The Scramble for Africa: A Visual History of the Continent in 1880
Related Articles: The Scramble for Africa: A Visual History of the Continent in 1880
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Scramble for Africa: A Visual History of the Continent in 1880. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Scramble for Africa: A Visual History of the Continent in 1880
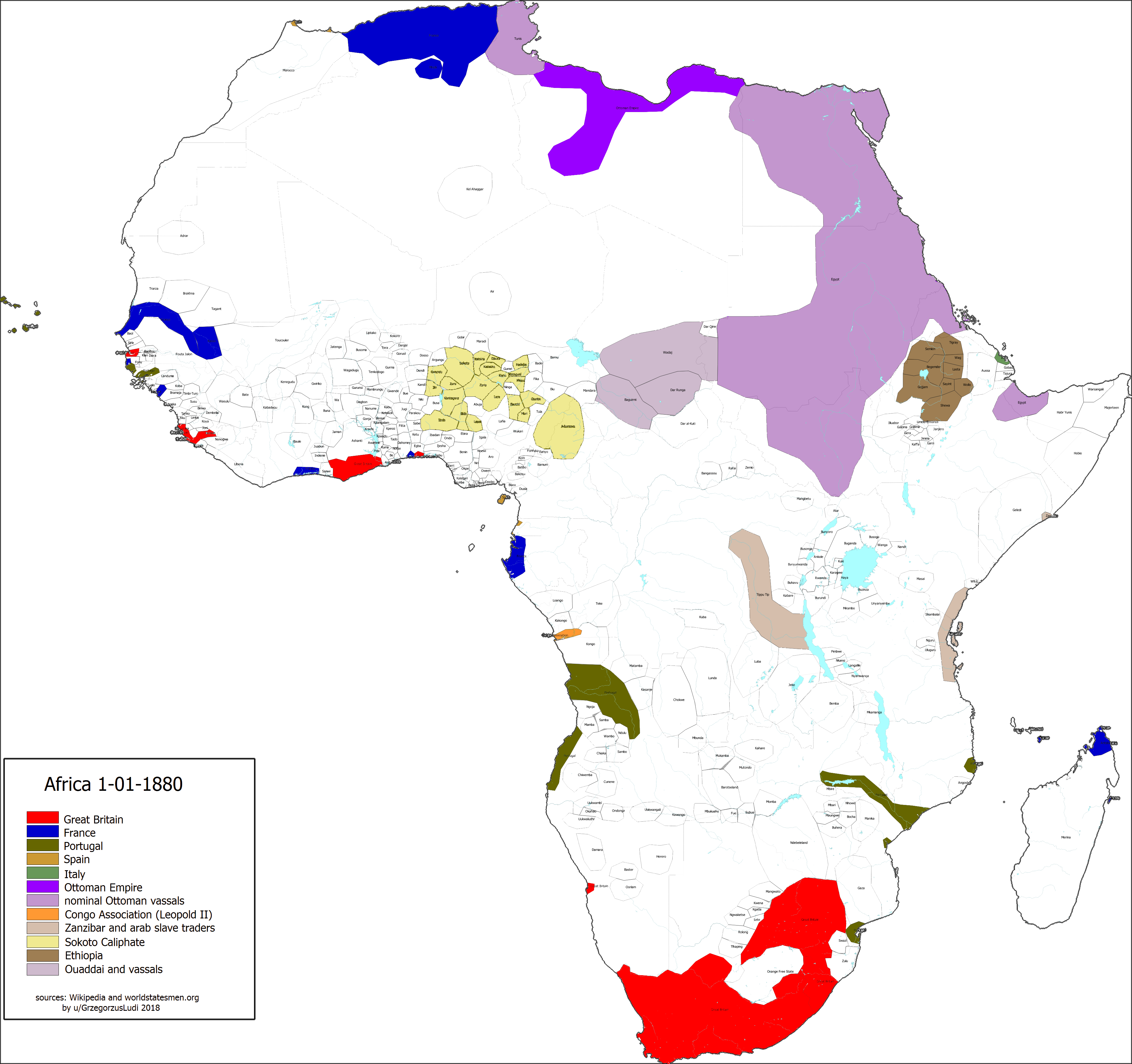
The year 1880 marks a pivotal moment in African history, a year that witnessed the beginning of the "Scramble for Africa," a period of intense European colonization that would dramatically reshape the continent’s political and social landscape. Examining the African map of 1880 offers a powerful visual narrative of this tumultuous era, revealing the intricate interplay of political ambitions, economic interests, and the consequences of European imperialism.
