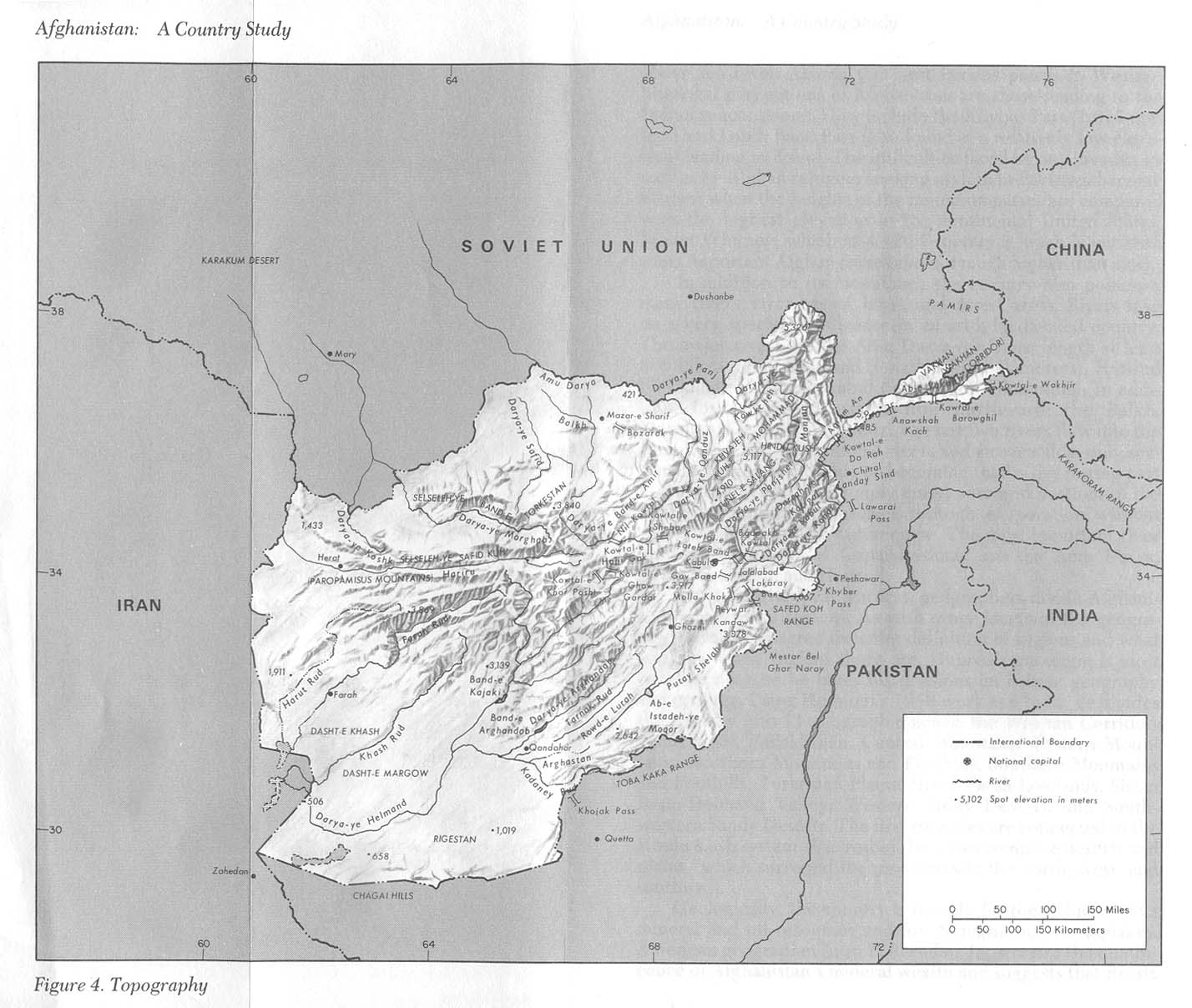
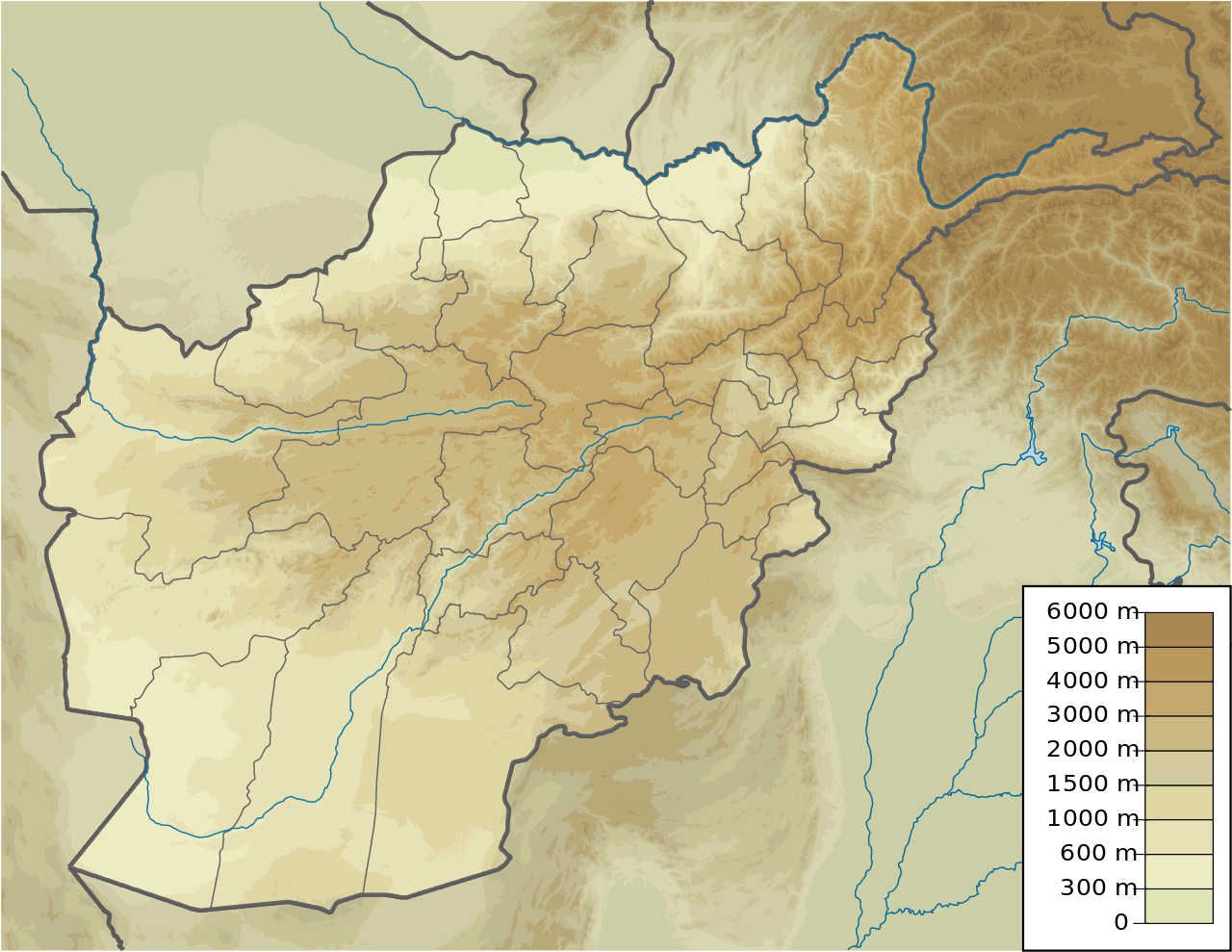


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Afghanistan’s Rugged Terrain: A Comprehensive Look at the Topographic Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!