A Journey Through the Female Body: Exploring the Map of Organs
Related Articles: A Journey Through the Female Body: Exploring the Map of Organs
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through the Female Body: Exploring the Map of Organs. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through the Female Body: Exploring the Map of Organs

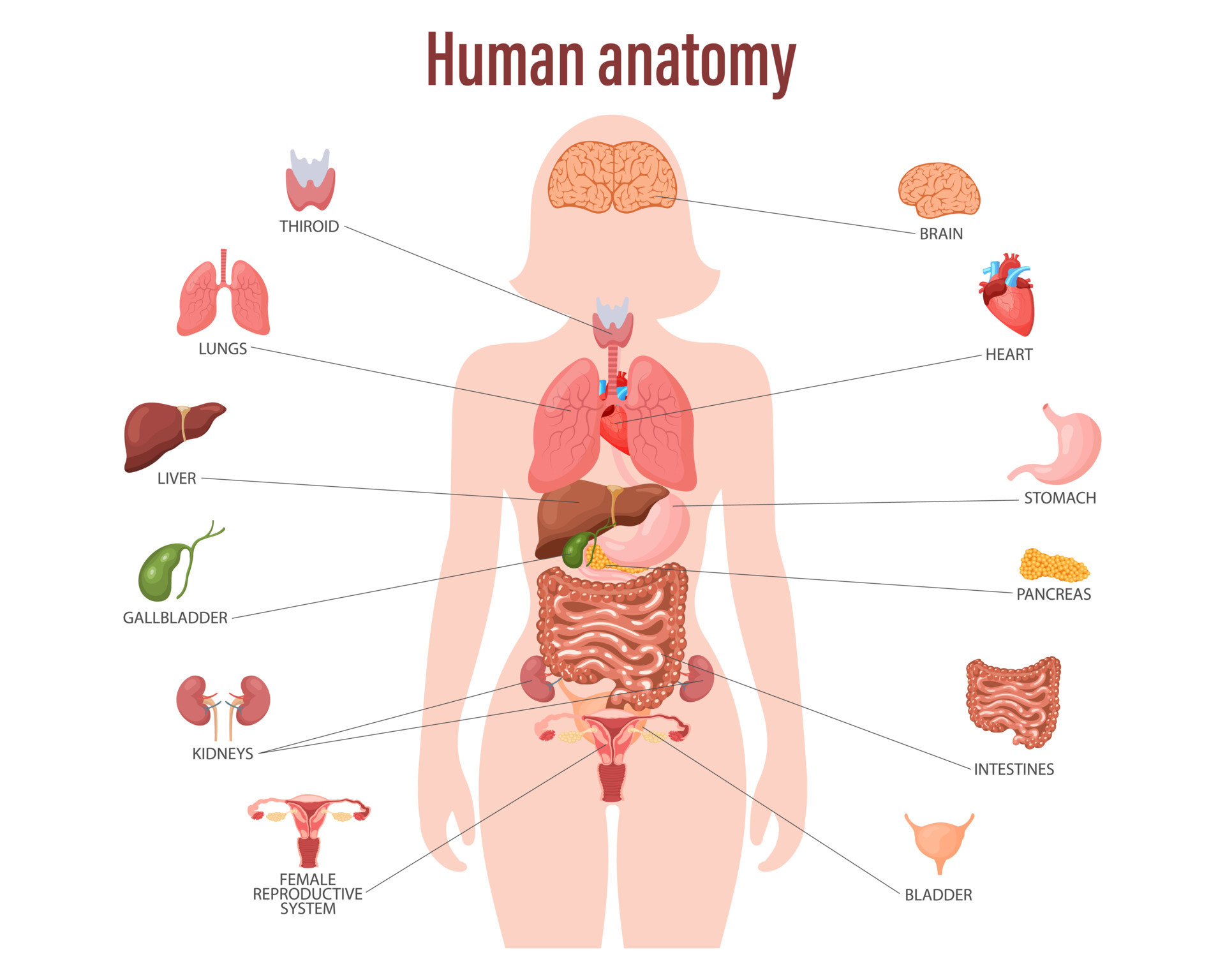
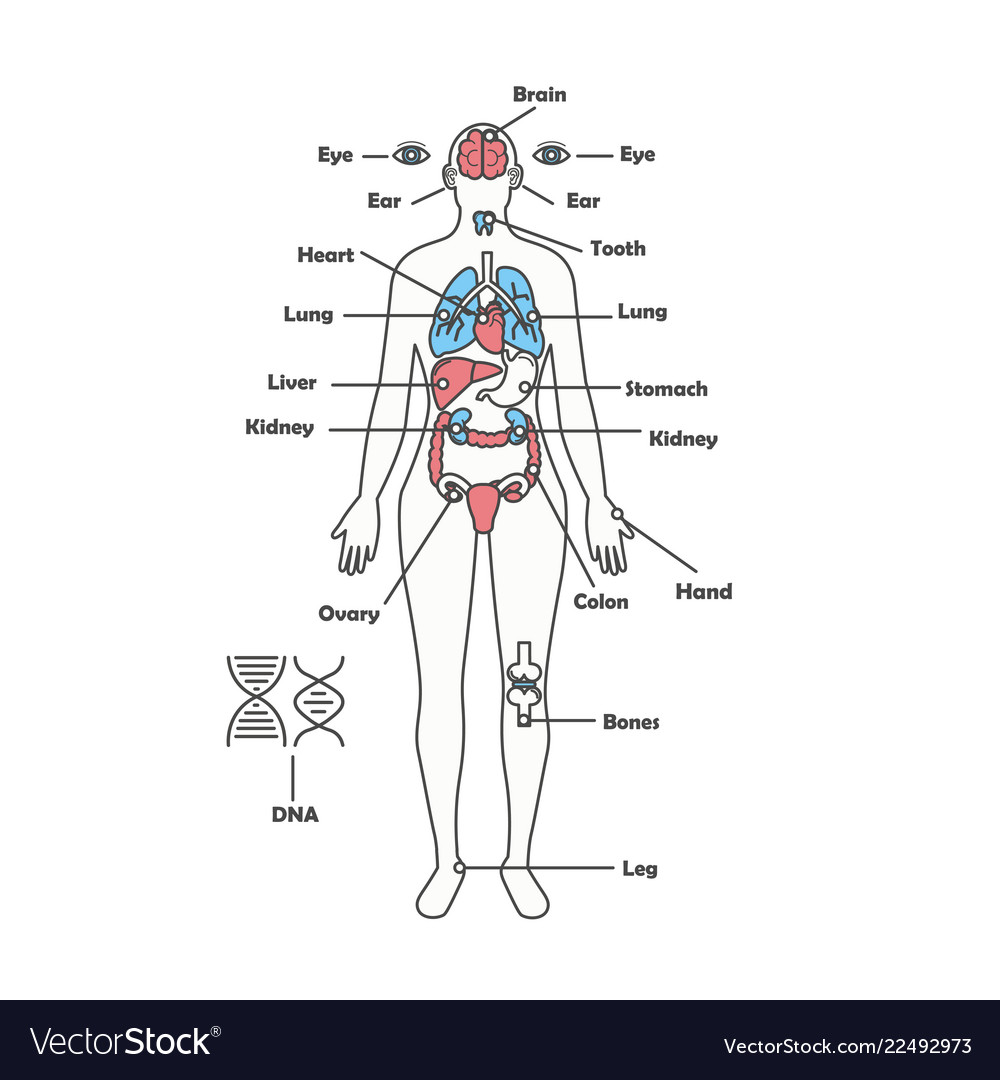
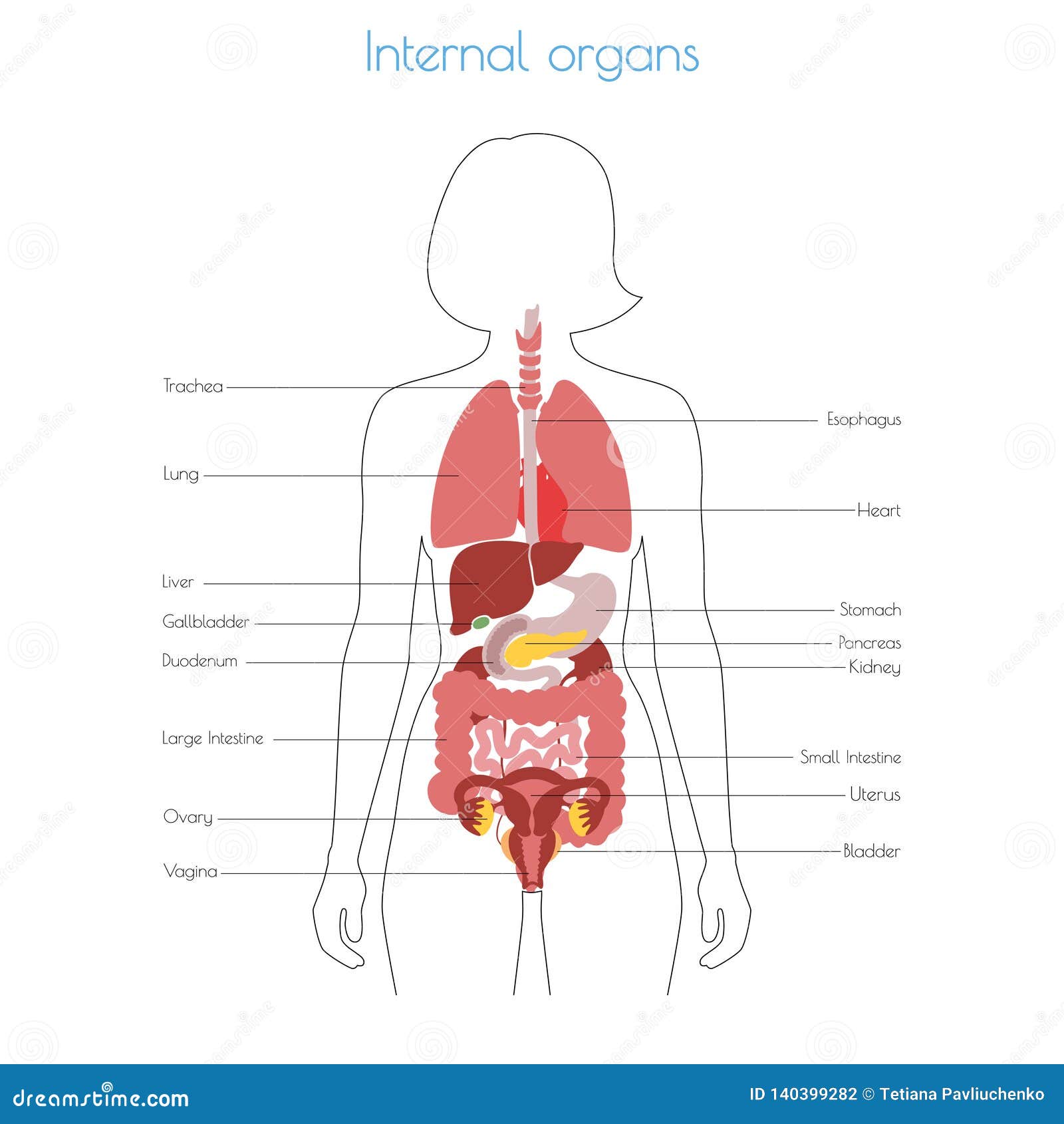
The human body is a complex and intricate system, and the female body is no exception. Understanding the arrangement and function of its various organs is crucial for maintaining health and well-being. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the map of organs in the female body, exploring each system and its role in sustaining life.
The Foundation: The Skeletal and Muscular Systems
The female body, like the male, is supported by a robust skeletal framework. The skeleton provides structure, protects vital organs, and serves as a base for muscle attachment. The female skeleton shares most features with the male skeleton but exhibits certain differences, primarily in the pelvis and rib cage, reflecting adaptations for childbirth.
The muscular system works in conjunction with the skeletal system, enabling movement, posture, and vital bodily functions. Muscles are responsible for breathing, digestion, and even blood circulation. While the muscle composition and distribution are similar in both sexes, women generally have a higher percentage of body fat and lower muscle mass compared to men.
The Heart and the Circulatory System
At the heart of the female body lies the circulatory system, a network of blood vessels that transport oxygen, nutrients, and hormones throughout the body. The heart, a powerful muscular organ, pumps blood through this network, ensuring every cell receives the resources it needs to function.
