Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale and Its Significance
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale and Its Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale and Its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale and Its Significance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale and Its Significance
- 3.1 What is Map Scale?
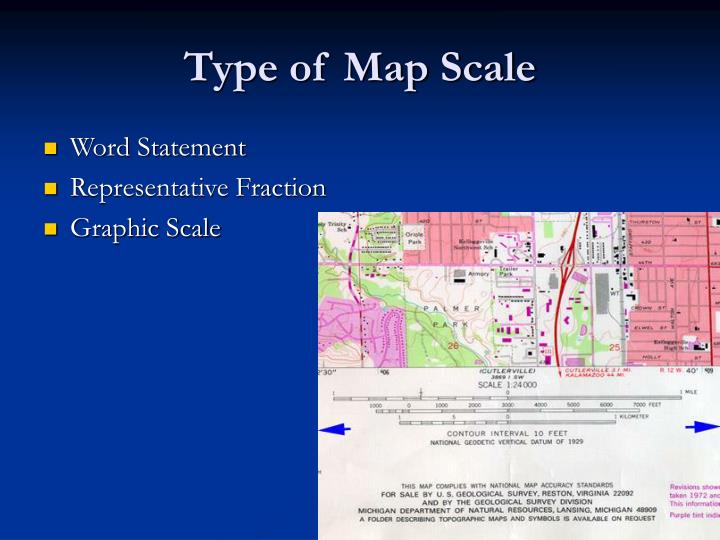
- 3.1.1 1. Verbal Scale:
- 3.1.2 2. Representative Fraction (RF):
- 3.1.3 3. Graphic Scale:
- 3.2 The Significance of Map Scale
- 3.3 The Importance of Choosing the Right Scale
- 3.4 Examples of Map Scale in Action
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Map Scale
- 3.6 Tips for Using Map Scale Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale and Its Significance
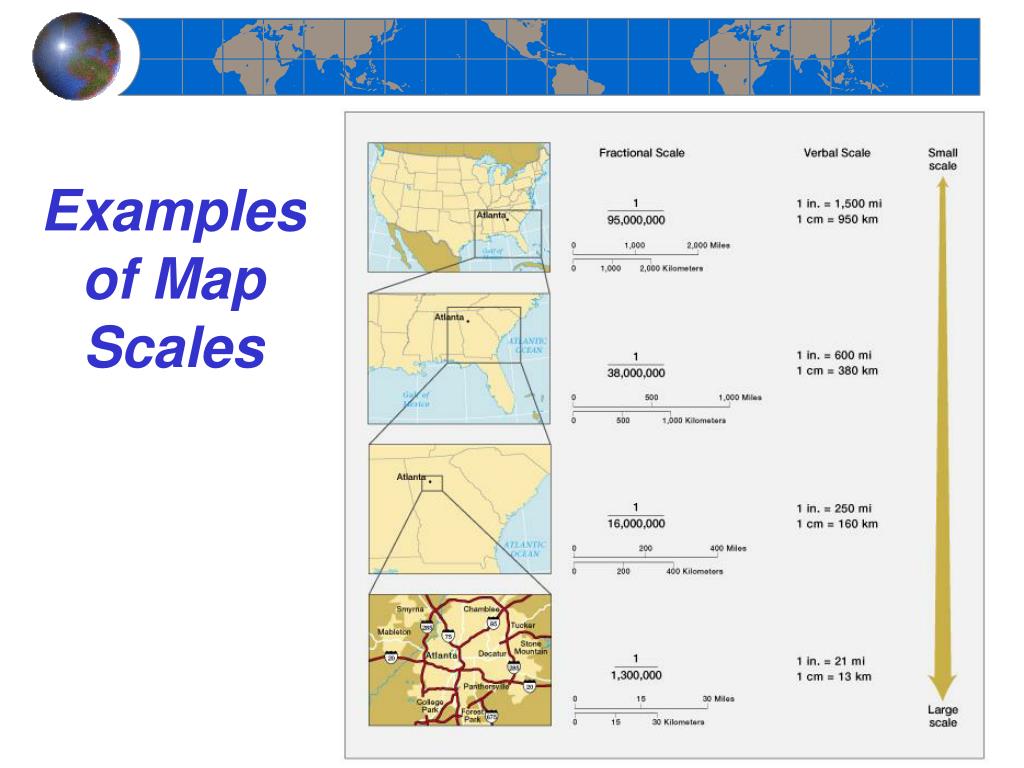
Maps are powerful tools that provide a visual representation of the world, condensing vast distances and intricate details into a manageable format. However, to accurately interpret the information presented on a map, it is crucial to understand the concept of map scale. Map scale serves as a fundamental bridge between the real world and its cartographic representation, allowing us to translate distances and measurements from the map to the actual terrain.
