Unraveling the Tapestry of Afghanistan: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geographical Outline
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Afghanistan: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geographical Outline
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Afghanistan: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geographical Outline. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Afghanistan: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geographical Outline

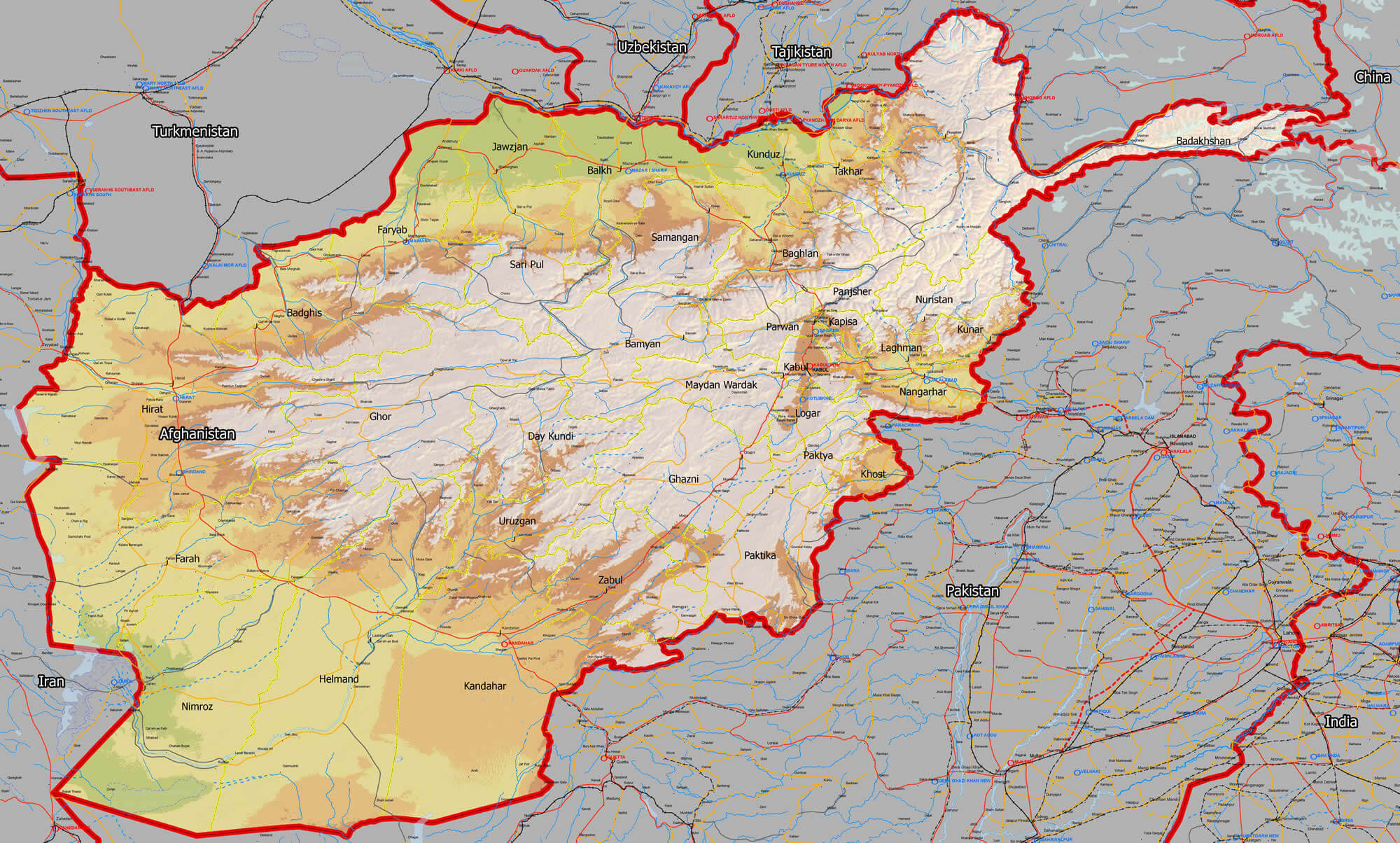
Afghanistan, nestled in the heart of Central Asia, is a country renowned for its rugged terrain, rich history, and enduring resilience. Understanding its geographical outline is crucial for appreciating its cultural, political, and economic landscape. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of Afghanistan’s map, delving into its diverse regions, significant features, and the impact these have on the country’s identity and development.
