Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Rivers of Iraq
Related Articles: Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Rivers of Iraq
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Rivers of Iraq. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Rivers of Iraq

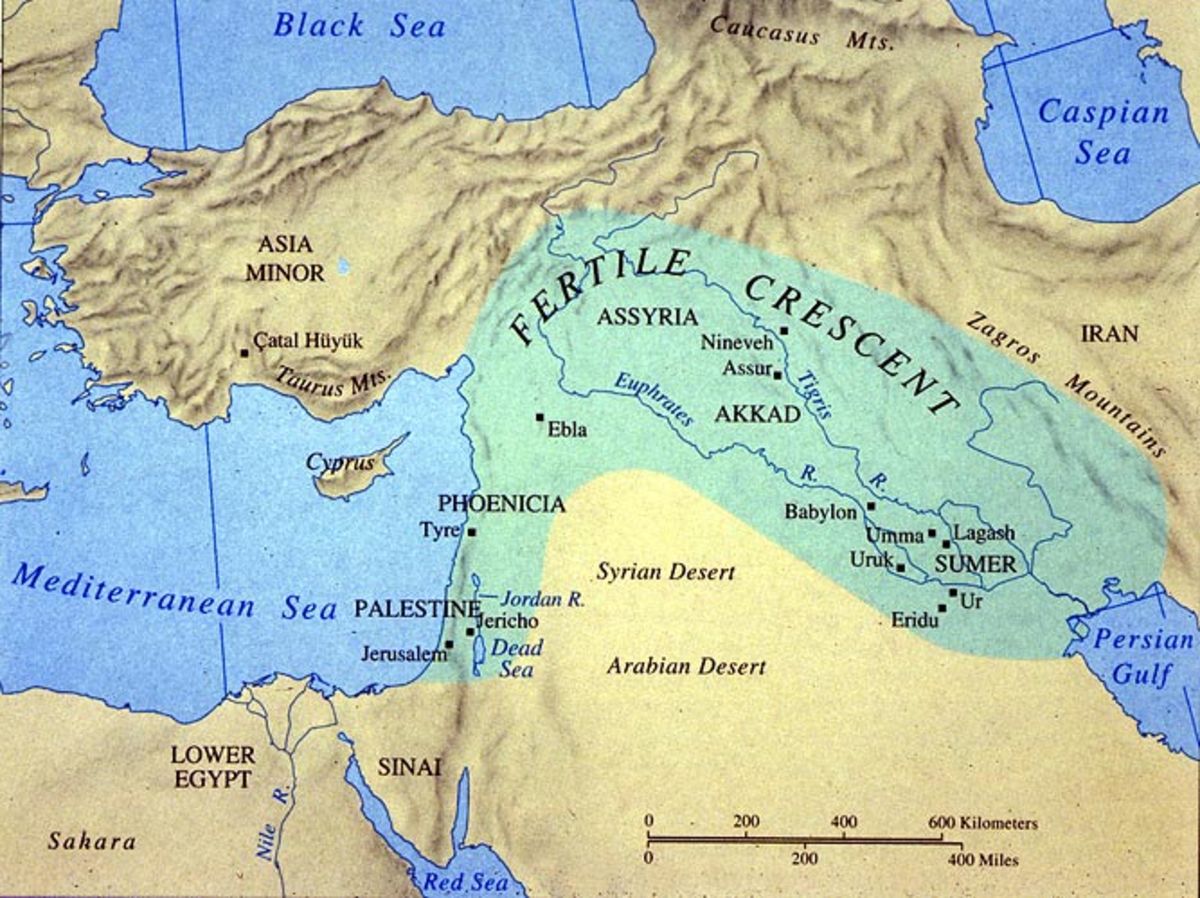
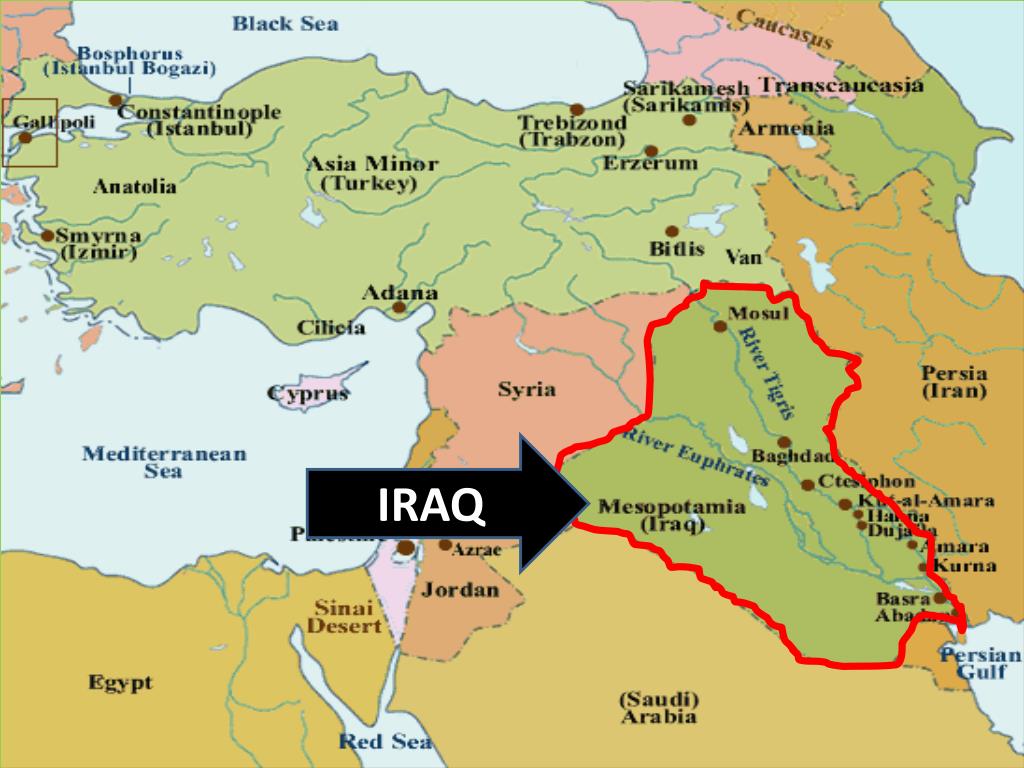
The Republic of Iraq, nestled in the heart of the Middle East, boasts a rich tapestry of history, culture, and natural resources. Among these resources, rivers play a vital role, shaping the country’s landscape, influencing its economy, and nurturing its people. This article delves into the intricate web of rivers that crisscross Iraq, exploring their significance, characteristics, and the challenges they face.
A Tapestry of Waterways: The Major Rivers of Iraq
The rivers of Iraq form a lifeline, connecting the country’s diverse regions and providing essential resources for its inhabitants. Here’s a detailed look at the key waterways:
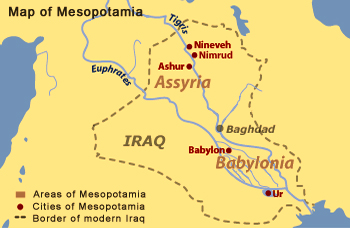
1. The Mighty Tigris:
- Origin: The Tigris River originates in the Taurus Mountains of Turkey, flowing southeast through Iraq and ultimately merging with the Euphrates River to form the Shatt al-Arab.
- Course: The Tigris winds through mountainous terrain, carving its way through the Zagros Mountains before traversing the Mesopotamian Plain. It passes through major cities like Mosul and Baghdad, contributing significantly to their growth and development.
- Significance: The Tigris River has been a cornerstone of Mesopotamian civilization for millennia. It provides irrigation for agriculture, serves as a crucial transportation route, and is a vital source of drinking water for millions of Iraqis.
