Understanding the Landscape of Infectious Diseases: A Guide to the CDC’s Surveillance Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the Landscape of Infectious Diseases: A Guide to the CDC’s Surveillance Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Landscape of Infectious Diseases: A Guide to the CDC’s Surveillance Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Landscape of Infectious Diseases: A Guide to the CDC’s Surveillance Maps
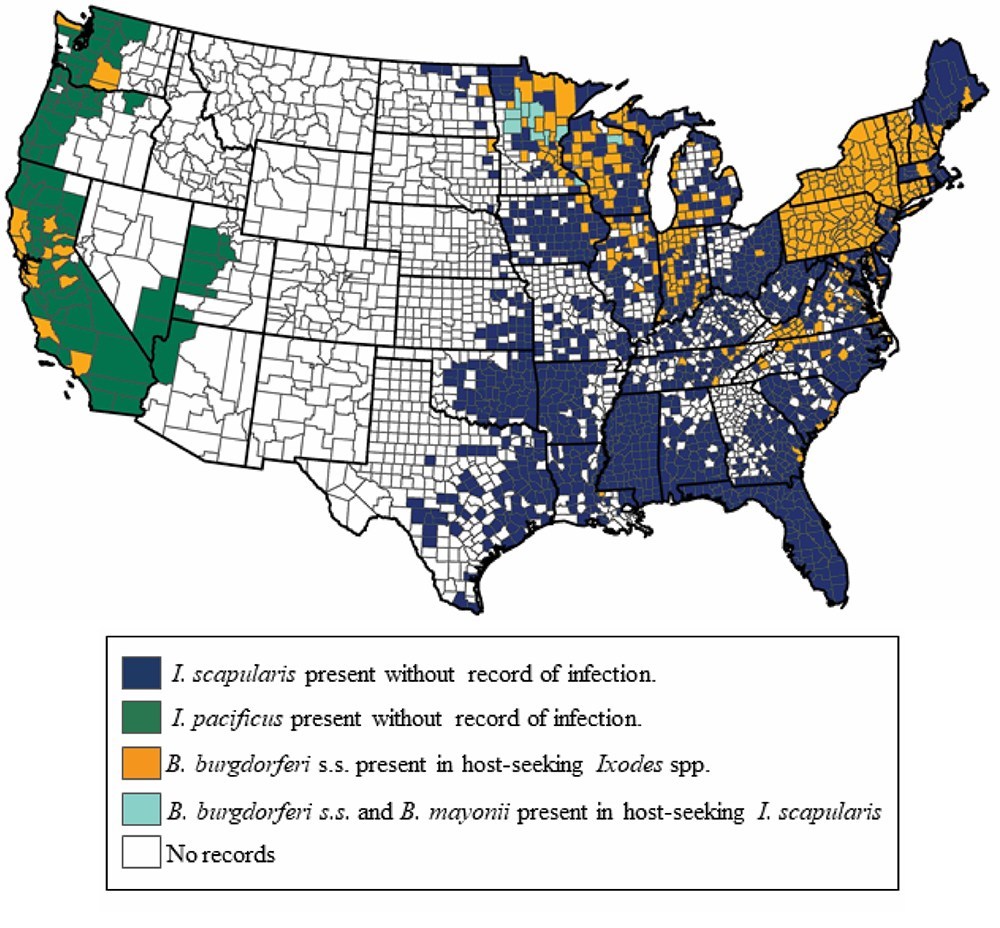
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) plays a crucial role in safeguarding public health by monitoring and responding to infectious diseases. A cornerstone of their efforts is the comprehensive collection and visualization of disease data through interactive maps. These maps, accessible online, provide a vital resource for understanding the spread and prevalence of various infectious diseases across the United States and beyond.
The Power of Visualizing Data:
Visualizing disease data through maps offers several advantages over traditional text-based reports. It allows for:
- Intuitive Understanding: Maps present complex data in a visually appealing and readily digestible format, enabling users to grasp patterns and trends quickly.
- Geographic Context: The spatial representation of disease occurrences provides crucial context, highlighting areas of high prevalence, potential outbreaks, and geographic disparities.
- Effective Communication: Maps serve as powerful tools for communicating disease information to a broad audience, including public health officials, healthcare providers, researchers, and the general public.
- Targeted Interventions: By identifying areas with elevated disease activity, public health officials can allocate resources and implement targeted interventions effectively.
Key Features of the CDC’s Infectious Disease Maps:
The CDC’s infectious disease maps encompass a wide range of diseases, including:
- Nationally Notifiable Diseases: These are diseases that are legally required to be reported to public health authorities, ensuring comprehensive surveillance data. Examples include measles, mumps, rubella, influenza, and HIV.