What is Map Scale?
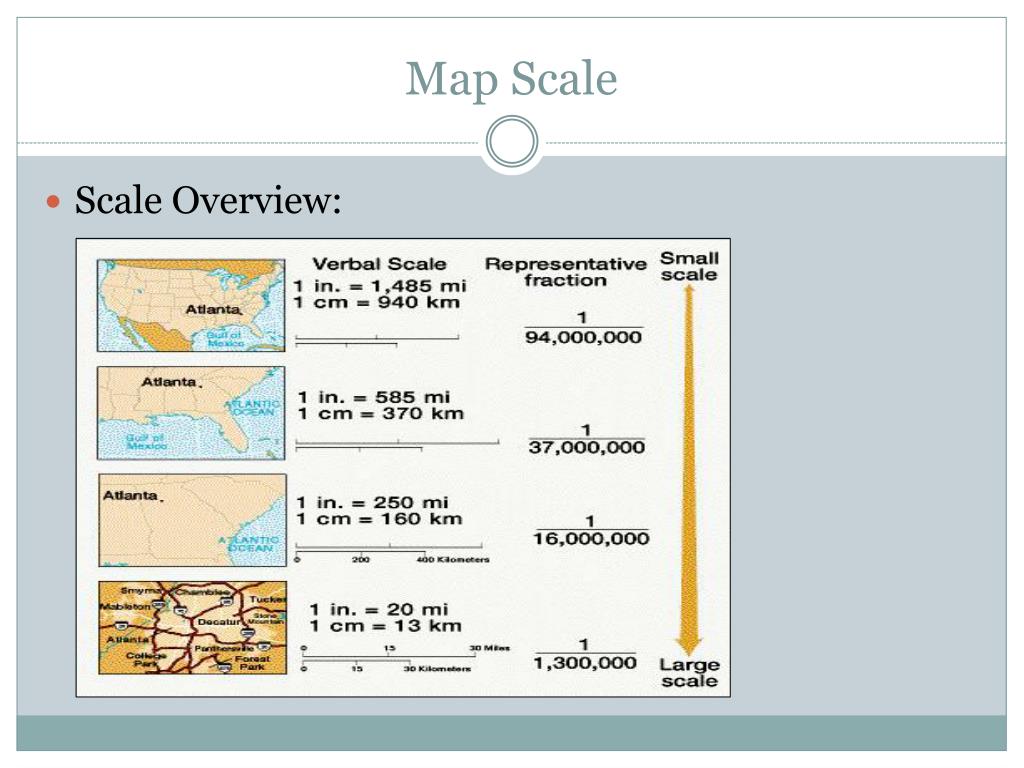
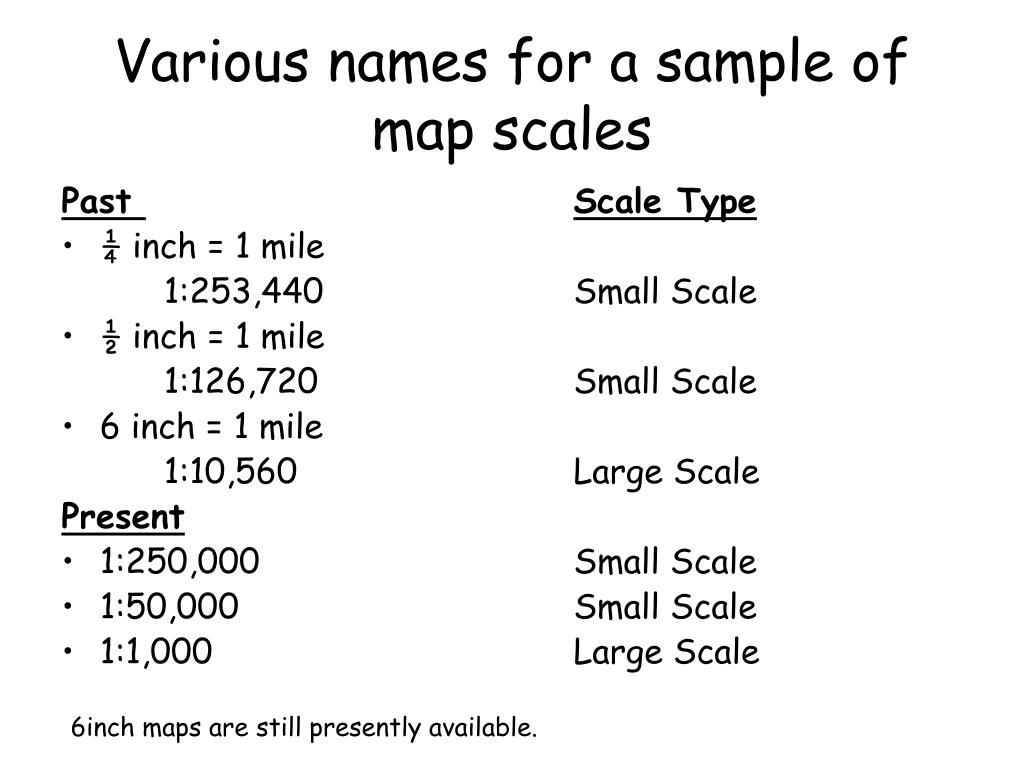
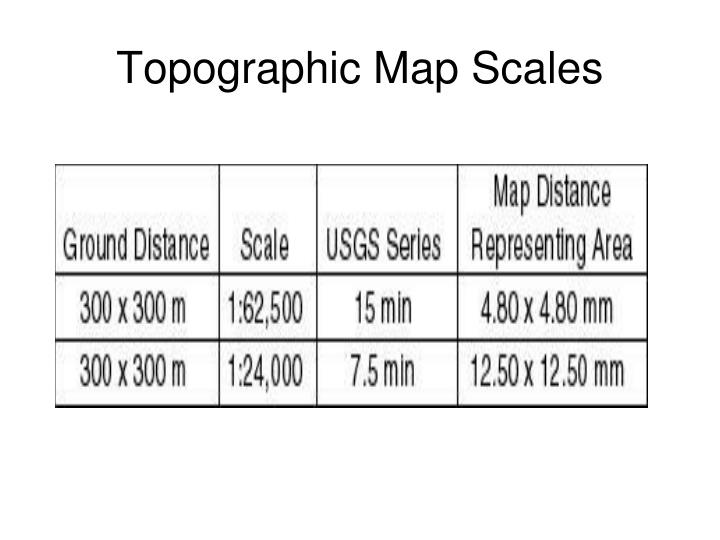
Map scale refers to the ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It essentially acts as a conversion factor, enabling us to determine the actual size of features depicted on the map. This ratio can be expressed in various ways, each offering a distinct visual representation and level of detail.
1. Verbal Scale:
The verbal scale expresses the relationship between map distance and ground distance in words. For instance, a verbal scale of "1:100,000" signifies that one unit of measurement on the map represents 100,000 units of the same measurement on the ground. This format is simple and straightforward, making it easy to understand at a glance.
2. Representative Fraction (RF):