2. The Fertile Euphrates:
- Origin: The Euphrates River, the longer of the two, originates in the Armenian Highlands, traversing through Turkey and Syria before entering Iraq.
- Course: The Euphrates flows predominantly through arid regions, creating fertile oases along its path. It passes through major cities like Ramadi and Nasiriyah, playing a critical role in their development.
- Significance: The Euphrates, like its counterpart, has been a source of life for millennia. It serves as a major irrigation source, supports diverse ecosystems, and provides water for drinking and industrial use.
3. The Shatt al-Arab:
- Formation: The Shatt al-Arab is formed by the confluence of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers near Al-Qurnah in southern Iraq.
- Course: It flows southeast through a marshland region, eventually emptying into the Persian Gulf.
- Significance: The Shatt al-Arab serves as a critical waterway for international trade, connecting Iraq to the world through its access to the Persian Gulf. It is also a vital source of fish for local communities.
4. The Lesser Known Rivers:
Beyond the Tigris and Euphrates, Iraq is home to several smaller rivers, each with its unique significance:
- The Diyala River: This river, a tributary of the Tigris, flows through the Diyala Governorate and contributes to the fertile Mesopotamian Plain.
- The Little Zab River: This tributary of the Tigris plays a crucial role in irrigation and provides water for agriculture in the Nineveh Governorate.
