Navigating the Complexities of the 606 Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of the 606 Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of the 606 Map: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complexities of the 606 Map: A Comprehensive Guide
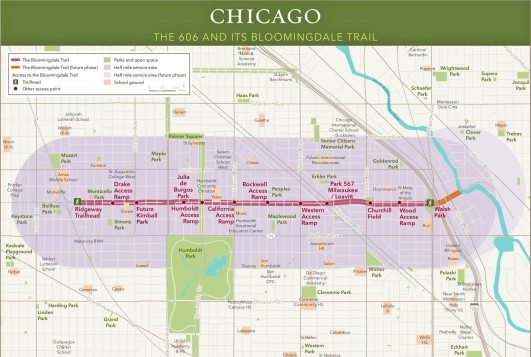
The 606 map, a term often used in the realm of data visualization and spatial analysis, represents a powerful tool for understanding and interpreting complex datasets. While the term itself might not be immediately familiar, its applications are far-reaching and touch upon various fields, from urban planning and healthcare to environmental research and market analysis. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the 606 map, exploring its core concepts, functionalities, and implications.
Understanding the 606 Map: A Visual Language for Data
At its core, the 606 map is a visual representation of data, typically presented as a grid-based structure. Each cell within this grid corresponds to a specific geographic area, such as a city block, census tract, or even a larger region. The numerical value within each cell represents a particular data point, often relating to population density, crime rates, income levels, or other socio-economic indicators.
The 606 map derives its name from the number of cells within the grid. A 606 map, for instance, would consist of 606 individual cells, each representing a distinct geographic unit. This structured approach allows for the clear visualization of data distribution across a defined area, revealing patterns, trends, and anomalies that might otherwise remain hidden within raw data.
Beyond the Visual: The Importance of 606 Maps
The significance of the 606 map lies in its ability to translate complex data into a readily understandable format. This visual representation facilitates:
-
Data Interpretation: By presenting data in a spatial context, the 606 map allows for a deeper understanding of the underlying relationships between different variables. For example, a 606 map depicting crime rates across a city could highlight specific areas with higher crime incidents, prompting targeted interventions.
-
Problem Identification: The visualization of data patterns on a 606 map can reveal areas requiring attention or resources. This could range from identifying areas with high poverty rates to pinpointing hotspots of environmental pollution.
-
Decision-Making Support: By offering a clear visual representation of data, the 606 map empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions based on solid evidence. This applies to various fields, including urban planning, resource allocation, and public health initiatives.
-
Trend Analysis: The 606 map facilitates the identification of trends and patterns over time. By comparing maps generated for different periods, users can observe shifts in data distribution and understand the underlying causes of these changes.
Applications of the 606 Map: A Multifaceted Tool
The versatility of the 606 map extends across diverse disciplines, making it an invaluable tool for:
-
Urban Planning: 606 maps are crucial for urban planners in understanding population distribution, identifying areas requiring infrastructure development, and optimizing resource allocation.
-
Public Health: Healthcare professionals utilize 606 maps to track disease outbreaks, identify areas with high disease prevalence, and target public health interventions effectively.
-
Environmental Research: Environmental scientists employ 606 maps to analyze pollution levels, monitor deforestation, and understand the impact of climate change on different regions.
-
Market Analysis: Businesses utilize 606 maps to identify target markets, understand customer demographics, and optimize marketing campaigns.
-
Social Research: Sociologists and researchers utilize 606 maps to study social inequalities, analyze poverty patterns, and assess the effectiveness of social programs.
Creating a 606 Map: A Step-by-Step Process
The creation of a 606 map typically involves the following steps:
-
Data Collection: The first step involves gathering relevant data related to the area of interest. This data could be sourced from government agencies, surveys, or other reliable sources.
-
Data Cleaning and Preparation: The collected data needs to be cleaned and prepared for visualization. This includes ensuring data consistency, handling missing values, and transforming data into a suitable format for mapping.
-
Geographic Mapping: The data needs to be linked to specific geographic locations. This can be achieved using geographic information systems (GIS) software, which allows for associating data points with their corresponding coordinates on a map.
-
Grid Creation: The next step involves creating a grid structure that encompasses the area of interest. The number of cells in the grid determines the resolution of the map.
-
Data Aggregation: The collected data is then aggregated based on the defined grid cells. This involves assigning the appropriate data value to each cell, reflecting the characteristics of the corresponding geographic area.
-
Map Visualization: Finally, the aggregated data is visualized using various mapping techniques. This could involve color-coding cells based on data values, using different symbols to represent specific categories, or employing other visual cues to highlight key trends and patterns.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Features of 606 Maps
While the fundamental concept of a 606 map is straightforward, advanced features and capabilities enhance its utility:
-
Dynamic Mapping: Interactive 606 maps allow users to explore data at different scales, zoom in on specific areas of interest, and filter data based on various criteria.
-
Time Series Analysis: 606 maps can be used to visualize data trends over time, enabling the identification of temporal patterns and shifts in data distribution.