The representative fraction (RF) expresses the map scale as a fraction, where the numerator always represents one unit. For example, an RF of 1/100,000 indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units in reality. This format is commonly used in scientific and technical contexts due to its precision and uniformity.
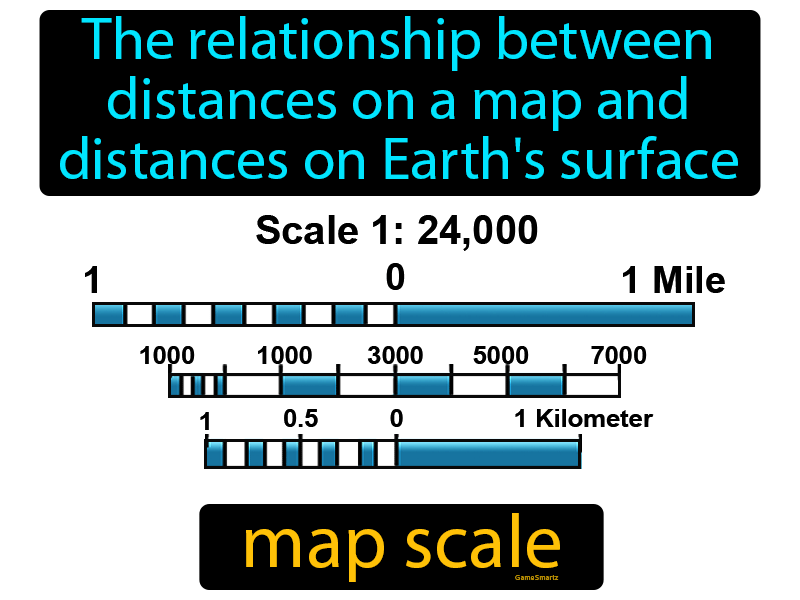
3. Graphic Scale:
A graphic scale, also known as a bar scale, provides a visual representation of the map scale using a graduated line. This line is divided into segments, each representing a specific distance on the ground. Users can directly measure distances on the map using a ruler and then refer to the graphic scale to determine the corresponding distance on the ground. This method offers a quick and intuitive way to estimate distances without complex calculations.
