The Complex Relationship Between China and Tibet: A Geographical Perspective
Related Articles: The Complex Relationship Between China and Tibet: A Geographical Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Complex Relationship Between China and Tibet: A Geographical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Relationship Between China and Tibet: A Geographical Perspective
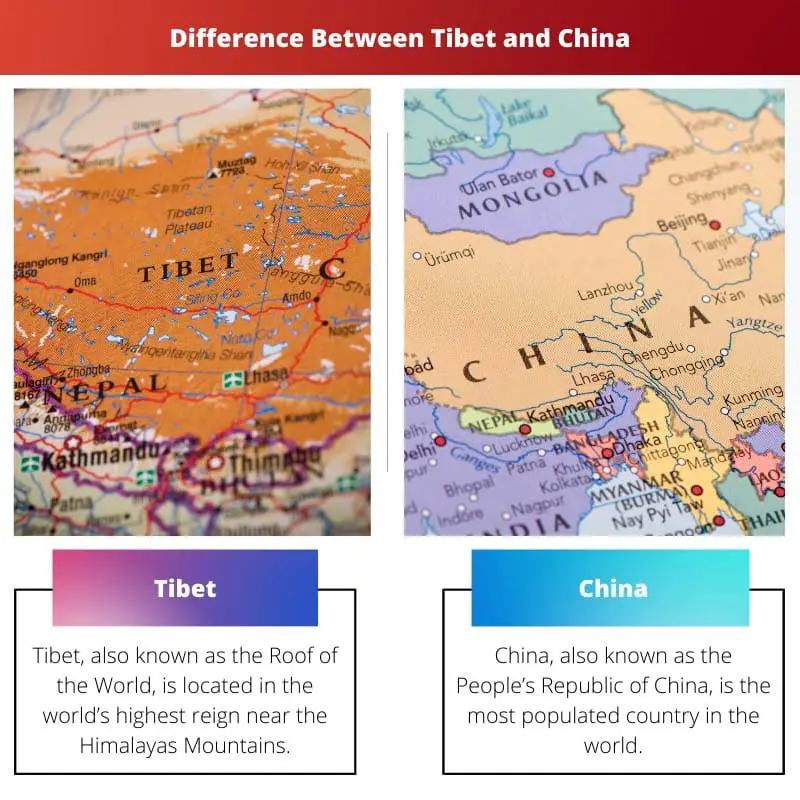
The relationship between China and Tibet is a multifaceted one, deeply intertwined with history, culture, and geography. Understanding the map of this region is crucial to grasping the complexities of their relationship. This article delves into the geographical aspects of China and Tibet, shedding light on their shared history, cultural exchange, and the ongoing debate surrounding their political and administrative ties.
A Glimpse into the Geography
Tibet, often referred to as the "Roof of the World," is a vast, mountainous plateau located in southwest China. Its average altitude is over 4,000 meters, making it one of the highest regions on Earth. The Tibetan Plateau is the source of several major rivers, including the Yangtze, Yellow, Mekong, and Brahmaputra, which flow through China and other Southeast Asian countries.
The geographical features of Tibet have significantly shaped its history and culture. The towering Himalayas, forming a natural barrier between Tibet and the Indian subcontinent, have historically limited contact and cultural exchange. This geographical isolation has allowed Tibet to develop its own unique culture and traditions, characterized by Buddhist practices, distinct languages, and a strong sense of cultural identity.
Historical Connections: From Trade Routes to Administration
The relationship between China and Tibet has a long and intricate history, dating back centuries. Historically, the two regions have been connected through trade routes, cultural exchanges, and political alliances. The Silk Road, a network of trade routes connecting the East and West, passed through Tibet, facilitating cultural and economic interactions between China and the outside world.
Over the centuries, Tibet has experienced periods of relative independence and periods of political and administrative integration with China. In the 13th century, the Yuan Dynasty established administrative control over Tibet. This period saw the introduction of Chinese administrative structures and the promotion of cultural exchange between the two regions.
