The Art and Science of Map Tracing: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Art and Science of Map Tracing: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Art and Science of Map Tracing: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Art and Science of Map Tracing: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
In the realm of cartography and geographic information systems (GIS), map tracing, also known as digitizing or vectorization, plays a pivotal role in converting analog maps into digital formats. This process, often considered a bridge between the physical and digital worlds, unlocks a wealth of possibilities for map analysis, visualization, and utilization.
Understanding Map Tracing
At its core, map tracing involves transforming a scanned image of a map into a digital representation. This digital representation, often in the form of vector data, consists of points, lines, and polygons that accurately depict the geographic features present on the original map. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Scanning: The physical map is scanned at a high resolution to capture the necessary detail.
- Image Pre-processing: The scanned image is often pre-processed to enhance its clarity and contrast, making it easier to trace features.
- Tracing: A skilled operator uses specialized software to trace the features on the map, creating a digital representation.
- Editing and Quality Control: The traced data is meticulously edited and checked for accuracy, ensuring consistency and completeness.
- Data Export: The finalized vector data can be exported in various formats, such as shapefiles, GeoJSON, or KML, suitable for use in GIS applications.
Types of Map Tracing
Map tracing can be broadly categorized into two main types:
- Manual Tracing: This involves using a mouse or digitizing tablet to manually trace the features on the map. While it offers greater control and flexibility, manual tracing is time-consuming and susceptible to human error.
- Automatic Tracing: This method leverages algorithms and image processing techniques to automatically identify and trace features. While efficient, automatic tracing requires high-quality source images and may not always achieve the desired accuracy.
Benefits of Map Tracing
The conversion of analog maps into digital formats through map tracing offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Data Accessibility: Digital maps are readily accessible and shareable, enabling wider distribution and utilization.
- Improved Data Accuracy: Vector data is more precise than raster data, allowing for accurate measurements and calculations.
- Advanced Analysis: Digital maps can be analyzed using sophisticated GIS tools, providing valuable insights into geographic patterns and relationships.
- Interactive Visualization: Digital maps can be displayed and interacted with on computer screens, facilitating dynamic exploration and analysis.
- Data Integration: Digital maps can be easily integrated with other datasets, enabling the creation of comprehensive geographic information systems.
- Preservation of Legacy Maps: Map tracing allows for the digitization and preservation of historical maps, safeguarding valuable cartographic information.
Applications of Map Tracing
Map tracing finds applications in a wide range of fields, including:
- Cartography: Creating digital maps for various purposes, such as navigation, planning, and research.
- Urban Planning: Analyzing urban development, infrastructure, and land use patterns.
- Environmental Management: Mapping natural resources, monitoring environmental changes, and assessing ecological risks.
- Transportation Planning: Designing efficient transportation networks, analyzing traffic flow, and managing logistics.
- Historical Research: Studying historical maps to understand past events, settlements, and land ownership.
- Archaeology: Mapping archaeological sites, analyzing spatial relationships, and reconstructing past landscapes.
Challenges in Map Tracing
While map tracing offers significant advantages, it also presents challenges:
- Data Quality: The accuracy of the traced data is heavily dependent on the quality of the original map and the skill of the operator.
- Time and Cost: Manual tracing can be time-consuming and expensive, especially for large-scale projects.
- Complexity of Features: Tracing complex features, such as intricate boundaries or overlapping layers, can be challenging.
- Data Standardization: Ensuring consistency in data formats and standards across different maps is crucial for efficient data integration.
FAQs on Map Tracing
1. What are the different file formats used for storing traced map data?
Common file formats for storing traced map data include shapefiles (.shp), GeoJSON (.geojson), KML (.kml), and geodatabases (.gdb).
2. What software is used for map tracing?
Popular software programs for map tracing include ArcGIS, QGIS, AutoCAD, and Adobe Illustrator.
3. What is the difference between raster and vector data?
Raster data represents geographic information as a grid of pixels, while vector data uses points, lines, and polygons to represent features.
4. How can I ensure the accuracy of traced data?
Accuracy can be improved by using high-resolution scans, employing skilled operators, and implementing rigorous quality control measures.
5. What are the ethical considerations involved in map tracing?
It is essential to respect copyright laws and obtain necessary permissions before tracing copyrighted maps.