While the structure and function of the female heart are largely similar to the male heart, there are subtle differences in size and electrical activity. Women’s hearts tend to be smaller and beat faster than men’s.
The Respiratory System: Breathing Life into the Body
The respiratory system, comprised of the lungs, trachea, bronchi, and diaphragm, is responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. The lungs, two spongy organs located in the chest cavity, are where gas exchange occurs. The diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle, contracts and relaxes to facilitate breathing.
The Digestive System: Breaking Down and Absorbing Nutrients
The digestive system, a long and winding pathway, breaks down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. This process begins in the mouth, where teeth grind food and saliva initiates digestion. The food then travels through the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, where it is further broken down and nutrients are absorbed.
The Urinary System: Maintaining Fluid Balance and Waste Removal
The urinary system plays a crucial role in regulating fluid balance and eliminating waste products. The kidneys, two bean-shaped organs located in the lower back, filter blood and produce urine, which is transported through the ureters to the bladder for storage and eventual expulsion through the urethra.
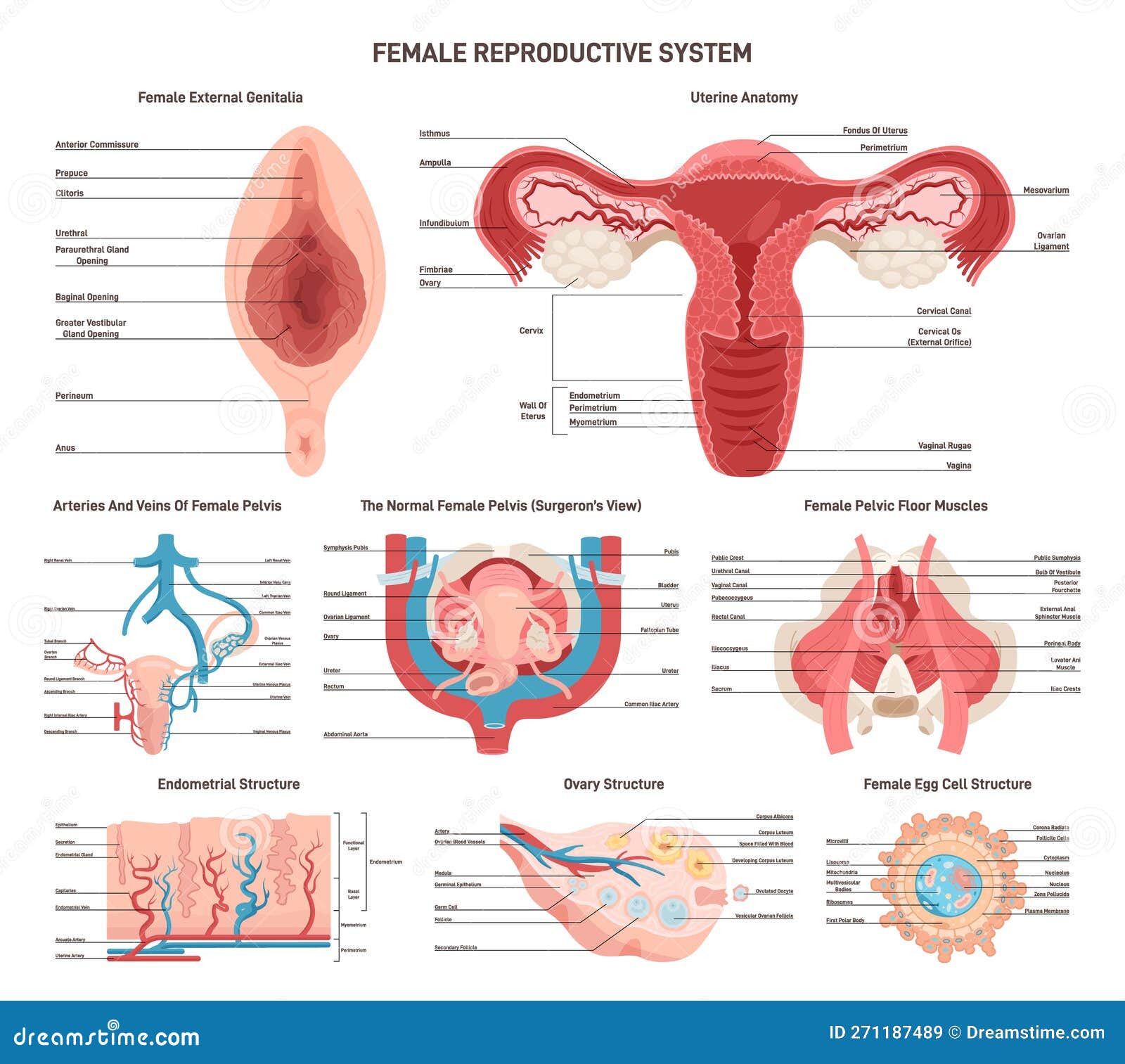
The Reproductive System: The Essence of Female Biology
The reproductive system is the defining characteristic of the female body, responsible for producing eggs, facilitating fertilization, and supporting pregnancy. The ovaries, two almond-shaped organs located in the pelvic cavity, produce eggs and hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
The fallopian tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus, the pear-shaped organ where a fertilized egg implants and develops. The cervix, the lower portion of the uterus, opens into the vagina, the birth canal and the passageway for menstrual flow.