-
Spatial Analysis: Advanced spatial analysis techniques can be applied to 606 maps to assess relationships between different data variables, identify clusters of similar values, and uncover hidden spatial dependencies.
-
Data Integration: 606 maps can be integrated with other data sources and visualization tools, facilitating a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of complex datasets.
FAQs Regarding 606 Maps
Q: What are the limitations of 606 maps?
A: While powerful, 606 maps have certain limitations. The resolution of the map depends on the size and number of grid cells. Fine-grained analysis may require a higher number of cells, potentially leading to data sparsity in sparsely populated areas. Additionally, 606 maps are susceptible to the Modifiable Areal Unit Problem (MAUP), where the results can vary depending on the chosen geographic units.
Q: How do I choose the appropriate number of cells for a 606 map?
A: The optimal number of cells depends on the specific data being analyzed and the desired level of detail. A higher number of cells provides a finer resolution but may lead to data sparsity. Conversely, a lower number of cells may mask subtle patterns but offers a more general overview.
Q: What software can I use to create 606 maps?
A: Various software options exist for creating 606 maps, including GIS software like ArcGIS, QGIS, and Google Earth Pro. Specialized data visualization tools such as Tableau and Power BI can also be used to create interactive 606 maps.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy and reliability of a 606 map?
A: The accuracy and reliability of a 606 map depend on the quality of the underlying data. Ensuring data accuracy, handling missing values appropriately, and using reliable data sources are crucial for generating trustworthy maps.
