A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Geography of Israel
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Geography of Israel
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Geography of Israel. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Geography of Israel

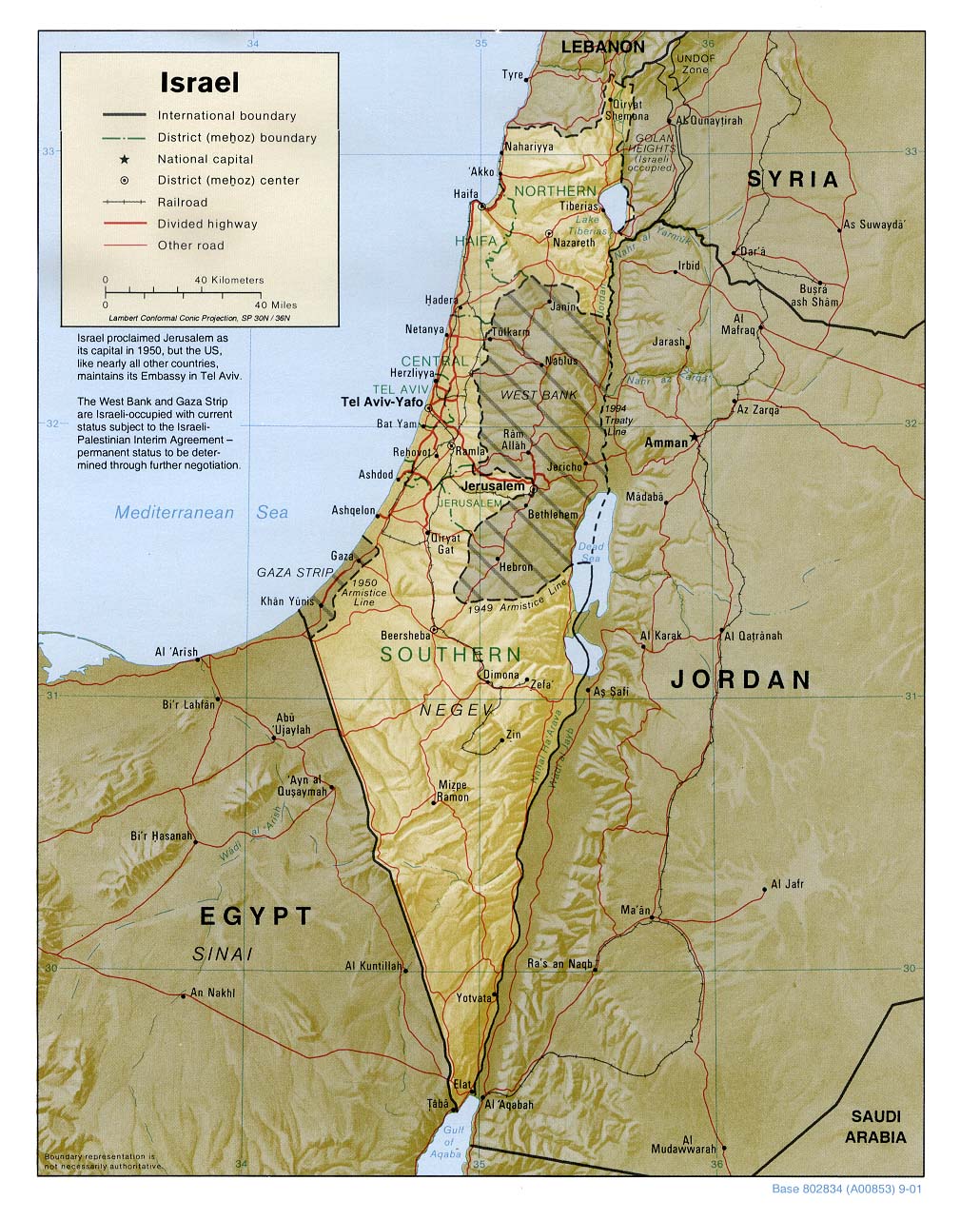
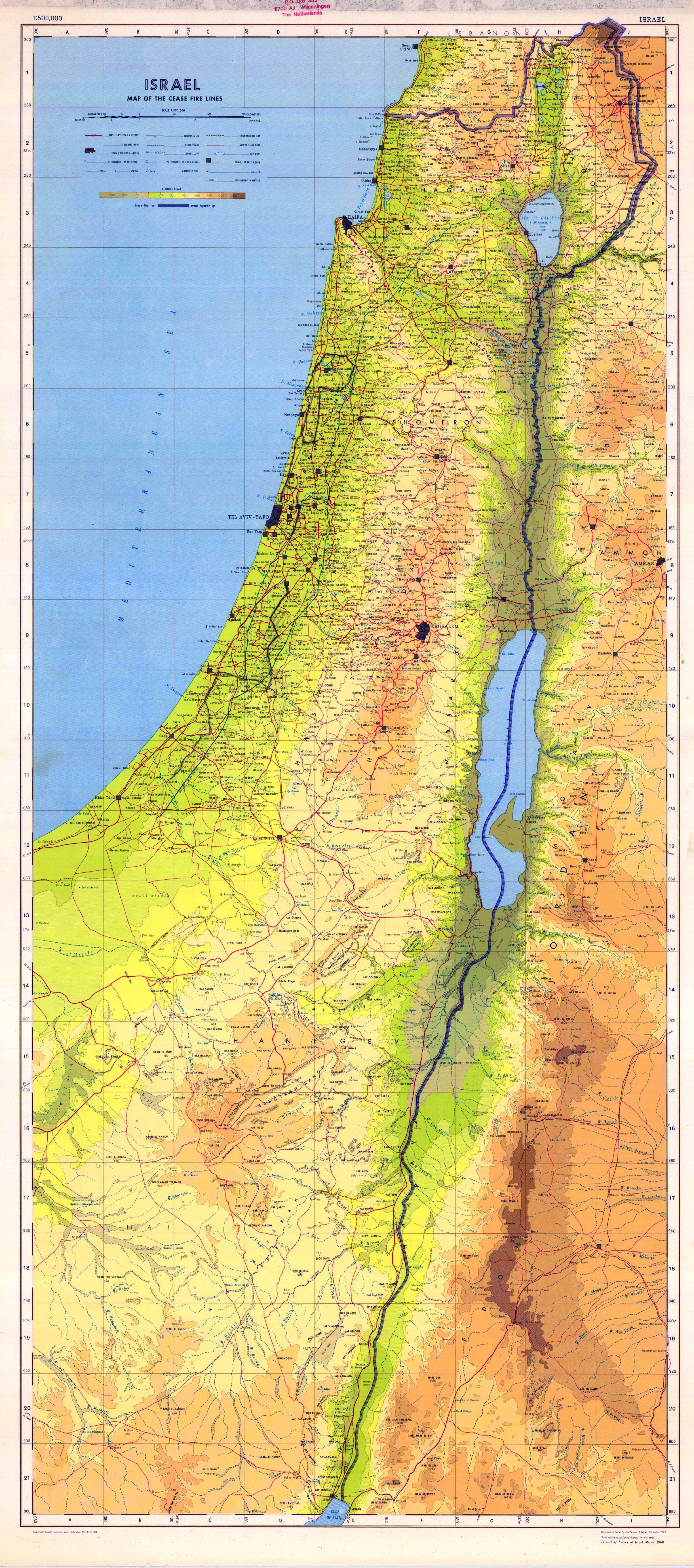
Israel, a nation nestled in the Middle East, possesses a complex and multifaceted geography that has shaped its history, culture, and politics. Understanding the physical landscape of Israel is essential for comprehending its contemporary challenges and opportunities. This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of Israel’s geography, using maps as a visual tool to elucidate its key features.