The Rugged Embrace of Mountains and Deserts
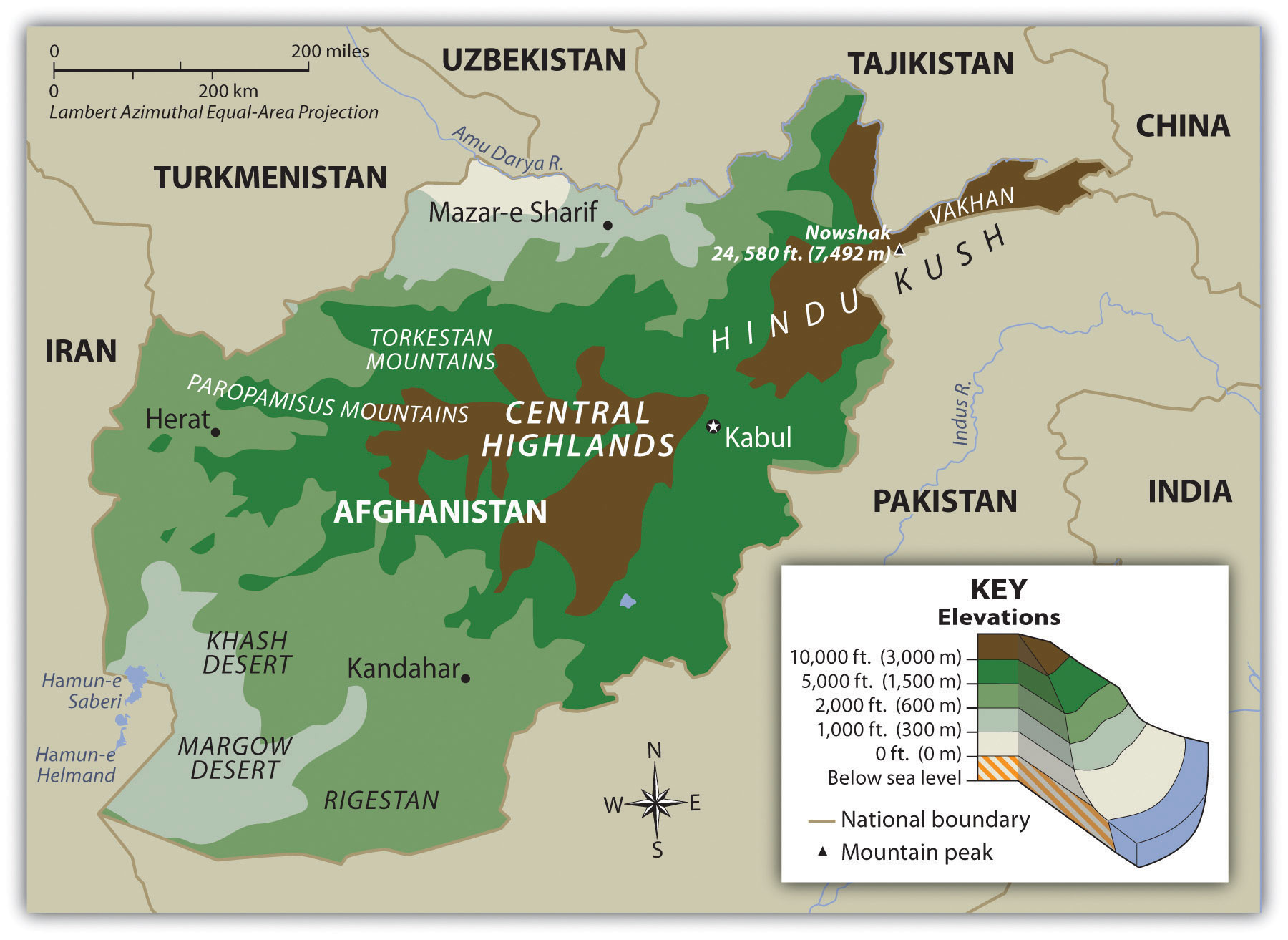
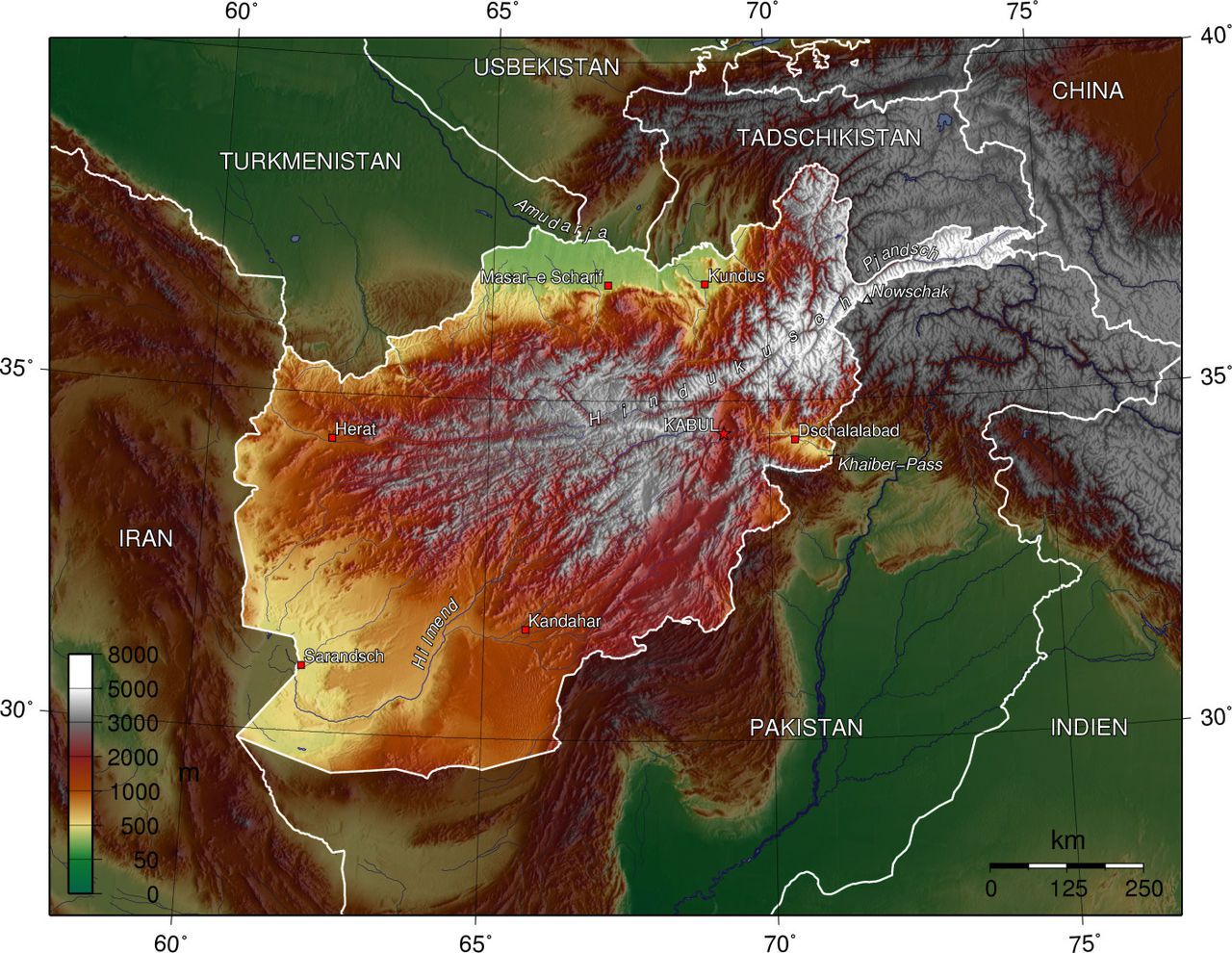
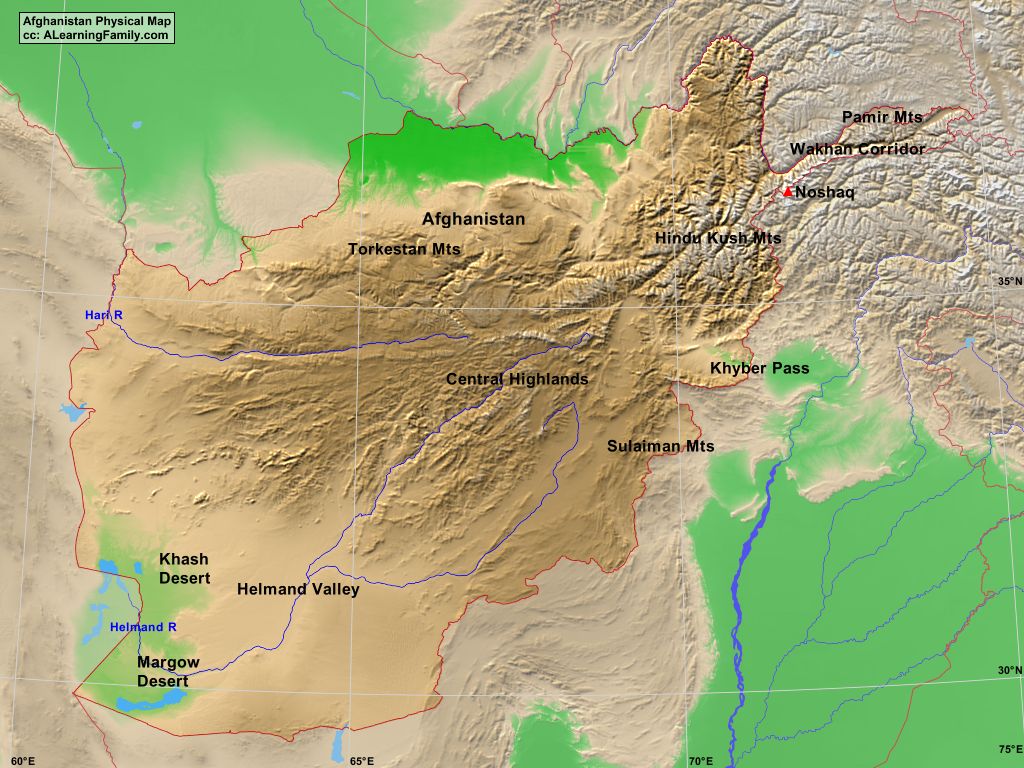