Tips for Effective 606 Map Creation and Interpretation
-
Clearly Define the Purpose: Before creating a 606 map, clearly define the research question or objective to ensure the map effectively addresses the intended goal.
-
Choose Appropriate Data: Select data relevant to the research question and ensure its accuracy and reliability.
-
Consider Data Scale: Choose an appropriate grid resolution based on the data scale and the desired level of detail.
-
Use Effective Visualization Techniques: Employ clear and informative visualization techniques to effectively communicate the data patterns and trends revealed by the map.
-
Provide Context: Include relevant context and information to aid in the interpretation of the 606 map.
-
Consider Ethical Implications: When working with sensitive data, ensure the responsible and ethical use of 606 maps, respecting privacy and avoiding potential biases.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of 606 Maps
The 606 map stands as a powerful tool for understanding complex data in a spatial context. Its ability to visualize data patterns, reveal trends, and support decision-making makes it invaluable across diverse fields. By embracing its capabilities and understanding its limitations, users can harness the power of the 606 map to gain deeper insights into the world around us and make informed decisions based on solid evidence.




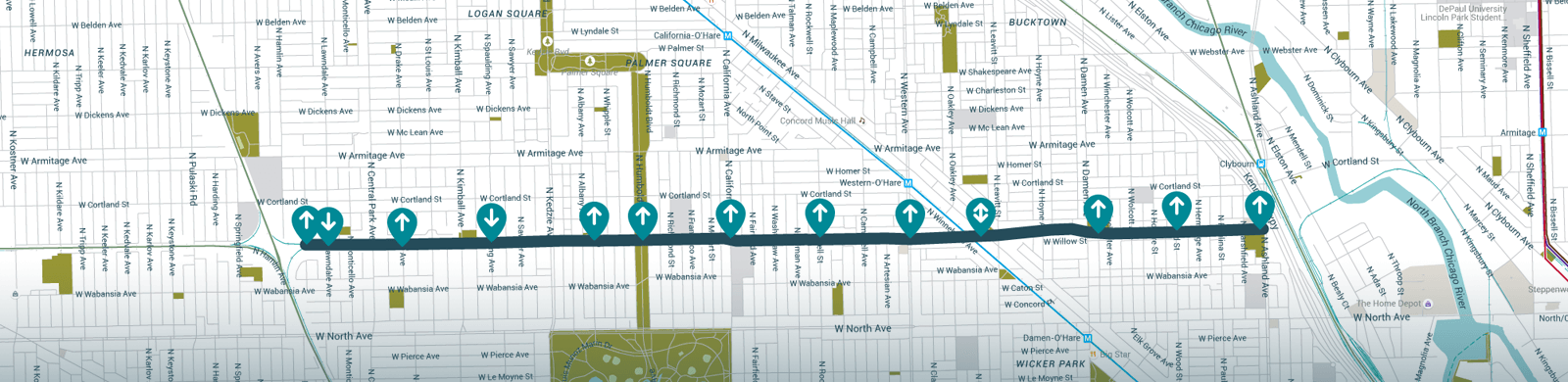
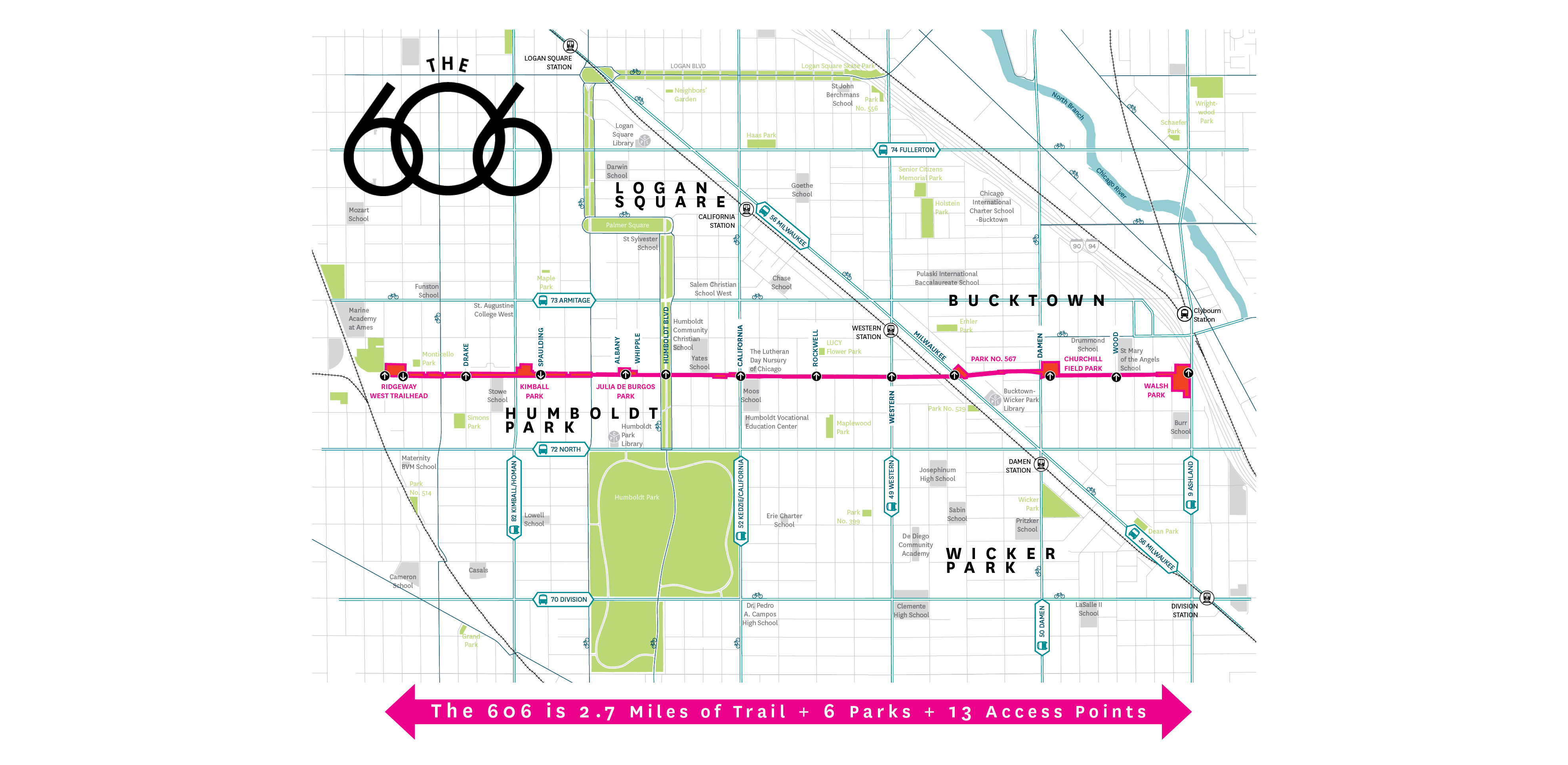
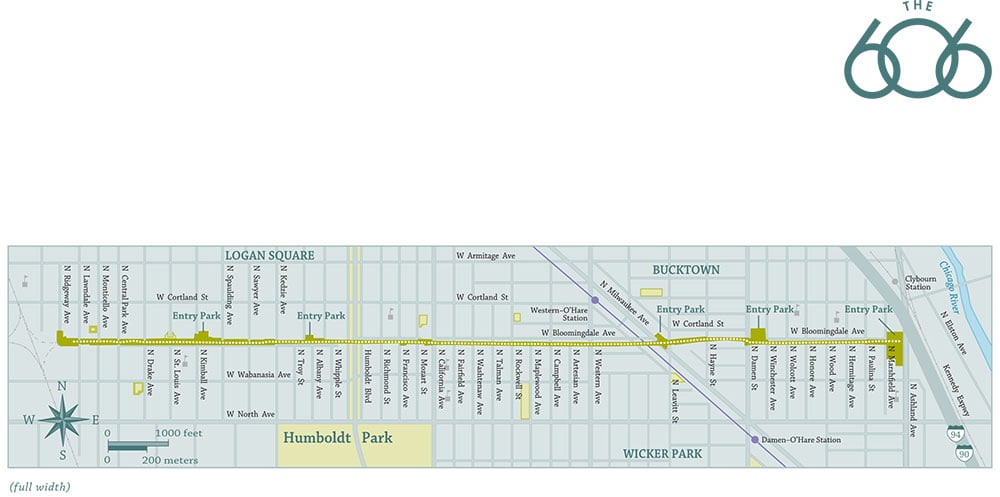
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of the 606 Map: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!