The Significance of Map Scale
Understanding map scale is paramount for several reasons:
-
Accurate Measurement and Interpretation: Map scale allows us to accurately measure distances, areas, and other spatial attributes depicted on the map. This is essential for various applications, including navigation, land surveying, environmental studies, and urban planning.
-
Contextualization of Features: By understanding the scale, we can comprehend the relative size and importance of different features on the map. A large-scale map will display greater detail and highlight smaller features, while a small-scale map will focus on broader patterns and relationships.
-
Comparison and Analysis: Map scale enables us to compare and analyze different maps effectively. By ensuring consistent scales, we can readily compare the spatial distribution of features across different regions or time periods.
-
Navigation and Orientation: Map scale is crucial for navigation, allowing us to estimate distances and determine the optimal route. It also helps us to understand the relative positions of features and navigate effectively in unfamiliar environments.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Scale
Selecting the appropriate map scale is crucial for achieving the desired level of detail and clarity. A large-scale map, with a smaller denominator in the ratio, provides a detailed view of a smaller area. This is suitable for tasks requiring precise measurements and the identification of specific features, such as urban planning, land surveying, or local navigation.
Conversely, a small-scale map, with a larger denominator in the ratio, depicts a broader area with less detail. This is ideal for understanding regional patterns, analyzing large-scale phenomena, or planning long-distance travel.
Examples of Map Scale in Action
-
Navigation Apps: Navigation apps utilize map scale to display routes and estimate travel times. As you zoom in or out on the map, the scale changes, providing a more detailed or broader view of the area.
-
Topographic Maps: Topographic maps, used for hiking and outdoor activities, often include a graphic scale to allow users to estimate distances between trails and landmarks.
-
Weather Maps: Weather maps utilize different scales to display various weather phenomena, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns. The scale used depends on the specific phenomenon being depicted and the geographical area covered.
Frequently Asked Questions about Map Scale
1. How do I determine the scale of a map if it is not explicitly stated?
If a map does not explicitly state its scale, you can determine it by measuring a known distance on the map and comparing it to the corresponding distance on the ground. For instance, if you know the distance between two points on the ground, you can measure the distance between these points on the map and calculate the scale using the formula:
Scale = Distance on Map / Distance on Ground2. Can I use a map with a different scale for the same area?
Yes, you can use maps with different scales for the same area, but it is essential to be aware of the implications. A larger-scale map will provide more detail but cover a smaller area, while a smaller-scale map will cover a broader area but with less detail.
3. How does map scale affect the accuracy of measurements?
The accuracy of measurements on a map is directly influenced by the scale. Larger-scale maps provide more accurate measurements due to the greater level of detail. Conversely, smaller-scale maps may introduce inaccuracies, particularly when measuring distances or areas.
4. What are the limitations of using map scale?
Map scale is a powerful tool, but it has limitations. Firstly, it is a simplified representation of the real world, and some distortion is inevitable. Secondly, the accuracy of map scale depends on the quality of the data used to create the map.
Tips for Using Map Scale Effectively
-
Always check the scale: Before using a map, ensure you understand the scale and its implications for the measurements and information presented.
-
Consider the purpose: Choose a map scale that aligns with your specific needs and the level of detail required for your task.
-
Use a ruler: When measuring distances on a map, use a ruler to ensure accurate measurements and avoid misinterpretations.
-
Be aware of distortions: Remember that map scale introduces some distortion, particularly at smaller scales. Be mindful of these limitations when interpreting the information presented.
Conclusion
Understanding map scale is essential for accurately interpreting and utilizing map information. It allows us to translate distances and measurements from the map to the real world, enabling us to navigate, measure, and analyze spatial data effectively. By recognizing the different types of map scale and their implications, we can harness the power of maps to gain valuable insights into the world around us.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scale and Its Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!