Navigating the Kankakee River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geographic and Ecological Significance
Related Articles: Navigating the Kankakee River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geographic and Ecological Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Kankakee River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geographic and Ecological Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Kankakee River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geographic and Ecological Significance

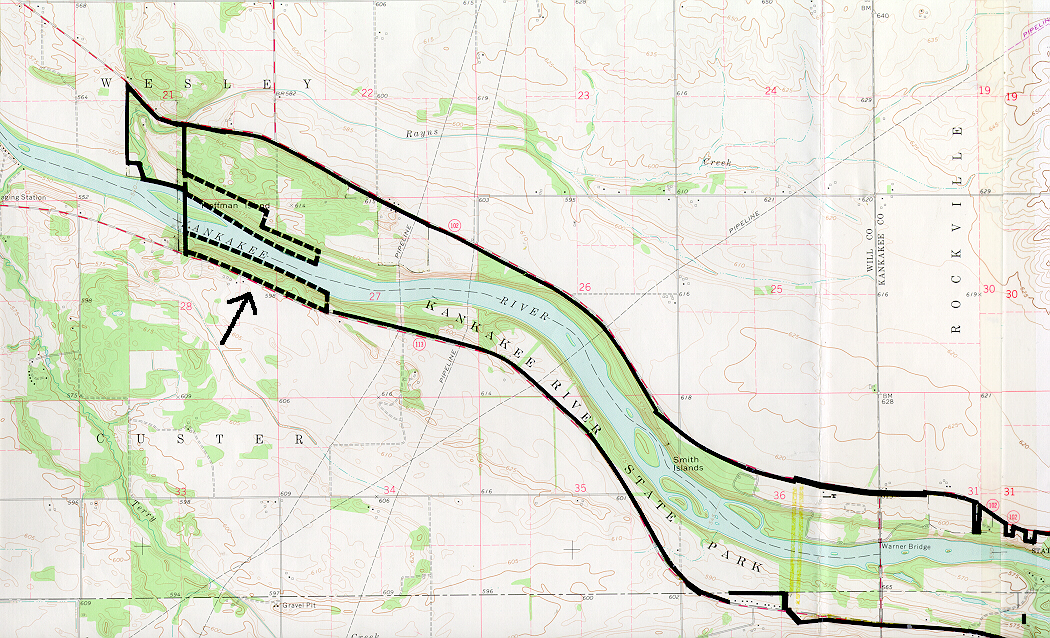
The Kankakee River, a vital artery winding through the heart of Illinois, holds a rich tapestry of history, ecology, and recreational opportunities. Understanding its geographic layout is crucial for appreciating its diverse impact on the surrounding landscape and communities. This article delves into the intricate map of the Kankakee River, unveiling its unique characteristics and underscoring its profound importance.
A River’s Journey: Tracing the Kankakee’s Path
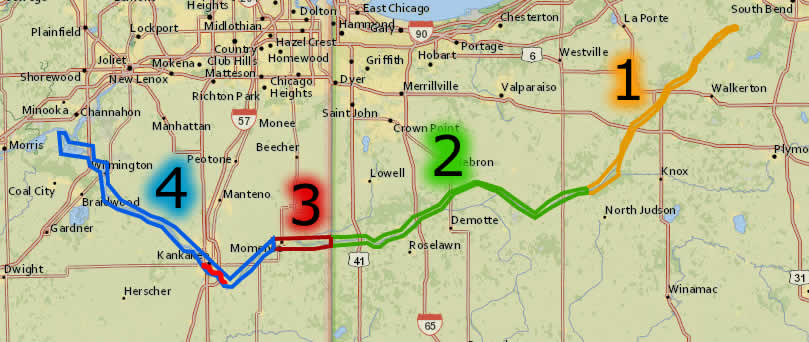
The Kankakee River, a major tributary of the Illinois River, originates in the glacial Lake Kankakee in northern Indiana. It flows westward for approximately 190 miles, traversing through the states of Indiana and Illinois before converging with the Iroquois River to form the Illinois River near the town of Morris, Illinois.
Unraveling the River’s Geography
The Kankakee River’s journey is marked by distinct geographic features that contribute to its unique character:
- Headwaters: The river’s source lies in the glacial Lake Kankakee, a shallow, marshy area in northern Indiana. This area provides a crucial habitat for various aquatic species and serves as a critical source of water for the river.
- The Kankakee Marsh: As the river meanders westward, it flows through a vast expanse of wetlands known as the Kankakee Marsh. This ecologically significant area, once covering thousands of acres, is now a fragmented but vital habitat for a diverse array of plant and animal life.
