The Andes Mountains: A Spine of Life Along the Western Hemisphere
Related Articles: The Andes Mountains: A Spine of Life Along the Western Hemisphere
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Andes Mountains: A Spine of Life Along the Western Hemisphere. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Andes Mountains: A Spine of Life Along the Western Hemisphere

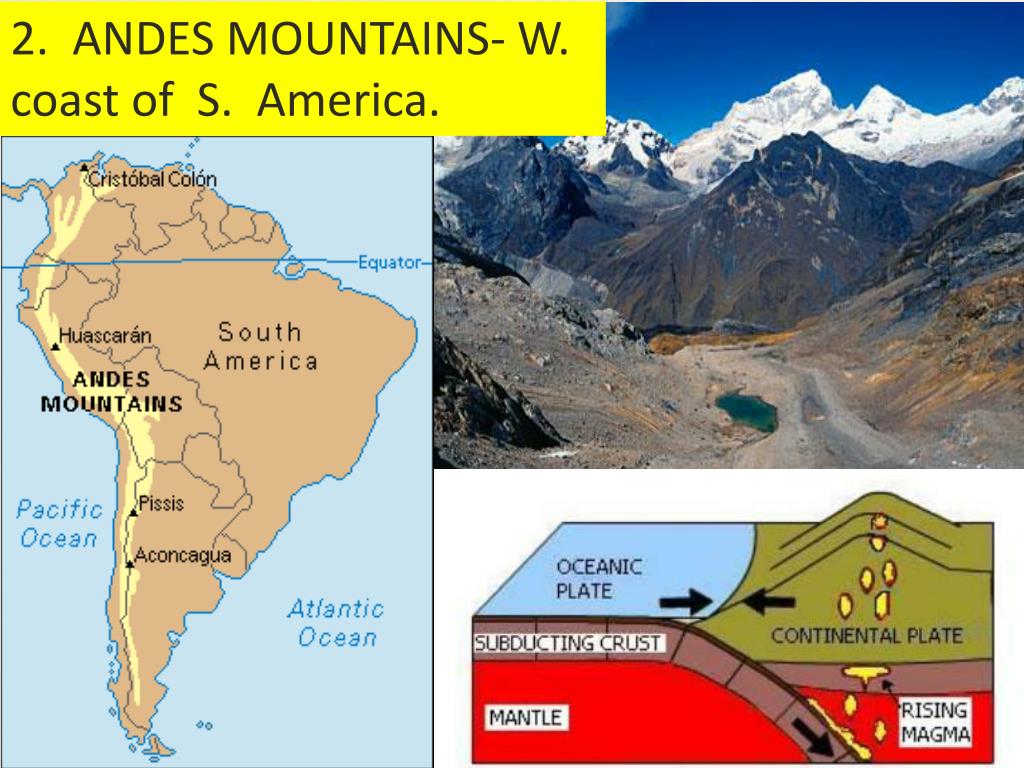
The Andes Mountains, a colossal chain of peaks stretching over 7,000 kilometers along the western edge of South America, stand as a testament to the Earth’s dynamic geological forces. This mountain range, the longest in the world outside of Asia, is a geographical marvel and a vital component of the continent’s ecosystem, shaping its climate, biodiversity, and human history.
A Geographical Tapestry:
The Andes are not a singular entity but rather a complex tapestry of diverse landscapes, ranging from towering snow-capped peaks to lush rainforests and arid deserts. Their location, along the western edge of South America, is crucial to understanding their significance.