The Land of Israel: A Diverse Landscape
Israel’s geography is defined by its location at the crossroads of three continents: Asia, Africa, and Europe. This strategic position has historically made it a vital trade route and a center of cultural exchange. The country’s diverse landscape, encompassing mountains, valleys, deserts, and coastal plains, contributes to its unique character.
Key Geographic Features:
- The Negev Desert: Covering approximately 60% of Israel’s landmass, the Negev Desert is a vast, arid expanse in the south. Its rugged terrain is punctuated by wadis (dry riverbeds) and isolated mountain ranges. The Negev’s harsh environment has historically challenged human settlement, but recent developments in water management and agricultural technology have enabled the region to become a hub for research and development.
- The Judean Desert: Located west of the Dead Sea, the Judean Desert is a rugged and barren landscape characterized by steep cliffs, canyons, and ancient cave systems. The desert’s harsh conditions have contributed to its historical significance as a refuge for early Jewish communities.
- The Coastal Plain: Stretching along the Mediterranean coast, the Coastal Plain is a fertile and densely populated region. It is home to major cities like Tel Aviv, Haifa, and Ashdod, and is characterized by sandy beaches, rolling hills, and agricultural lands.
- The Galilee: Located in northern Israel, the Galilee is a mountainous region known for its picturesque landscapes, including the Sea of Galilee (Lake Tiberias), the Golan Heights, and Mount Meron. The Galilee is a significant cultural and religious center, with historical sites like Capernaum and Nazareth drawing visitors from around the world.
- The Jordan Valley: A rift valley running along the eastern border of Israel, the Jordan Valley is home to the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth. The valley’s unique geological formations and mineral-rich waters have attracted tourists and researchers alike.
The Importance of Maps in Understanding Israel’s Geography
Maps are invaluable tools for comprehending the complexities of Israel’s geography. They provide a visual representation of the country’s physical features, political boundaries, and demographic distribution.
- Political Maps: These maps illustrate the current political boundaries of Israel, including the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. They also highlight major cities, towns, and administrative divisions.
- Physical Maps: These maps depict the country’s topography, showing elevation changes, mountain ranges, rivers, and lakes. They offer a detailed understanding of the physical landscape and its impact on human settlement and economic activities.
- Thematic Maps: These maps focus on specific themes, such as population density, agricultural production, or resource distribution. They provide valuable insights into the country’s economic activities, environmental challenges, and social demographics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Israel’s Geography:
- What is the size of Israel? Israel is relatively small, covering approximately 22,072 square kilometers (8,522 square miles).
- What is the highest point in Israel? Mount Meron, located in the Galilee, is the highest point in Israel, reaching an elevation of 1,208 meters (3,963 feet).
- What is the lowest point on Earth? The Dead Sea, located on the border between Israel and Jordan, is the lowest point on Earth, at 430.5 meters (1,412 feet) below sea level.
- What is the climate of Israel? Israel experiences a Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry summers and mild, rainy winters. However, the country’s diverse geography leads to variations in climate across different regions.
Tips for Exploring Israel’s Geography:
- Use online mapping tools: Websites like Google Maps, Bing Maps, and OpenStreetMap offer detailed maps of Israel, allowing you to explore its diverse landscapes and historical sites.
- Visit museums and historical sites: Museums and historical sites provide insights into the human history and cultural heritage of Israel, enriching your understanding of the country’s geography.
- Engage with local communities: Talking to locals can offer valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities presented by Israel’s geography.
Conclusion:
Israel’s geography is a complex and fascinating tapestry woven together by diverse landscapes, historical influences, and contemporary challenges. Understanding the country’s physical features, political boundaries, and demographic distribution is crucial for appreciating its unique character and navigating its multifaceted realities. Through the use of maps and other visual aids, we can gain a deeper understanding of Israel’s geography and its impact on the nation’s history, culture, and future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Geography of Israel. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!