- The Kankakee River Valley: The river carves a path through a valley characterized by rolling hills and fertile farmland. This region, once a haven for Native American tribes, now supports a thriving agricultural industry.
- The Illinois River Confluence: The Kankakee River’s journey culminates in its confluence with the Iroquois River, forming the Illinois River. This point marks a significant transition in the river’s character, as it enters a larger, more navigable waterway.
The Kankakee River: A Vital Ecosystem
The Kankakee River’s map tells a story of ecological significance. It serves as a crucial habitat for a diverse array of flora and fauna, including:
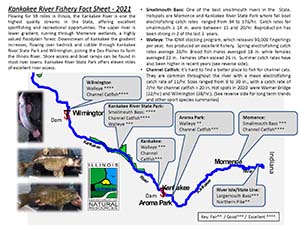
- Aquatic Life: The river supports a rich population of fish species, including bass, catfish, and walleye. Its waters also provide a home for various amphibians, reptiles, and invertebrates.
- Birdlife: The Kankakee River and its surrounding wetlands attract a wide variety of birds, including migratory waterfowl, wading birds, and raptors.
- Plant Life: The river’s banks and surrounding areas are home to a variety of plants, including cattails, reeds, and willows. These plants provide essential food and shelter for wildlife and help to stabilize the river’s banks.
Navigating the Kankakee: Recreation and Tourism
The Kankakee River’s map reveals a network of recreational opportunities for outdoor enthusiasts:
- Boating: The river is navigable for much of its length, offering opportunities for canoeing, kayaking, and fishing.
- Hiking and Biking: The Kankakee River Trail, a paved path running along the river’s banks, provides scenic hiking and biking opportunities.
- Fishing: The river is known for its excellent fishing, with opportunities to catch a variety of fish species.
- Wildlife Viewing: The Kankakee River and its surrounding wetlands offer excellent wildlife viewing opportunities, with the chance to spot a variety of birds, mammals, and other wildlife.
Conservation Challenges and Efforts
Despite its ecological importance, the Kankakee River faces a number of challenges, including:
- Water Quality: Agricultural runoff and urban development have impacted the river’s water quality, leading to concerns about pollution and nutrient loading.
- Habitat Loss: The conversion of wetlands to agricultural land has led to significant habitat loss for a variety of wildlife species.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of invasive species, such as carp and zebra mussels, has disrupted the river’s ecosystem.
Conservation efforts are underway to address these challenges, including:
- Water Quality Improvement: Organizations are working to reduce agricultural runoff and improve wastewater treatment to protect the river’s water quality.
- Habitat Restoration: Projects are underway to restore wetlands and other habitats along the river’s banks.
- Invasive Species Control: Efforts are being made to control the spread of invasive species and protect native species.
The Kankakee River: A Legacy of Importance
The Kankakee River’s map is a testament to its vital role in the region’s history, ecology, and economy. It serves as a reminder of the need to protect this vital resource for future generations. By understanding the river’s geography and appreciating its ecological significance, we can work towards ensuring its continued health and vitality.
FAQs
- What is the length of the Kankakee River? The Kankakee River is approximately 190 miles long.
- Where does the Kankakee River originate? The Kankakee River originates in the glacial Lake Kankakee in northern Indiana.
- What is the Kankakee Marsh? The Kankakee Marsh is a vast expanse of wetlands that the river flows through. It is a vital habitat for a diverse array of plant and animal life.
- What are some of the recreational activities available on the Kankakee River? The Kankakee River offers opportunities for boating, fishing, hiking, biking, and wildlife viewing.
- What are some of the conservation challenges facing the Kankakee River? The Kankakee River faces challenges related to water quality, habitat loss, and invasive species.
Tips
- Visit the Kankakee River Trail: This paved path offers scenic hiking and biking opportunities along the river’s banks.
- Go fishing: The Kankakee River is known for its excellent fishing, with opportunities to catch a variety of fish species.
- Observe wildlife: The river and its surrounding wetlands provide excellent opportunities for wildlife viewing.
- Support conservation efforts: Donate to or volunteer with organizations working to protect the Kankakee River.
Conclusion
The map of the Kankakee River reveals a rich tapestry of geographic, ecological, and recreational significance. From its headwaters in the glacial Lake Kankakee to its confluence with the Iroquois River, the river plays a vital role in the region’s history, economy, and environment. By understanding the river’s unique characteristics and appreciating its importance, we can work towards ensuring its continued health and vitality for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Kankakee River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geographic and Ecological Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!