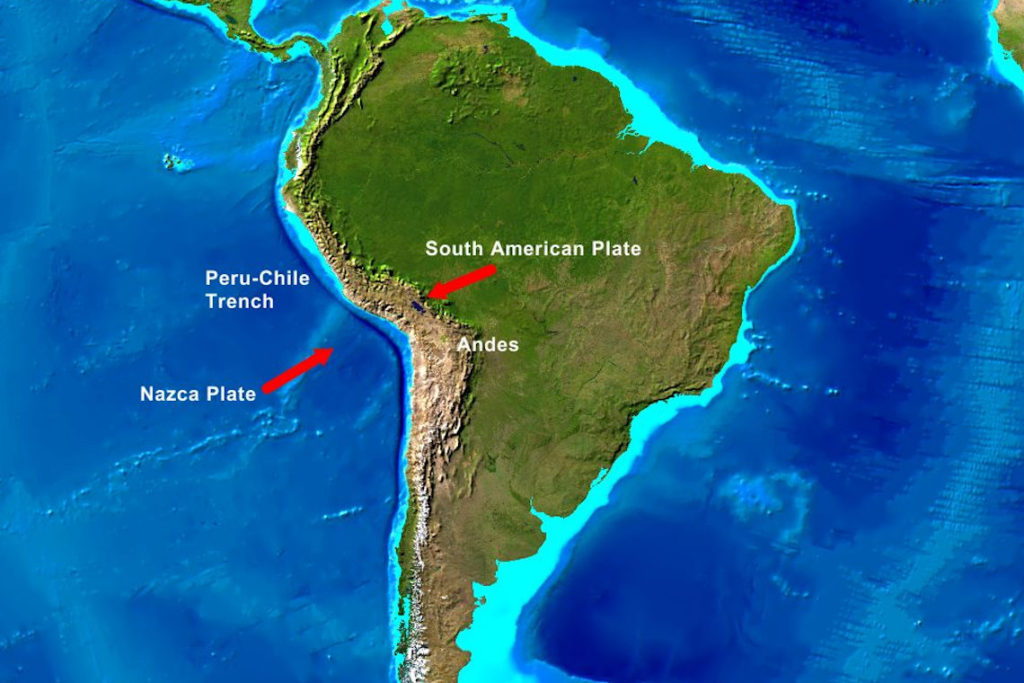
- The Pacific Ring of Fire: The Andes are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a zone of intense volcanic and seismic activity. This geological activity is responsible for the formation of the Andes, as the Nazca Plate subducts beneath the South American Plate, pushing up the Earth’s crust to create the towering peaks.
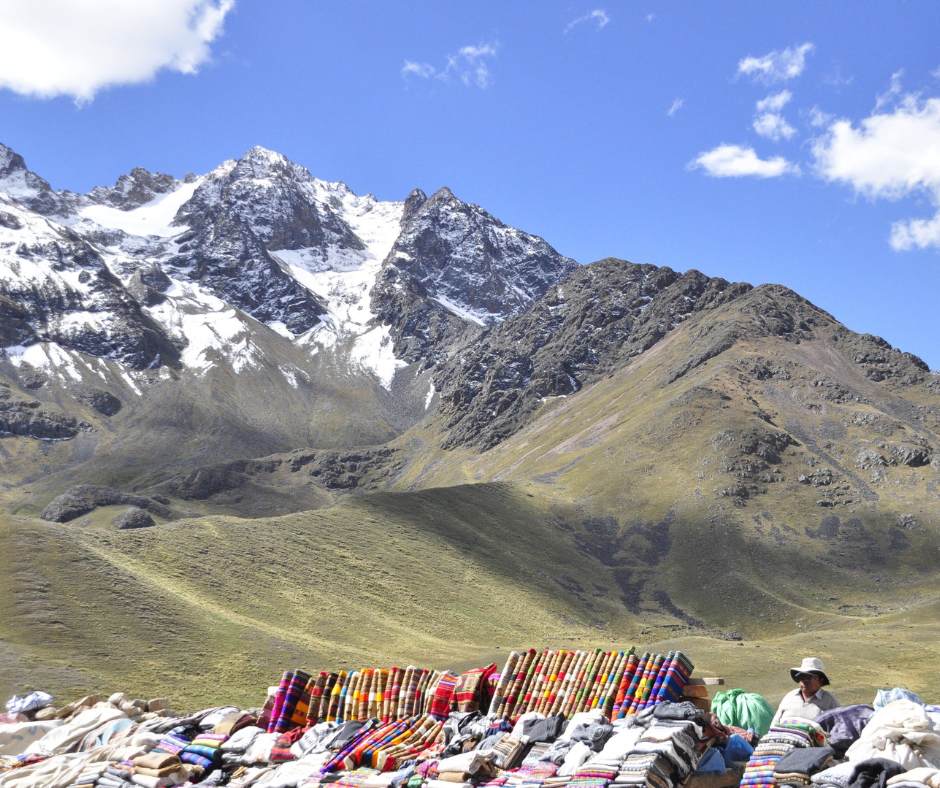
- A Diverse Landscape: The Andes traverse seven countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. This journey across diverse latitudes and climates results in a wide range of ecosystems. From the parched Atacama Desert in Chile to the Amazon rainforest in Ecuador, the Andes showcase the full spectrum of South American biodiversity.