The Modern Era: A Complex Relationship
The relationship between China and Tibet in the 20th century has been marked by political tensions and ongoing debates surrounding autonomy and cultural preservation. In 1951, the People’s Republic of China (PRC) established control over Tibet. This event led to a significant shift in the political and administrative landscape of the region, with the PRC implementing policies aimed at integrating Tibet into the Chinese state.
The PRC’s policies have been met with varying degrees of acceptance and resistance within Tibet. While some Tibetans support the economic development and infrastructure improvements brought about by Chinese administration, others have expressed concerns about the erosion of Tibetan culture and the suppression of Tibetan autonomy.
Understanding the Map: A Key to Understanding the Complexities
The map of China and Tibet provides a crucial visual aid for understanding the complexities of their relationship. It highlights the vast geographical expanse of Tibet, its mountainous terrain, and its strategic location at the crossroads of major trade routes. The map also reveals the proximity of Tibet to other countries, including India, Nepal, and Bhutan, which have their own historical and cultural ties to the region.
Examining the map allows us to appreciate the challenges involved in governing such a vast and geographically diverse region. It also underscores the importance of considering the perspectives of different stakeholders, including the Tibetan people, the Chinese government, and neighboring countries, in order to find sustainable solutions for the future of Tibet.
FAQs
1. What is the current political status of Tibet?
Tibet is currently an autonomous region of China, governed by the PRC. The PRC’s administration of Tibet has been the subject of ongoing debate and controversy.
2. How does the Chinese government view the relationship between China and Tibet?
The Chinese government views Tibet as an integral part of China, emphasizing its historical and cultural ties to the region. It maintains that Tibet has been part of China for centuries and that the PRC’s administration is essential for maintaining stability and development.
3. What are the main concerns of Tibetans regarding the relationship with China?
Many Tibetans express concerns about the erosion of their cultural identity, the suppression of their language and religious practices, and the limitations on their political autonomy. They advocate for greater self-determination and the preservation of their unique cultural heritage.
4. What are the key issues involved in the relationship between China and Tibet?
Key issues include the political status of Tibet, the preservation of Tibetan culture and language, the extent of economic development in Tibet, and the role of the Dalai Lama in Tibetan society.
5. What are the prospects for the future of the relationship between China and Tibet?
The future of the relationship between China and Tibet remains uncertain. Finding a solution that addresses the concerns of both the Tibetan people and the Chinese government will require ongoing dialogue, compromise, and a commitment to mutual respect.
Tips for Understanding the Relationship
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from both Chinese and Tibetan sources to gain a balanced understanding of the complexities of the relationship.
- Learn about Tibetan history and culture: Understanding the rich cultural heritage of Tibet can provide valuable context for understanding the current situation.
- Follow current events and news reports: Stay informed about ongoing developments and debates related to China and Tibet.
- Support organizations working to promote dialogue and understanding: Encourage constructive dialogue and peaceful resolution of the issues facing Tibet.
Conclusion
The relationship between China and Tibet is a complex and multifaceted one, shaped by geography, history, and cultural exchange. The map of China and Tibet serves as a visual reminder of the vastness of the region, the challenges of governance, and the importance of understanding diverse perspectives. Finding a sustainable solution for the future of Tibet will require continued dialogue, respect, and a commitment to preserving the unique cultural heritage of the region.