A Continent Divided: The African Map of 1880
The African map of 1880 presented a continent largely independent of European control. While European presence was established in coastal areas, vast swathes of the interior remained under the control of diverse indigenous societies. The map showcased a mosaic of independent kingdoms, empires, and tribal territories, each with its unique cultural and political identity.
The Rise of European Influence
The latter half of the 19th century witnessed a dramatic shift in the European perception of Africa. Driven by economic ambitions, fueled by the Industrial Revolution’s demand for raw materials and new markets, and spurred by the growing belief in European superiority, European powers embarked on a quest to colonize Africa.
The 1880s saw the Berlin Conference, a pivotal event that formally established the rules of the "Scramble." European powers, without any African representation, carved up the continent, dividing it into colonies based on their own strategic interests. This division was marked by arbitrary borders that disregarded existing ethnic and cultural boundaries, setting the stage for future conflicts and instability.
The Impact of European Colonization
The colonization of Africa brought about significant changes:
- Political Transformation: The map of 1880 transformed into a tapestry of European colonial possessions. Local rulers were replaced by European administrators, and traditional systems of governance were dismantled.
- Economic Exploitation: Africa’s resources, including rubber, diamonds, gold, and ivory, were exploited for the benefit of European powers. Indigenous economies were disrupted, and forced labor was employed to extract resources.
- Social Disruption: European colonization brought with it the imposition of European values and institutions, often at the expense of traditional African cultures and practices. This led to the erosion of indigenous languages, cultural traditions, and social structures.
The Legacy of the African Map of 1880
The African map of 1880 serves as a stark reminder of the lasting impact of colonialism on the continent. The arbitrary borders drawn by European powers continue to shape political and social realities in Africa, contributing to conflicts and instability. The legacies of economic exploitation and social disruption continue to be felt in contemporary Africa.
Understanding the African Map of 1880: A Deeper Dive
Key Regions and Their Significance
- North Africa: While North Africa was already under European influence, the 1880s saw a strengthening of French control in Algeria and Tunisia.
- West Africa: The coastal regions of West Africa, including Senegal and the Gold Coast, were under French and British control respectively.
- Central Africa: The Congo Free State, established by King Leopold II of Belgium, was a notorious example of brutal exploitation and human rights abuses.
- East Africa: German East Africa (present-day Tanzania, Burundi, and Rwanda) and British East Africa (present-day Kenya and Uganda) were strategically important for their potential as trade routes and sources of resources.
- Southern Africa: The British Empire had a strong presence in South Africa, with the Boer Republics (present-day South Africa) remaining independent.
The Importance of the African Map of 1880
- Historical Context: It provides a visual snapshot of the pre-colonial African landscape, highlighting the diversity and complexity of pre-colonial societies.
- Understanding Colonialism: It reveals the process of European colonization, the arbitrary division of the continent, and the impact of colonial policies on African societies.
- Contemporary Relevance: It sheds light on the ongoing challenges faced by African nations, including ethnic tensions, economic disparities, and political instability, which can be traced back to the legacies of colonialism.
FAQs about the African Map of 1880
Q: What were the main motives behind European colonization of Africa?
A: The primary motives behind European colonization of Africa were economic, political, and ideological. The Industrial Revolution fueled the demand for raw materials and new markets, while the desire for strategic ports and trade routes played a significant role. Additionally, European powers believed in their own cultural and racial superiority, justifying their claim to dominate Africa.
Q: How did the Berlin Conference impact the African map?
A: The Berlin Conference, held in 1884-1885, formalized the "Scramble for Africa." European powers, without any African representation, divided the continent into colonies based on their own strategic interests. This resulted in the imposition of arbitrary borders that disregarded existing ethnic and cultural boundaries.
Q: What were the consequences of European colonization for African societies?