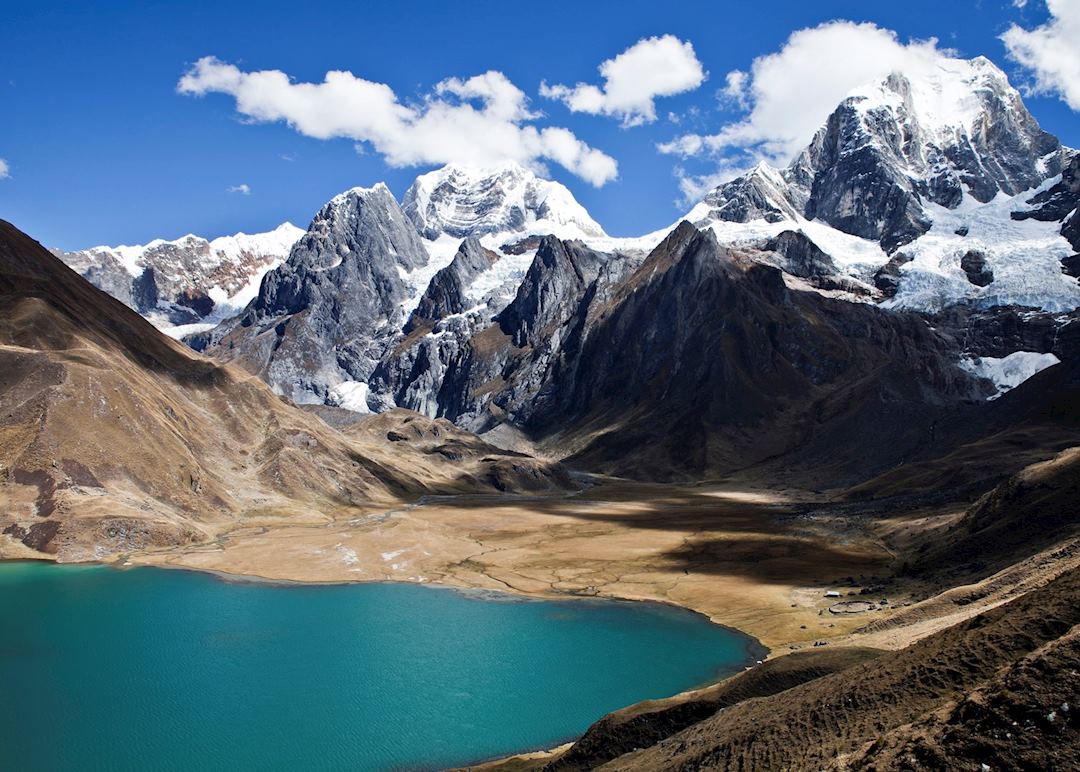
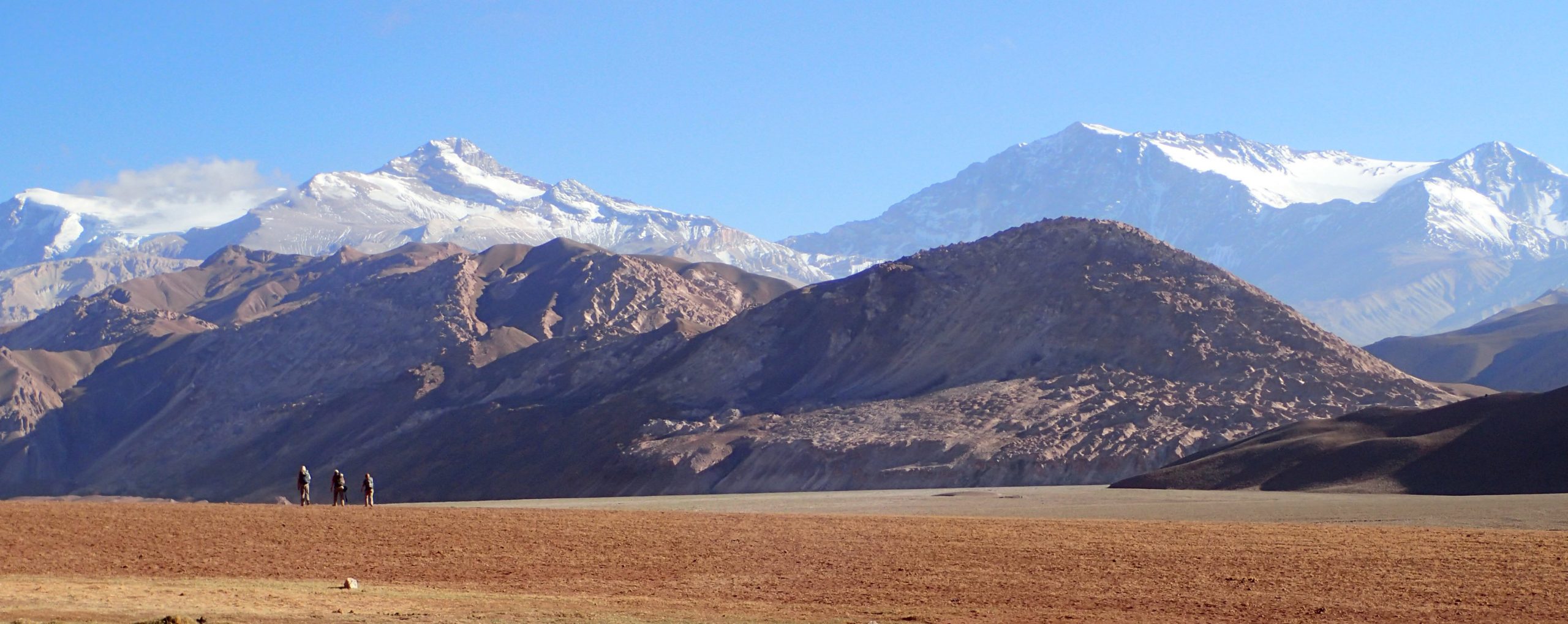
- High Altitude and Glacial Systems: The Andes are home to some of the world’s highest peaks, including Aconcagua, the highest mountain outside of Asia. These peaks are crowned with vast glaciers, playing a crucial role in regulating water supply for millions of people in the region.
The Andes: A Lifeline for South America:
The Andes are more than just a majestic mountain range; they are a vital lifeline for South America. Their impact on the continent is profound, influencing everything from climate and biodiversity to human settlements and economic development.
- Climate Regulation: The Andes act as a barrier, blocking moist air from the east and creating a rain shadow effect. This results in distinct climates on either side of the range, with the eastern slopes receiving abundant rainfall while the western slopes are often arid.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The Andes harbor a vast array of endemic species, many found nowhere else on Earth. This rich biodiversity is a testament to the unique and isolated ecosystems that have evolved within the mountain range.
- Water Resources: The Andes are the source of many major rivers, including the Amazon, the Orinoco, and the Paraná. These rivers provide water for agriculture, industry, and drinking for millions of people.
- Human Settlement: The Andes have been home to indigenous populations for thousands of years. Their cultures have adapted to the unique challenges of the high altitude, creating intricate social structures and agricultural practices that are still in use today.
