Unlocking the Secrets of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Geological Maps
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Geological Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Geological Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Geological Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking the Secrets of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Geological Maps
- 3.1 What are Geological Maps?
- 3.2 Construction of Geological Maps: A Journey Through Time and Space
- 3.3 The Many Faces of Geological Maps: A Spectrum of Applications
- 3.4 FAQs about Geological Maps: Unveiling the Mysteries
- 3.5 Conclusion: Unveiling the Earth’s Secrets, One Map at a Time
- 4 Closure
Unlocking the Secrets of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Geological Maps

The Earth’s surface, with its diverse landscapes and hidden geological treasures, holds a wealth of information waiting to be deciphered. Geological maps, like intricate puzzles, provide a visual key to understanding the Earth’s history, composition, and processes. They are essential tools for geologists, environmental scientists, engineers, and anyone interested in exploring the planet’s hidden depths. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of geological maps, revealing their construction, applications, and the invaluable insights they offer.
What are Geological Maps?
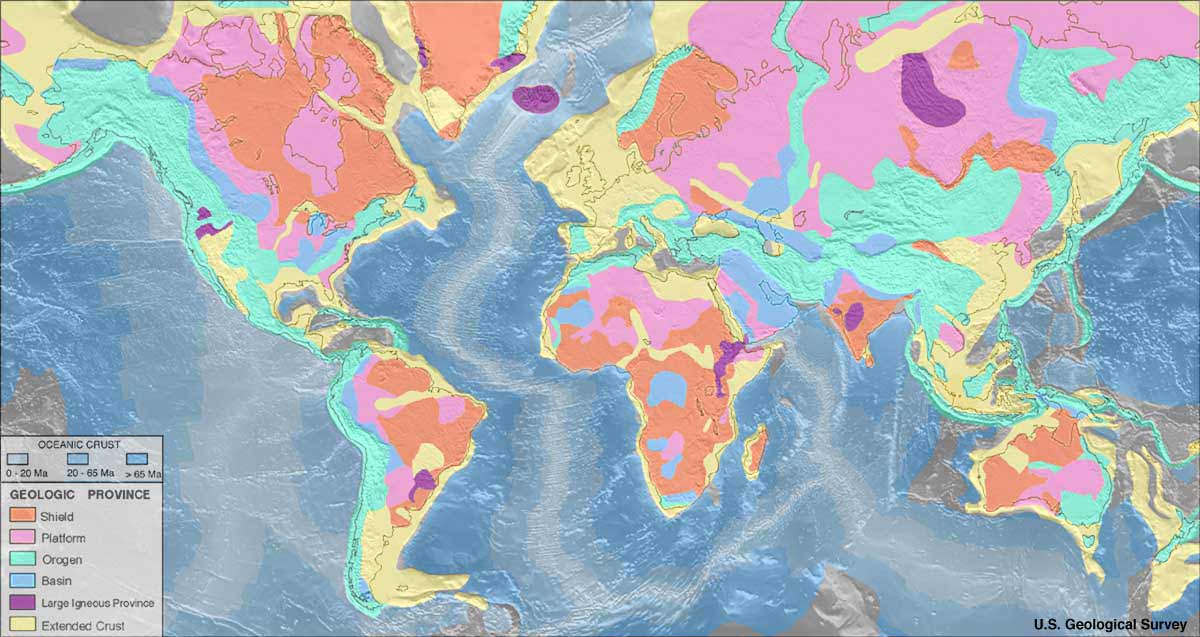
Geological maps are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, depicting the distribution and characteristics of different rock formations, geological structures, and mineral deposits. They serve as a visual encyclopedia of the Earth’s geological history, providing a snapshot of the planet’s evolution over millions of years.
Unlike traditional topographic maps that focus on elevation and physical features, geological maps emphasize the underlying geological structures and materials. They utilize a specific color code and symbols to represent different rock types, ages, and geological events. These maps are not mere static representations; they are dynamic tools that inform decision-making in diverse fields.
Construction of Geological Maps: A Journey Through Time and Space
The creation of a geological map is a meticulous process that involves a blend of field observation, laboratory analysis, and data interpretation. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
-
Field Mapping: Geologists embark on expeditions to the study area, meticulously observing and recording the rock formations, their textures, structures, and relationships. They collect rock samples for further analysis.
-
Laboratory Analysis: The collected rock samples are analyzed in laboratories to determine their composition, age, and origin. Techniques like petrography, geochemistry, and radiometric dating are employed to unlock the secrets of these rock fragments.
-
Data Compilation: The collected field data and laboratory results are meticulously compiled and organized. This involves plotting the locations of different rock units, geological structures, and mineral deposits on base maps.
-
Interpretation and Synthesis: Geologists interpret the compiled data to reconstruct the geological history of the area. They analyze the relationships between different rock units, identify geological structures, and infer the processes that shaped the landscape.
-
Map Production: The final stage involves creating the geological map using specialized software. The map displays the distribution of different rock units, geological structures, and mineral deposits using a specific color code and symbols.
The Many Faces of Geological Maps: A Spectrum of Applications
Geological maps are not confined to the realm of academic research; they serve as vital tools in various fields, influencing crucial decisions that impact our lives. Here are some key applications:
1. Natural Resource Exploration: Geological maps are indispensable for locating and evaluating mineral deposits, oil and gas reserves, and groundwater resources. They reveal the distribution of valuable resources, enabling efficient exploration and extraction.