A: European colonization had a profound and enduring impact on African societies. It led to the disruption of traditional economies and social structures, the exploitation of resources, and the imposition of European values and institutions. The arbitrary borders created by European powers continue to contribute to conflicts and instability in Africa.
Q: How does the African map of 1880 relate to the contemporary African landscape?
A: The African map of 1880 is a crucial lens for understanding the contemporary African landscape. The arbitrary borders drawn by European powers continue to influence political and social realities, contributing to conflicts and instability. The legacies of economic exploitation and social disruption continue to be felt in contemporary Africa.
Tips for Understanding the African Map of 1880
- Context is key: It is crucial to understand the historical context of the African map of 1880. It is important to consider the motivations behind European colonization, the impact of the Berlin Conference, and the consequences of colonial policies.
- Beyond the borders: The map should not be viewed solely as a geographical representation but also as a reflection of the social, cultural, and political realities of the time.
- Connecting the past to the present: The African map of 1880 is not simply a historical artifact. It is a crucial tool for understanding the challenges and opportunities faced by African nations today.
Conclusion
The African map of 1880 represents a turning point in African history, marking the beginning of a period of intense European colonization that would have profound and lasting consequences. It provides a visual narrative of the "Scramble for Africa," highlighting the arbitrary division of the continent, the exploitation of resources, and the disruption of traditional societies. Understanding this map is essential for grasping the complexities of the African continent and its journey through history. It serves as a reminder of the enduring legacies of colonialism and the challenges faced by African nations in navigating the complex realities of the post-colonial world.
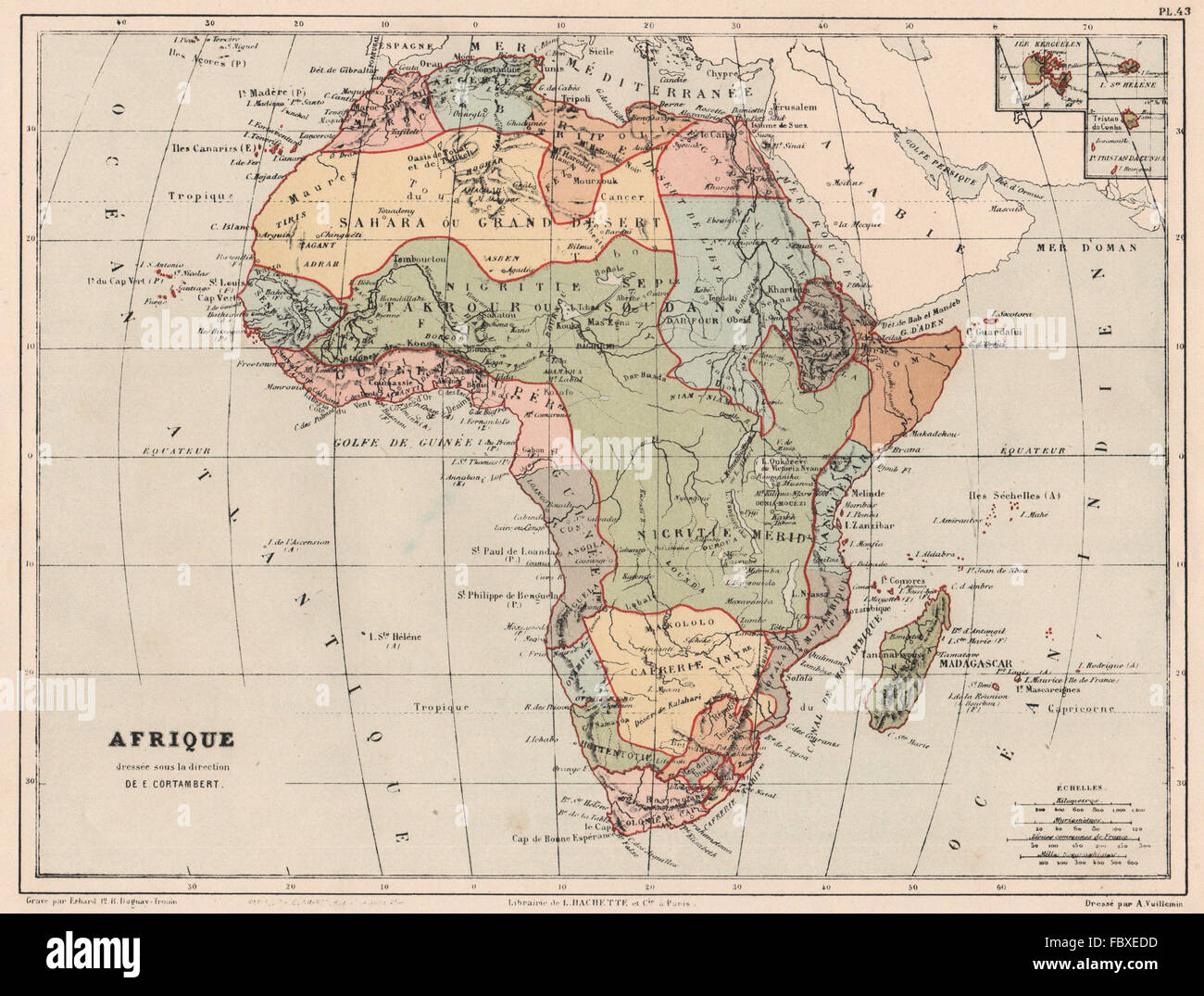



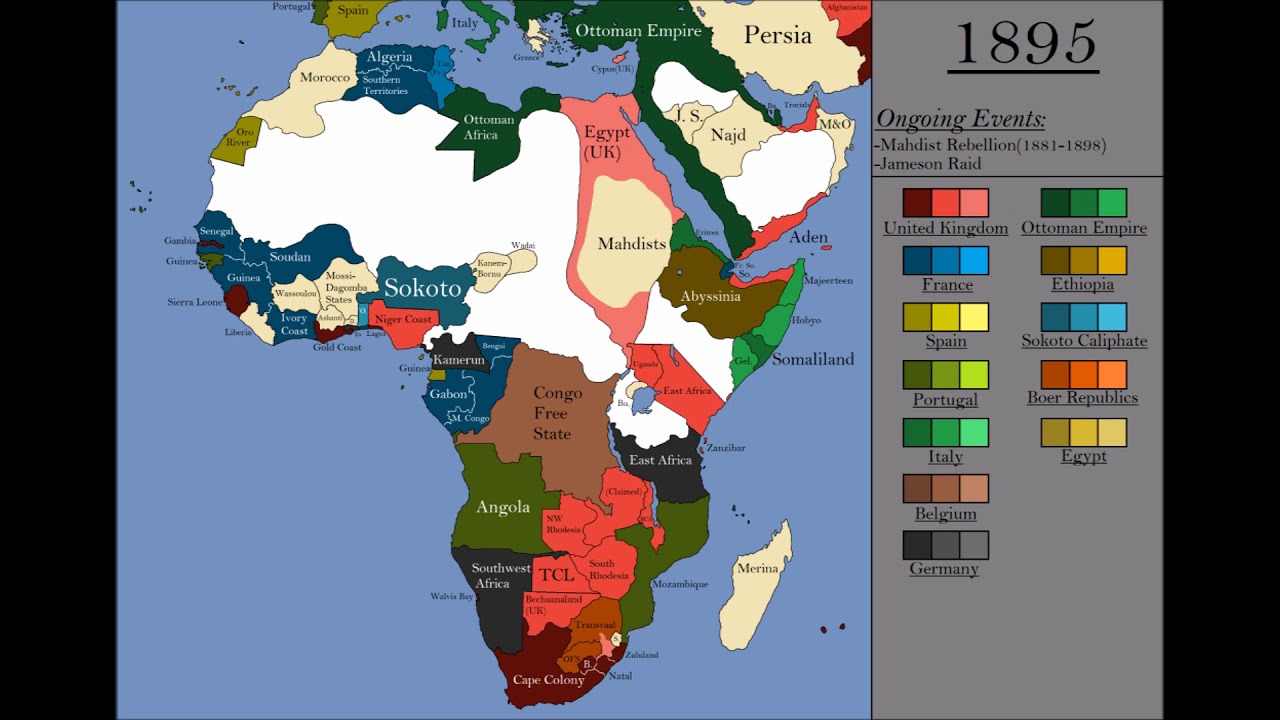


![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Scramble for Africa: A Visual History of the Continent in 1880. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!