The Andes: A Legacy of Challenges and Opportunities:
The Andes, while a source of life, also present significant challenges. The fragile ecosystems of the mountains are vulnerable to human activities such as deforestation, mining, and climate change.
- Deforestation and Mining: The demand for timber and minerals has led to widespread deforestation and mining in the Andes. This has resulted in habitat loss, soil erosion, and pollution, threatening the biodiversity of the region.
- Climate Change: The glaciers of the Andes are retreating at an alarming rate due to climate change. This has implications for water security, as these glaciers provide a crucial source of water for many communities.
- Sustainable Development: The Andes offer opportunities for sustainable development, such as ecotourism, sustainable agriculture, and renewable energy. Protecting the natural resources of the Andes is essential for ensuring the long-term well-being of the region.
FAQs about the Andes Mountains:
Q: What are the highest peaks in the Andes Mountains?
A: The highest peak in the Andes is Aconcagua, reaching an elevation of 6,961 meters (22,838 feet). Other notable peaks include Mount Huascarán (6,768 meters), Ojos del Salado (6,893 meters), and Llullaillaco (6,739 meters).
Q: What are some of the major rivers that originate in the Andes?
A: The Andes are the source of many major rivers, including the Amazon River, the Orinoco River, the Paraná River, and the Río de la Plata. These rivers are crucial for water supply, agriculture, and transportation in South America.
Q: What are some of the major cities located in the Andes?