2. Environmental Management: Geological maps play a crucial role in understanding the geological processes that influence environmental conditions. They help assess the risks of natural hazards like landslides, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions.
3. Civil Engineering: Geological maps provide vital information for planning and constructing infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, and dams. They help identify suitable locations for construction, assess the stability of the ground, and predict potential hazards.
4. Land Use Planning: Geological maps are essential for land use planning, ensuring sustainable development and mitigating environmental impacts. They inform decisions regarding agriculture, forestry, and urbanization, considering the underlying geological conditions.
5. Education and Research: Geological maps serve as valuable educational tools, illustrating the principles of geology and providing insights into the Earth’s history. They are also crucial for scientific research, supporting investigations into various geological phenomena.
FAQs about Geological Maps: Unveiling the Mysteries
1. What are the different types of geological maps?
Geological maps come in various forms, each designed to highlight specific aspects of the Earth’s geology. Some common types include:
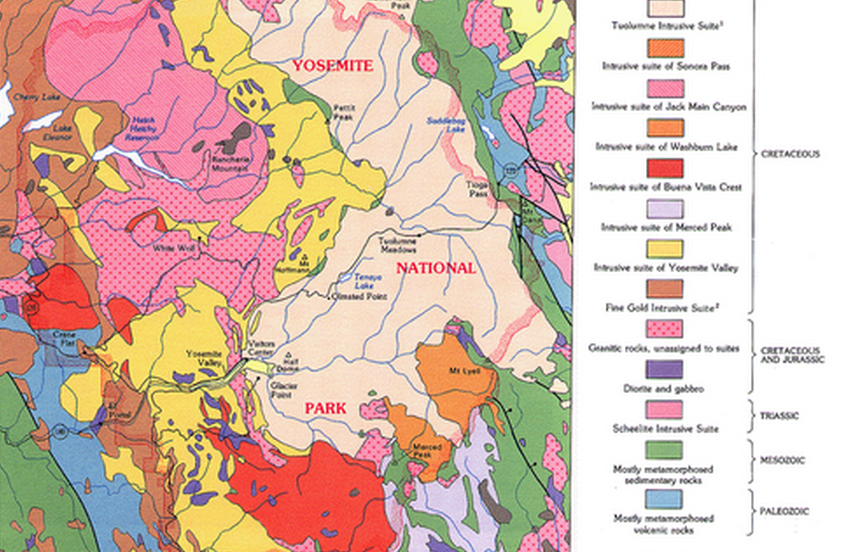
- Geologic Bedrock Maps: These maps display the distribution of bedrock formations, providing information on the underlying geology.
- Surficial Geologic Maps: These maps focus on the unconsolidated materials covering the bedrock, such as soil, sand, and gravel.
- Hydrogeologic Maps: These maps emphasize the distribution of groundwater resources and aquifers.
- Mineral Resource Maps: These maps depict the locations of mineral deposits, highlighting their potential economic value.
- Tectonic Maps: These maps focus on the major geological structures and tectonic plates, providing insights into the Earth’s dynamic processes.
2. How do geological maps help in understanding the Earth’s history?
Geological maps act as time capsules, recording the Earth’s history through the distribution and characteristics of different rock formations. They reveal evidence of past geological events, such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and mountain building, allowing us to reconstruct the Earth’s evolution over millions of years.
3. What are some examples of how geological maps are used in real-world applications?
- Mineral Exploration: Geological maps guide mining companies in locating and evaluating potential mineral deposits, contributing to the extraction of essential resources.
- Earthquake Hazard Assessment: Geological maps help identify areas prone to earthquakes, informing building codes and disaster preparedness plans.
- Groundwater Management: Geological maps assist in understanding the distribution and movement of groundwater, crucial for managing water resources and preventing contamination.
- Infrastructure Development: Geological maps are essential for planning and constructing roads, bridges, and tunnels, ensuring their stability and longevity.
4. How can I access geological maps?
Geological maps are readily available from various sources:
- Government Agencies: Geological surveys and mapping agencies in different countries provide access to their geological maps, often online.
- Academic Institutions: Universities and research institutions frequently maintain geological map collections and data repositories.
- Professional Organizations: Organizations like the American Geological Institute and the Geological Society of America offer access to geological maps and related resources.
5. What are some tips for reading and interpreting geological maps?
- Understanding the Legend: Pay close attention to the map’s legend, which explains the symbols, colors, and patterns used to represent different geological features.
- Identifying Rock Units: Observe the distribution of different rock units, their ages, and their relationships to each other.
- Recognizing Geological Structures: Look for features like folds, faults, and unconformities, which indicate past geological events.
- Interpreting the Context: Consider the map’s location, surrounding geological features, and the regional geological history to understand the context of the information presented.
Conclusion: Unveiling the Earth’s Secrets, One Map at a Time
Geological maps are more than just static representations of the Earth’s surface; they are powerful tools that unlock the secrets of our planet’s history, composition, and processes. They are essential for understanding the Earth’s dynamic nature, managing natural resources, mitigating environmental risks, and planning for sustainable development. As we continue to explore the Earth’s depths, geological maps will remain indispensable guides, revealing the intricate tapestry of our planet’s geological history and guiding us towards a sustainable future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of the Earth: A Comprehensive Guide to Geological Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!