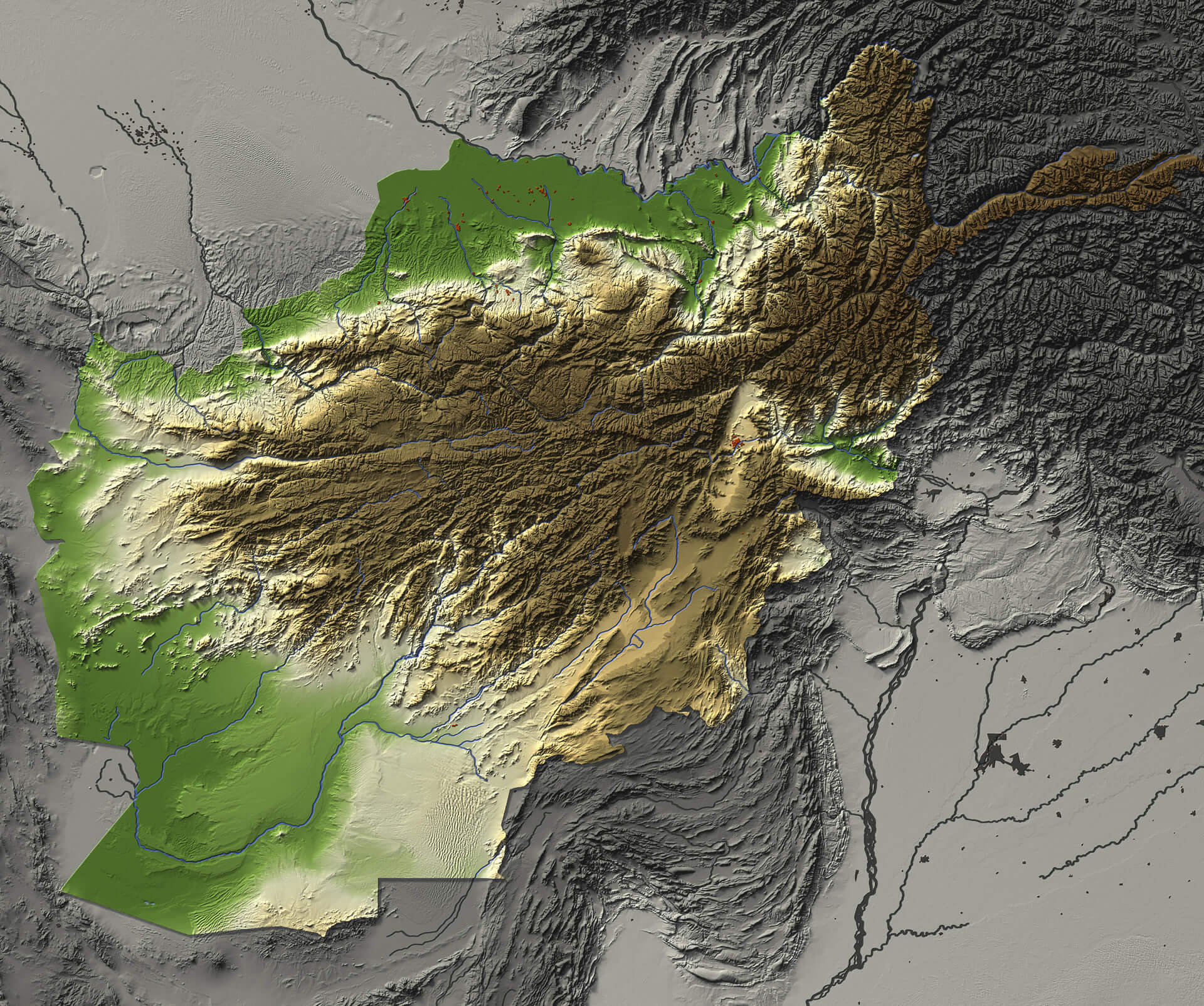
Afghanistan’s map is dominated by a tapestry of mountains, plateaus, and deserts, creating a landscape of stark beauty and formidable challenges. The towering Hindu Kush mountain range, a natural barrier stretching across the country, divides Afghanistan into distinct geographical regions.