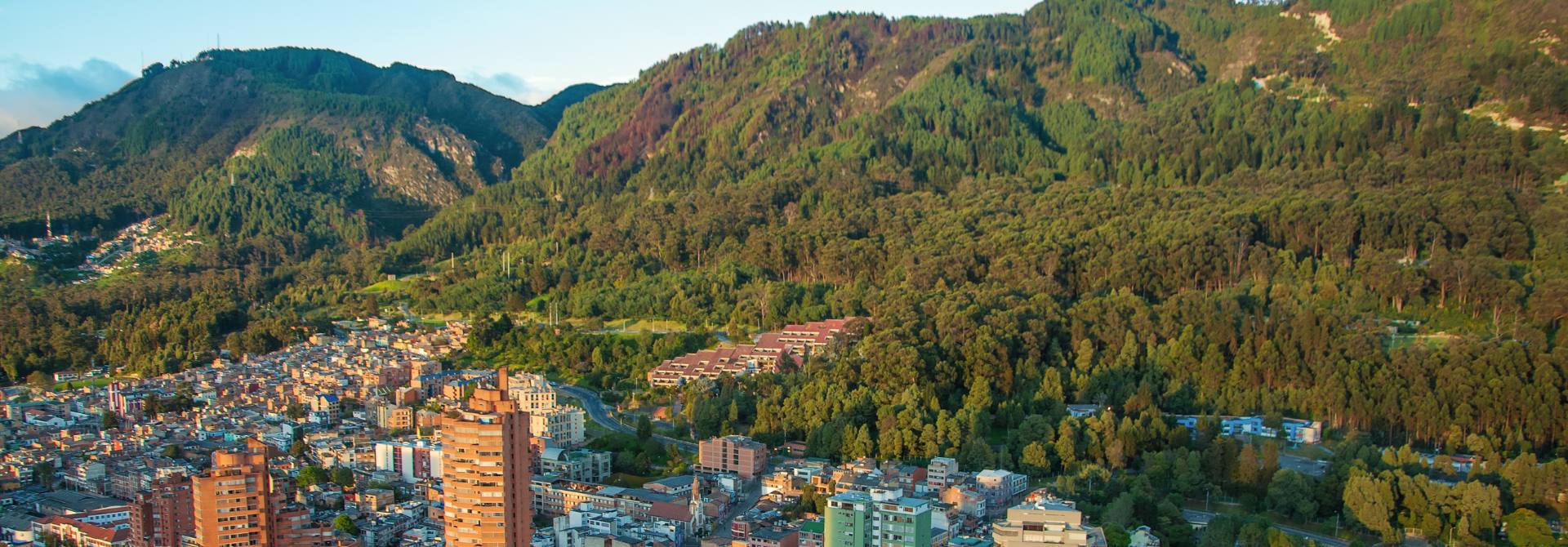
A: Major cities located in the Andes include Quito (Ecuador), Bogotá (Colombia), Lima (Peru), La Paz (Bolivia), and Santiago (Chile). These cities are important centers of culture, commerce, and tourism.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the Andes Mountains?
A: The Andes face several challenges, including deforestation, mining, climate change, and pollution. These challenges threaten the biodiversity, water resources, and well-being of the region.
Q: What are some of the opportunities for sustainable development in the Andes?
A: The Andes offer opportunities for sustainable development, such as ecotourism, sustainable agriculture, and renewable energy. Protecting the natural resources of the Andes is essential for ensuring the long-term well-being of the region.
Tips for Visiting the Andes:
- Plan Your Trip Carefully: The Andes are a vast and diverse region. Research your destination and choose activities that suit your interests and fitness level.
- Respect the Environment: Pack out what you pack in, avoid littering, and be mindful of the local ecosystems.
- Be Prepared for Altitude: High altitude can affect your health. Acclimate gradually and stay hydrated.
- Respect Local Cultures: Learn about the local customs and traditions, and be respectful of the indigenous communities.
- Support Sustainable Tourism: Choose tour operators and accommodations that prioritize environmental sustainability and community development.
Conclusion:
The Andes Mountains are a defining feature of South America, shaping the continent’s geography, climate, and culture. This extraordinary mountain range is a testament to the Earth’s geological forces and a vital lifeline for the people and ecosystems it supports. Understanding the importance of the Andes and the challenges they face is crucial for ensuring their protection and sustainable development for future generations.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Andes Mountains: A Spine of Life Along the Western Hemisphere. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!