- Emerging Infectious Diseases: The CDC closely monitors the emergence and spread of new and re-emerging infectious diseases, such as Zika virus, Ebola virus, and novel coronaviruses.
- Foodborne Illnesses: Maps track outbreaks of foodborne illnesses, helping to identify contaminated food sources and implement preventative measures.
- Vector-Borne Diseases: The CDC maps the distribution and incidence of diseases transmitted by insects and other vectors, such as Lyme disease, West Nile virus, and dengue fever.
Beyond the Maps: Exploring the CDC’s Disease Data Portal:
The CDC’s infectious disease maps are part of a larger online portal that provides access to a vast repository of disease data. This portal offers users the ability to:
- Download Data: Users can download raw data in various formats, enabling further analysis and research.
- Customize Maps: The portal allows for customization of maps, enabling users to filter data by specific time periods, geographic regions, and disease categories.
- Access Reports and Publications: The CDC publishes comprehensive reports and scientific articles based on its surveillance data, providing detailed insights into disease trends and patterns.
The Importance of the CDC’s Infectious Disease Maps:
The CDC’s infectious disease maps play a critical role in public health by:
- Early Detection of Outbreaks: Maps help identify areas with elevated disease activity, facilitating early detection of outbreaks and enabling prompt response efforts.
- Disease Surveillance and Monitoring: The ongoing surveillance of infectious diseases provides valuable information on disease trends, geographic distribution, and potential risk factors.
- Targeted Public Health Interventions: By understanding disease patterns, public health officials can tailor interventions to specific populations and geographic areas, maximizing their impact.
- Public Awareness and Education: The maps serve as a valuable resource for educating the public about infectious diseases, promoting awareness of potential risks, and encouraging preventative measures.
- Research and Innovation: The CDC’s data and maps provide a foundation for research into infectious diseases, contributing to the development of new vaccines, treatments, and prevention strategies.
FAQs about the CDC’s Infectious Disease Maps:
1. What diseases are included on the CDC’s maps?
The CDC’s maps cover a wide range of infectious diseases, including nationally notifiable diseases, emerging infectious diseases, foodborne illnesses, and vector-borne diseases.
2. How often is the data on the maps updated?
The frequency of data updates varies depending on the specific disease and data source. Some maps are updated weekly, while others are updated monthly or annually.
3. Can I download the data from the maps?
Yes, the CDC’s disease data portal allows users to download raw data in various formats, enabling further analysis and research.
4. How can I use the maps to identify potential outbreaks?
By observing areas with elevated disease activity or unusual patterns, users can identify potential outbreaks and alert public health officials for further investigation.
5. Are the maps only for the United States?
While the CDC’s maps primarily focus on the United States, they also include data from other countries, particularly for diseases of global health concern.
Tips for Using the CDC’s Infectious Disease Maps:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Data: Understand the data sources, reporting methods, and potential limitations of the maps.
- Explore Different Time Periods: Compare data from different time periods to identify trends and patterns.
- Consider Geographic Context: Analyze disease distribution in relation to geographic factors, such as population density, climate, and environmental conditions.
- Use the Maps in Conjunction with Other Data Sources: Integrate data from the maps with other relevant information, such as demographic data, socioeconomic data, and healthcare utilization data.
- Share the Maps with Others: Disseminate the maps and their insights to relevant stakeholders, including public health officials, healthcare providers, and the general public.
Conclusion:
The CDC’s infectious disease maps represent a powerful tool for understanding the landscape of infectious diseases in the United States and beyond. They provide a visual representation of disease occurrences, enabling public health officials, researchers, and the general public to track disease trends, identify potential outbreaks, and implement targeted interventions. By leveraging the information provided by these maps, we can collectively work towards preventing and controlling infectious diseases, safeguarding public health, and building a healthier future.


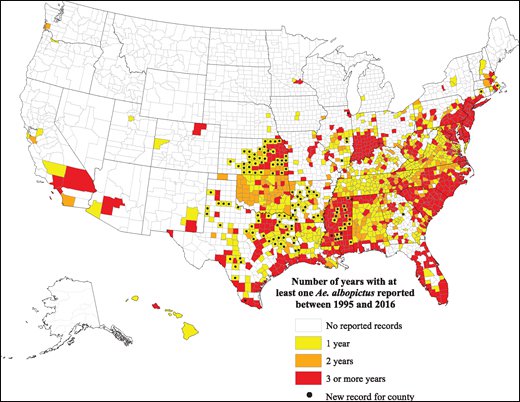


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Landscape of Infectious Diseases: A Guide to the CDC’s Surveillance Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!