- The Northern Highlands: This region, characterized by the Pamir Mountains and the Wakhan Corridor, is home to the highest peaks in Afghanistan, including Noshaq, which reaches a staggering elevation of 7,492 meters.
- The Central Highlands: This region, dominated by the Hindu Kush, features fertile valleys and high-altitude pastures, making it suitable for agriculture and livestock herding.
- The Western Highlands: This region, encompassing the Band-e Turkestan and the Sistan Basin, is characterized by arid plains and rugged mountains, presenting challenges for agriculture and development.
- The Eastern Highlands: This region, encompassing the Safid Koh and the Spin Ghar mountains, is marked by valleys and passes, connecting Afghanistan to neighboring Pakistan and the Indian subcontinent.
The Significance of Geographic Features
The mountainous terrain of Afghanistan has played a pivotal role in shaping its history, culture, and identity. Its rugged landscape has served as a natural barrier, protecting the country from external influences and fostering a sense of independence. However, it has also presented significant obstacles to communication, transportation, and economic development.
The Impact of Geographic Features
The geographic features of Afghanistan have a profound impact on its economy, infrastructure, and social dynamics. The mountainous terrain makes transportation and communication challenging, isolating communities and hindering access to essential services. The arid climate, particularly in the western and southern regions, poses significant challenges to agriculture and water management.
The Importance of Understanding Afghanistan’s Geography
Understanding the geographic outline of Afghanistan is crucial for:
- Effective Policy Development: Understanding the challenges posed by the terrain is vital for formulating effective policies in areas such as infrastructure development, transportation, and resource management.
- Regional Planning and Development: Recognizing the unique characteristics of different regions is essential for developing tailored strategies for economic growth and social development.
- Conflict Resolution and Peacebuilding: Understanding the geographic factors that contribute to conflict and instability is vital for promoting peace and reconciliation.
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Response: Knowledge of the terrain is crucial for delivering humanitarian aid and responding effectively to natural disasters.
FAQs about Afghanistan’s Map
Q: What is the highest peak in Afghanistan?
A: The highest peak in Afghanistan is Noshaq, located in the Pamir Mountains, reaching a height of 7,492 meters.
Q: What are the major rivers in Afghanistan?
A: The major rivers in Afghanistan include the Amu Darya, the Helmand River, the Kabul River, and the Hari Rud.
Q: What are the major cities in Afghanistan?
A: The major cities in Afghanistan include Kabul (the capital), Kandahar, Herat, Mazar-i-Sharif, Jalalabad, and Ghazni.
Q: How does the geography of Afghanistan affect its culture?
A: The rugged terrain and diverse regions of Afghanistan have contributed to the development of distinct cultures and traditions in different parts of the country.
Q: What are the major natural resources found in Afghanistan?
A: Afghanistan is rich in natural resources, including copper, iron ore, lithium, and natural gas.
Tips for Understanding Afghanistan’s Map
- Use an interactive map: Interactive maps with zoom capabilities allow you to explore different regions and identify key geographic features.
- Refer to a physical map: Physical maps with elevation contours and landforms provide a better understanding of the terrain.
- Read about the history of Afghanistan: Understanding the historical context will help you appreciate the impact of geographic features on the country’s development.
- Explore online resources: Websites like the CIA World Factbook and the United Nations Development Programme provide valuable information about Afghanistan’s geography and demographics.
Conclusion
The geographical outline of Afghanistan, with its rugged mountains, vast deserts, and diverse regions, is a defining element of the country’s identity. Understanding its intricate landscape is crucial for appreciating the challenges and opportunities that Afghanistan faces, and for developing effective strategies for its future development. By exploring the map of Afghanistan, we gain a deeper understanding of its complex history, rich culture, and enduring resilience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Afghanistan: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geographical Outline. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!