Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map-Making Tools
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map-Making Tools
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map-Making Tools. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map-Making Tools

In the age of digital information, the ability to visualize and understand complex data is paramount. Maps, with their inherent ability to represent spatial relationships, have become essential tools for navigating the digital landscape. From understanding global trends to analyzing local demographics, map-making tools empower users to gain insights and make informed decisions.
Understanding the Power of Visual Representation
Humans are visual creatures. Our brains are wired to process information more effectively when presented visually. Maps, with their ability to translate abstract data into tangible representations, harness this innate human capacity. By visualizing data on a map, users can readily identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that might otherwise remain hidden within spreadsheets or datasets.
Beyond Traditional Cartography: The Evolution of Map-Making Tools
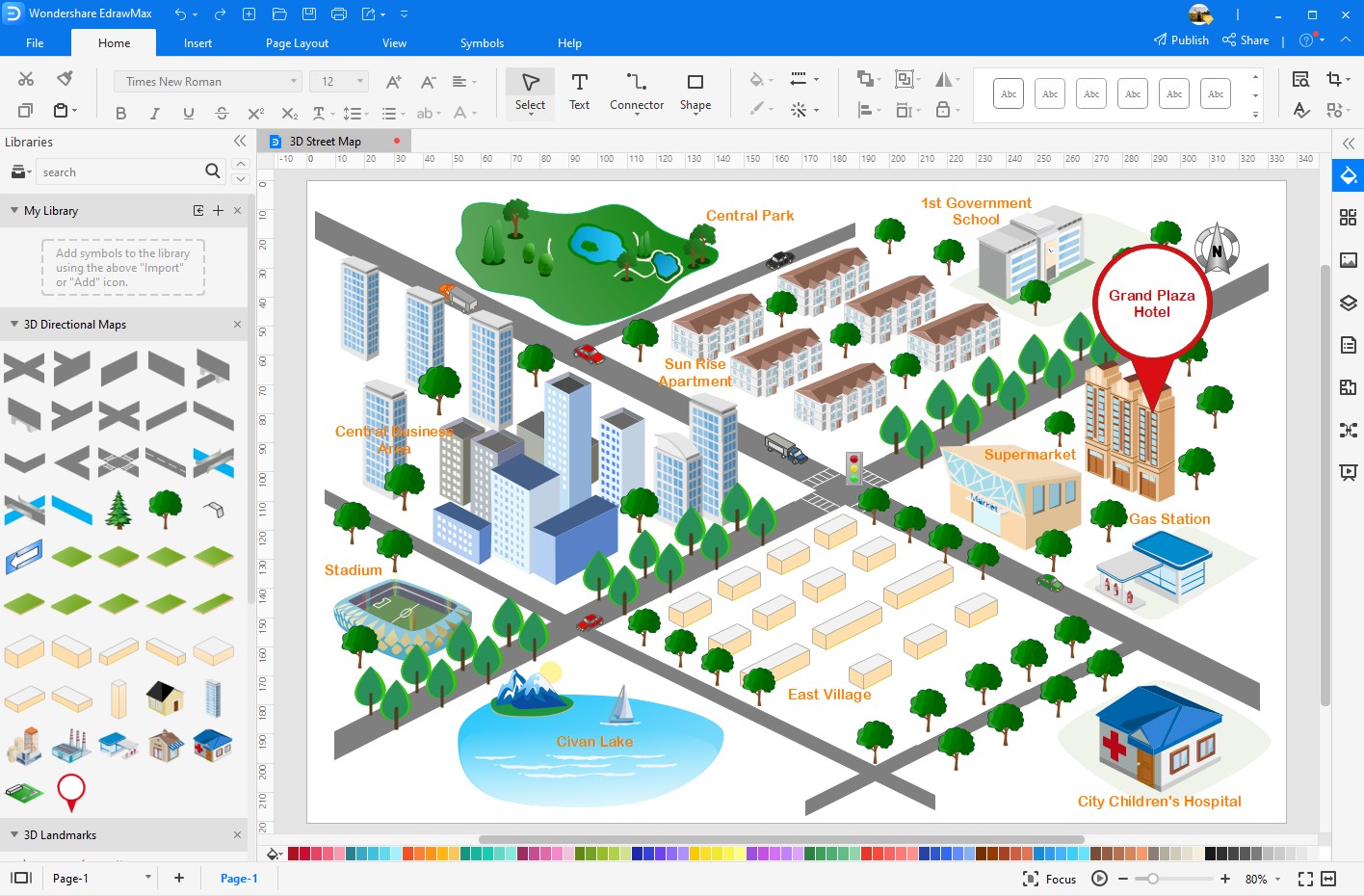
Traditional map-making, once the domain of cartographers and geographers, has undergone a dramatic transformation. Modern map-making tools are no longer limited to static, paper-based representations. They have evolved into dynamic, interactive platforms that integrate data from diverse sources, enabling users to create maps that are both informative and engaging.
Key Features of Modern Map-Making Tools
Modern map-making tools offer a range of features that empower users to create custom maps tailored to their specific needs. These features include:
- Data Integration: The ability to import and integrate data from various sources, such as spreadsheets, databases, and APIs.