- The Greater Zab River: This tributary also flows into the Tigris and is important for irrigation in the Erbil and Sulaymaniyah Governorates.
The Importance of Iraq’s Rivers
The rivers of Iraq are not just geographic features; they are the lifeblood of the nation, contributing to its economic, social, and cultural well-being. Here’s a breakdown of their key roles:
1. Agriculture and Food Security:
- Irrigation: The rivers provide a vital source of water for irrigation, sustaining a significant portion of Iraq’s agricultural production.
- Food Production: The fertile land along the rivers supports the cultivation of staple crops like wheat, barley, rice, and dates, ensuring food security for the nation.
2. Water Supply and Sanitation:
- Drinking Water: The rivers are a primary source of drinking water for millions of Iraqis, especially in urban areas.
- Sanitation: River water is also used for sanitation, contributing to public health and hygiene.
3. Transportation and Trade:
- Waterways: The rivers serve as navigable waterways, facilitating transportation of goods and people within the country.
- Trade: The Shatt al-Arab provides access to the Persian Gulf, enabling international trade and economic development.
4. Cultural and Historical Significance:
- Cradle of Civilization: The rivers of Iraq have been central to the development of ancient Mesopotamian civilizations, leaving behind a rich legacy of archaeological sites and historical monuments.
- Cultural Heritage: The rivers are deeply embedded in Iraqi culture, inspiring literature, art, and folklore.
Challenges Facing Iraq’s Rivers
Despite their importance, Iraq’s rivers face significant challenges, impacting their ability to fulfill their vital roles:
1. Water Scarcity and Drought:
- Climate Change: Climate change is leading to increased evaporation and reduced rainfall, putting pressure on water resources.
- Upstream Dams: Dams constructed upstream in Turkey and Syria reduce the flow of water reaching Iraq, further exacerbating water scarcity.
- Water Management: Inefficient water management practices, including over-extraction and pollution, exacerbate water scarcity.
2. Pollution and Degradation:
- Industrial Waste: Industrial activities, including oil extraction and refining, contribute to water pollution, harming aquatic life and human health.
- Agricultural Runoff: Runoff from agricultural fields carrying fertilizers and pesticides contaminates the rivers, impacting their ecosystem and water quality.
- Sewage Discharge: Untreated sewage discharge from urban areas pollutes the rivers, posing health risks to communities.
3. Conflict and Instability:
- Environmental Damage: Conflicts and instability often lead to environmental damage, including destruction of infrastructure and pollution.
- Displaced Populations: Conflict and displacement can lead to increased pressure on water resources, exacerbating scarcity and pollution.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Iraq’s Rivers
1. What is the significance of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers for Iraq?
The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers are the lifelines of Iraq, providing water for agriculture, drinking, and sanitation, as well as serving as critical transportation routes and sources of cultural heritage.
2. How do the rivers contribute to Iraq’s economy?
The rivers support a significant portion of Iraq’s agricultural sector, provide access to transportation routes, and facilitate international trade through the Shatt al-Arab.
3. What are the main environmental challenges facing Iraq’s rivers?
Water scarcity, pollution from industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge, as well as conflict-related damage, pose significant challenges to the rivers’ health and sustainability.
4. How can Iraq address the challenges facing its rivers?
Addressing the challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, including:
- Water Management: Implementing efficient water management practices, including water conservation and desalination.
- Pollution Control: Implementing stricter regulations to reduce industrial and agricultural pollution.
- Infrastructure Development: Investing in infrastructure to improve sewage treatment and waste management.
- Regional Cooperation: Collaborating with neighboring countries to manage shared water resources.
Tips for Understanding Iraq’s Rivers:
- Explore Maps: Utilize online maps and resources to visualize the course of the rivers and their surrounding areas.
- Read Historical Accounts: Delve into historical accounts and literature to understand the role of rivers in shaping Iraqi civilization.
- Follow Environmental News: Stay informed about the latest developments regarding water scarcity, pollution, and conservation efforts.
- Support Sustainable Practices: Encourage and support initiatives promoting sustainable water management and environmental protection.
Conclusion: Preserving the Lifeline
The rivers of Iraq are a testament to the country’s rich history, natural beauty, and cultural identity. They provide essential resources for its people and contribute significantly to its economy. However, the challenges they face, particularly water scarcity and pollution, require urgent attention. By implementing effective water management practices, addressing pollution, and fostering regional cooperation, Iraq can ensure the sustainability of its rivers and secure its future. The preservation of these vital waterways is not just an environmental imperative, but a fundamental step towards ensuring the well-being of the Iraqi people and the nation’s sustainable development.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Rivers of Iraq. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!