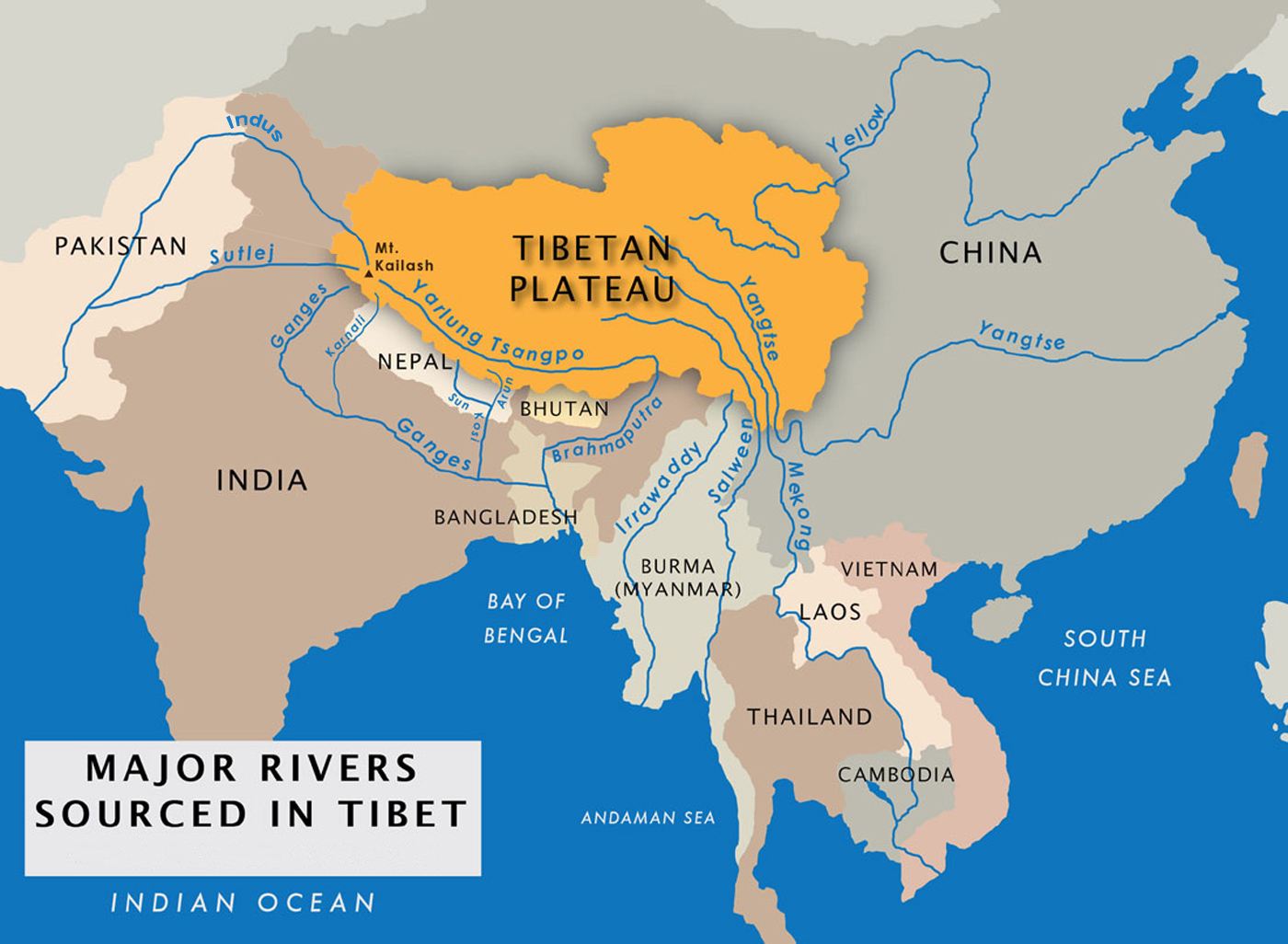
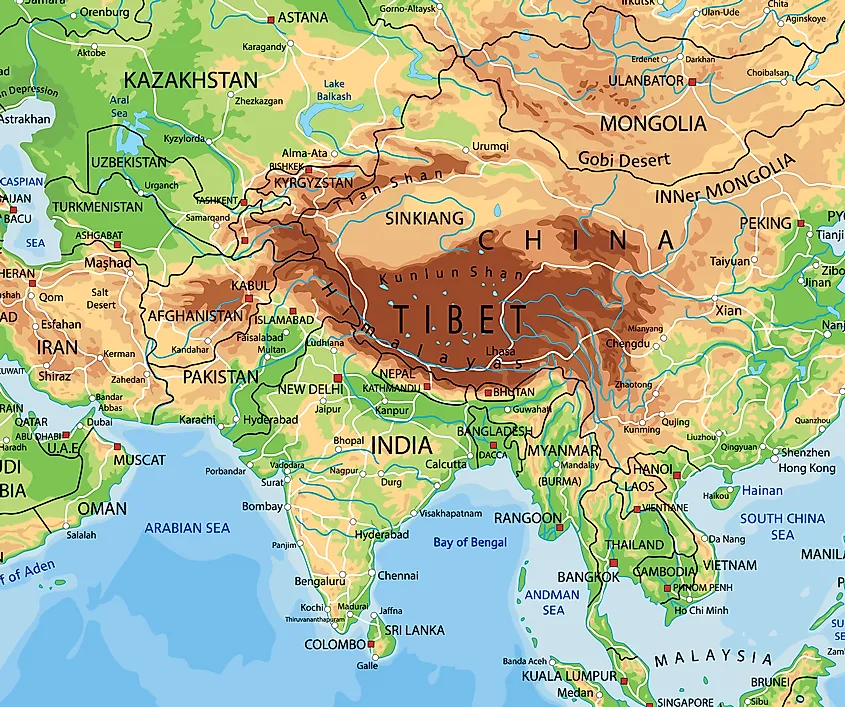
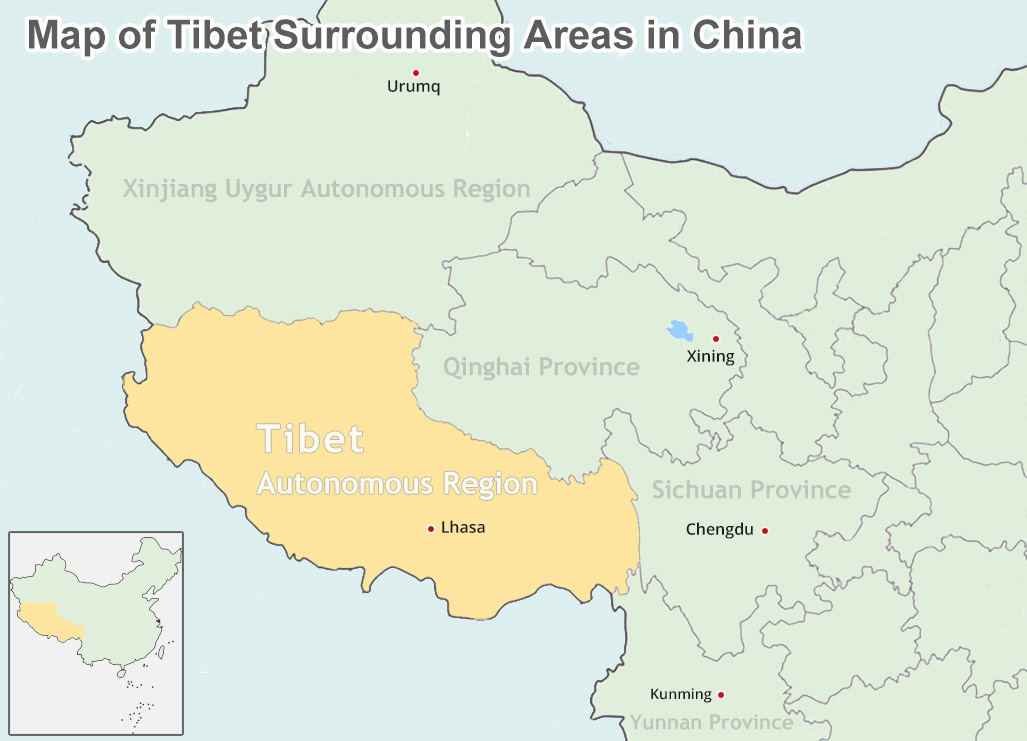
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Relationship Between China and Tibet: A Geographical Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!