- Visualization Options: A wide array of visualization options, including markers, lines, polygons, heatmaps, and choropleth maps.
- Customization: The ability to customize map styles, colors, legends, and labels to enhance clarity and visual appeal.
- Interactive Elements: The inclusion of interactive features, such as pop-ups, tooltips, and clickable elements, to provide additional information and insights.
- Sharing and Collaboration: The capability to share maps with others, either publicly or privately, facilitating collaboration and communication.
Applications of Map-Making Tools Across Industries
The versatility of map-making tools extends across diverse industries, enabling users to address a wide range of challenges and opportunities:
- Business and Marketing: Businesses leverage map-making tools to analyze customer demographics, identify potential markets, optimize logistics, and track sales performance.
- Government and Public Sector: Governments utilize map-making tools for disaster management, urban planning, environmental monitoring, and public health initiatives.
- Education and Research: Educators and researchers employ map-making tools to visualize historical data, analyze geographic patterns, and communicate research findings.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Non-profit organizations utilize map-making tools to track project progress, identify areas of need, and raise awareness about social issues.
- Environmental Management: Environmental scientists and organizations use map-making tools to monitor deforestation, track wildlife populations, and assess the impact of climate change.
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Popular Map-Making Tools
Numerous map-making tools are available, each with its unique strengths and limitations. Understanding the different options can help users choose the tool that best suits their specific needs.
1. Google Maps Platform
Google Maps Platform is a comprehensive suite of tools and APIs that enable developers to integrate Google Maps into their websites and applications. Its key features include:
- Google Maps API: Enables developers to embed interactive maps into their websites and applications.
- Google Maps SDK: Provides tools for building native mobile applications that integrate with Google Maps.
- Google My Maps: Allows users to create custom maps, add markers, and share them with others.
2. ArcGIS
ArcGIS is a powerful Geographic Information System (GIS) platform developed by Esri. It offers a wide range of tools for creating, analyzing, and sharing geographic data. Key features include:
- ArcGIS Online: A web-based platform for creating, sharing, and collaborating on maps.
- ArcGIS Pro: A desktop application for advanced GIS analysis and mapping.
- ArcGIS Field Maps: A mobile application for data collection and field mapping.
3. Mapbox
Mapbox is a cloud-based platform that provides tools for creating custom maps and integrating them into applications. Key features include:
- Mapbox Studio: A web-based editor for designing and customizing maps.
- Mapbox GL JS: A JavaScript library for creating interactive maps.
- Mapbox Maps SDKs: Provides tools for integrating Mapbox maps into native mobile applications.
4. Leaflet
Leaflet is an open-source JavaScript library for creating interactive maps. It is lightweight, fast, and easy to use, making it a popular choice for developers. Key features include:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Leaflet works on all major web browsers and platforms.
- Extensive Plugin Ecosystem: A wide range of plugins are available to extend Leaflet’s functionality.
- Open-Source Nature: Leaflet is free to use and modify, fostering a collaborative community of developers.
5. Carto
Carto is a cloud-based platform for creating and sharing maps and data visualizations. Key features include:
- User-Friendly Interface: Carto offers a simple and intuitive interface for creating maps.
- Data Analysis Capabilities: Carto integrates with various data sources and provides tools for data analysis.
- Collaboration Features: Carto enables users to collaborate on maps and share them with others.
FAQs about Map-Making Tools
1. What are the benefits of using map-making tools?
Map-making tools offer numerous benefits, including:
- Visualizing Complex Data: Maps provide a clear and concise way to represent complex data, making it easier to understand and interpret.
- Identifying Trends and Patterns: Maps can reveal trends and patterns that might be hidden within raw data, enabling users to make informed decisions.
- Improving Communication: Maps facilitate communication by providing a shared visual language for conveying information.
- Enhancing Collaboration: Maps foster collaboration by providing a common platform for sharing and discussing data.
2. How do I choose the right map-making tool?
The best map-making tool depends on your specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as:
- Your budget: Some tools are free, while others require paid subscriptions.
- Your technical skills: Some tools are easier to use than others.
- Your data sources: Ensure the tool can integrate with your existing data sources.
- Your desired features: Consider the specific features you need, such as data analysis capabilities, visualization options, and sharing options.
3. Are map-making tools difficult to learn?
Many map-making tools are designed to be user-friendly, even for those with limited technical experience. Some tools offer tutorials, online documentation, and community support to help users get started.
4. What are some tips for creating effective maps?
To create effective maps, consider the following tips:
- Keep it Simple: Avoid cluttering the map with too much information.
- Use Clear and Concise Labels: Ensure labels are legible and easy to understand.
- Choose Appropriate Colors: Use colors that are visually appealing and contrast well.
- Provide Context: Include a legend and other information to provide context for the map.
- Test and Iterate: Create multiple versions of the map and test them with others to get feedback.
Conclusion
Map-making tools have become essential tools for navigating the digital landscape. They empower users to visualize complex data, identify trends, and make informed decisions. By understanding the features, applications, and available tools, individuals and organizations can harness the power of maps to gain insights and drive innovation. As technology continues to evolve, the role of map-making tools in our digital world will only become more prominent, enabling us to navigate the complexities of data and make sense of the world around us.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map-Making Tools. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!