Tips for Effective Map Tracing
- Use high-quality scans: Ensure the scanned image is clear, sharp, and at a high resolution.
- Pre-process the image: Enhance the image’s contrast and clarity for easier tracing.
- Choose the right software: Select software that offers the necessary tools and features for efficient tracing.
- Establish clear guidelines: Define clear standards for feature representation and data formatting.
- Implement quality control: Regularly review and edit traced data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Conclusion
Map tracing is an essential process for bridging the gap between analog and digital maps. By converting physical maps into digital formats, it unlocks a wealth of possibilities for geographic data analysis, visualization, and utilization. While challenges exist, advancements in technology and best practices continue to improve the efficiency and accuracy of map tracing, making it a crucial tool in various fields.




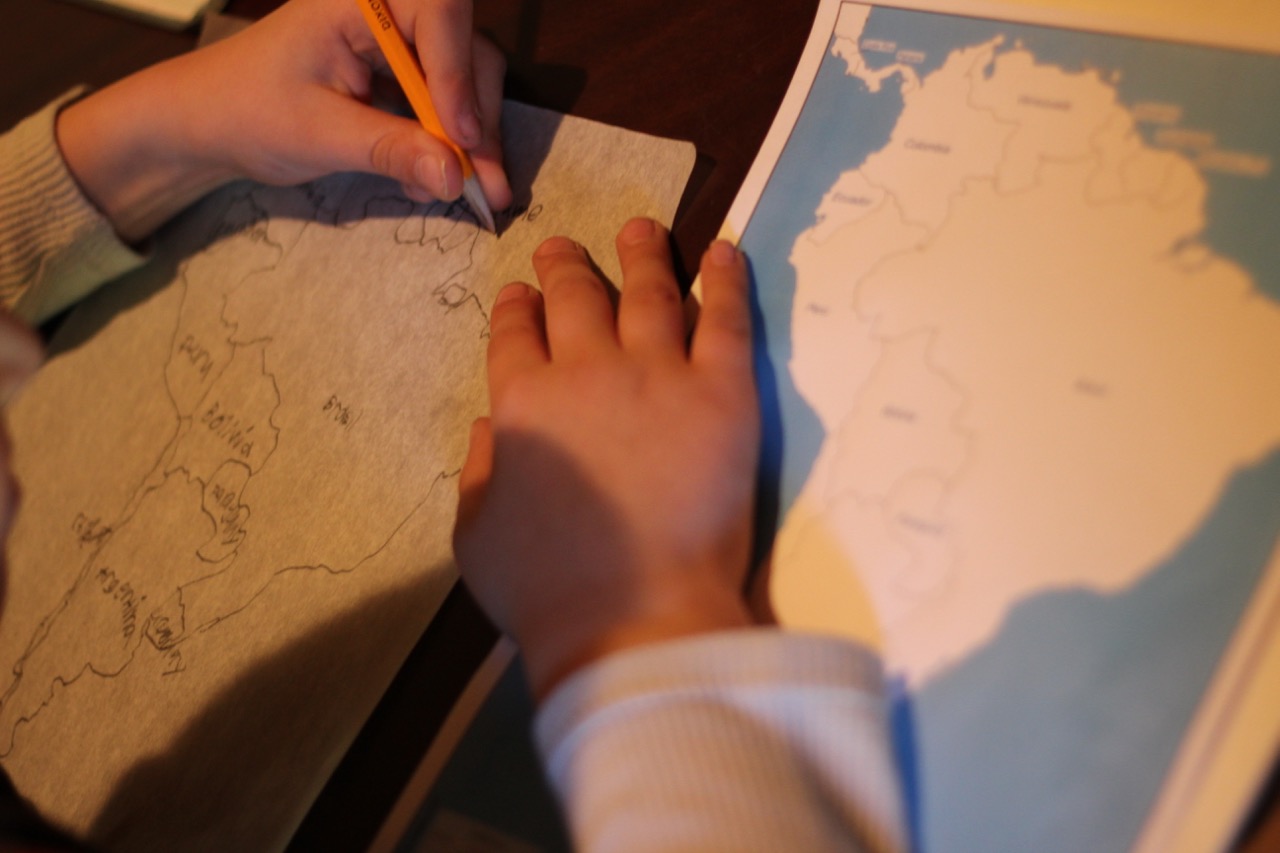


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art and Science of Map Tracing: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!