The Endocrine System: A Symphony of Hormones
The endocrine system, composed of glands that secrete hormones, plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including growth, metabolism, reproduction, and mood. Key endocrine glands in the female body include the ovaries, thyroid gland, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands.
The Nervous System: The Body’s Control Center
The nervous system, the body’s communication network, transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body. The brain, the central processing unit, receives and interprets information from the senses and sends signals to muscles and glands.
The spinal cord, a long bundle of nerves extending from the brain, relays signals between the brain and the rest of the body. The peripheral nervous system, a network of nerves throughout the body, connects the central nervous system to the organs and tissues.
The Lymphatic System: The Body’s Defense Force
The lymphatic system, a network of vessels and nodes, plays a vital role in the immune system, defending the body against infection and disease. Lymph fluid, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, circulates through the lymphatic vessels, collecting waste products and pathogens.
The Integumentary System: The Body’s Protective Barrier
The integumentary system, comprising the skin, hair, and nails, serves as the body’s first line of defense against infection and injury. The skin, the largest organ in the body, provides a barrier against pathogens, regulates temperature, and senses touch.
Understanding the Map of Organs: A Foundation for Health
Understanding the location, structure, and function of the organs in the female body is essential for maintaining health and well-being. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health, seek appropriate medical care when needed, and take proactive steps to prevent disease.
FAQs: Exploring the Map of Organs in the Female Body
Q: What are the major differences between the male and female skeletal systems?
A: The most significant differences lie in the pelvis and rib cage. The female pelvis is wider and shallower, accommodating childbirth. The female rib cage is generally more rounded and less angled than the male rib cage.
Q: What are the key hormones produced by the female reproductive system?
A: The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone, hormones crucial for regulating menstrual cycles, supporting pregnancy, and influencing secondary sexual characteristics.
Q: What is the role of the lymphatic system in the immune response?
A: The lymphatic system plays a critical role in immune defense by transporting lymph fluid, containing white blood cells, throughout the body. These white blood cells identify and destroy pathogens, preventing infection and disease.
Q: How does the nervous system regulate bodily functions?
A: The nervous system transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body, controlling muscle movement, regulating organ function, and processing sensory information.
Q: What are some common health concerns specific to women?
A: Common health concerns specific to women include breast cancer, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Female Body
- Maintain a balanced diet: Consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats to provide the nutrients your body needs.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Get adequate sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support hormonal balance and overall well-being.
- Manage stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Seek regular medical check-ups: Schedule annual checkups with your doctor to monitor your overall health and screen for potential health problems.
Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity of the Female Body
The female body is a remarkable and intricate system, a testament to the power and resilience of life. Understanding the map of organs in the female body is not merely an academic pursuit; it is a journey of self-discovery, empowering individuals to take charge of their health and well-being. By appreciating the complexity and interconnectedness of the female body, we can cultivate a deeper understanding of its capabilities, vulnerabilities, and the profound beauty of its design.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through the Female Body: Exploring the Map of Organs. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!